-
Groundwater pumping causes sea level rise, canceling out effect of dams
Those in charge of infrastructure protection must now worry about another source of sea level rise: water pumped out of the ground for irrigation, drinking water, and industrial use; this water ends up emptying into the world’s oceans, and scientists calculate that by 2050, groundwater pumping will cause a global sea level rise of about 0.8 millimeters per year
-
-
Groundwater pumping causes sea level rise, canceling out effect of dams
Those in charge of infrastructure protection must now worry about another source of sea level rise: water pumped out of the ground for irrigation, drinking water, and industrial use; this water ends up emptying into the world’s oceans, and scientists calculate that by 2050, groundwater pumping will cause a global sea level rise of about 0.8 millimeters per year
-
-
The American West running low on water
The American West has a drinking problem; on farms and in cities, people who live in that region are guzzling water at an alarming rate; scientists say that to live sustainably, they should use no more than 40 percent of the water from the Colorado River Basin; currently, however, they use 76 percent, nearly double the sustainable benchmark
-
-
Direct drinking water recycling could prevent floods
The use of a more streamlined process to recycle wastewater could have saved Brisbane from severe flooding in 2011 and mitigated recent flood risks in NSW, a leading water expert says
-
-
Water vulnerability in U.S. border region
The Arizona-Sonora region has been called the front line of ongoing climate change, with global climate models projecting severe precipitation decreases and temperature increases coupled with vulnerability from urbanization, industrialization and agricultural intensification
-
-
Water scarcity in California's Bay-Delta necessitates “hard decisions”

Simultaneously attaining a reliable water supply for California and protecting and rehabilitating its Bay-Delta ecosystem cannot be realized until better planning can identify how trade-offs between these two goals will be managed when water is limited
-
-
Increase in groundwater demands due to climate change
As precipitation becomes less frequent due to climate change, lake and reservoir levels will drop and people will increasingly turn to groundwater for agricultural, industrial, and drinking water needs; the resource accounts for nearly half of all drinking water worldwide, but recharges at a much slower rate than aboveground water sources and in many cases is nonrenewable
-
-
Poultry feathers-based filters remove arsenic from water
Thousands of people die each year in developing countries from drinking arsenic-contaminated water; researchers develop inexpensive filters made from the modified protein (keratin) in poultry feathers to remove arsenic from drinking water
-
-
U.S. water shortages loom

More than 1 in 3 counties in the United States could face a “high” or “extreme” risk of water shortages due to climate change by the middle of the twenty-first century; 7 in 10 of the more than 3,100 U.S. counties could face “some” risk of shortages of fresh water for drinking, farming, and other uses
-
-
Proposed EPA budget cuts funding from clean air and water grants
President Obama’s latest proposed budget for fiscal year 2013 cuts $105 million from the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) budget, primarily from funds aimed at treating wastewater and drinking water
-
-
A nano method to clean polluted water
Decontaminating polluted waste water costs millions, but a new discovery by scientists at the University of Brighton could result in huge savings as well as delivering safer, cleaner water
-
-
Collecting rainwater could save U.S. residents $90 million a year
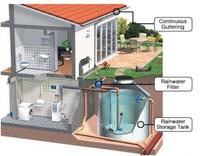
Simply collecting rainwater could save U.S. residents millions of dollars each year on their water bills and drastically cut down on water consumption; a new study by the Natural Resources Defense Council examined the potential cost-savings in eight U.S. cities and found that residents could collectively save $90 million or more annually
-
-
Groundwaterin some parts of U.S. susceptible to radium contamination
A recent U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) study found that groundwater in aquifers on the East Coast and in the Central United States has the highest risk of contamination from radium, a naturally occurring radioactive element and known carcinogen
-
-
GAO: critical infrastructure operators need more coherent regulations
A recent Government Accountability Office (GAO) report found that the bulk of U.S. critical infrastructure is inadequately protected as operators lack a coherent set of guidelines
-
-
Protecting U.S. water supplies

Aside from possible cyberatacks on water utilities, security officials are worried that terrorists could contaminate water supplies with volatile chemicals that can poison thousands of individuals and even cause explosions; DHS warned local water utilities of “backpressure” — a simple tactic terrorists could use to introduce a chemical or biological agent into the water supply and spread it over long distances without immediate detection
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies