EpidemicsSatellites help assess risk of epidemics
Changes in the environment, global trade, and travel are all factors in the ever-increasing numbers and movement of pests. Identifying and predicting the distribution of existing local species as well as the spread of new exotic ones are essential in assessing the risk of potential epidemics. Researchers have developed Vecmap — an all-encompassing software and services package including a smartphone app for field studies with a time and location information system, all linked to an online database. The database pools satellite information with results from field research, and satnav adds location information. The new approach greatly reduces the complexity of tracking species compared to traditional methods.
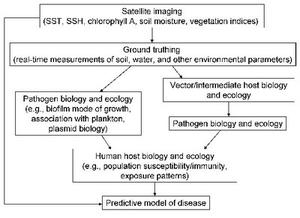
Flowchart showing satellite's contribution to predicting pathogen spread // Source: cdc.gov
Changes in the environment, global trade, and travel are all factors in the ever-increasing numbers and movement of pests. Identifying and predicting the distribution of existing local species as well as the spread of new exotic ones are essential in assessing the risk of potential epidemics.
An ESA release reports that a consortium led by Avia-GIS in Belgium and supported by the European Space Agency (ESA) has developed Vecmap — an all-encompassing software and services package including a smartphone app for field studies with a time and location information system, all linked to an online database.
The database pools satellite information with results from field research. Satnav adds location information, helps researchers find their way to testing sites, and helps field teams locate traps for return and analysis in the lab.
Traps are left in target areas chosen from satellite observations. The information helps researchers choose the most representative testing sites, saving time and cost of fieldwork — traditionally the most expensive part of gathering data. The results collected online ultimately enable researchers to map high-risk areas using a wide range of satellite images.
The new approach greatly reduces the complexity of tracking species compared to traditional methods.
Currently, public health authorities use field sampling and statistical analysis to predict those areas most at risk, but a lack of integration between the various services results in a highly complex system requiring specialized knowledge.
Vecmap provides all the data and services for vector mapping and acts as a single entry point for all information needed to predict and prevent infection, making it easy for researchers to collaborate on risk-mapping.
The release notes that twelve institutions in nine European countries tested Vecmap for producing area-wide risk maps during the course of ESA’s ARTES project, confirming its viability and the operational benefits for users.
Potential users range from governmental health organizations working with researchers to industry.
In parallel, other applications are being developed to support landscape mapping in the Caribbean.
“The support given to us by ESA’s ARTES Integrated Applications Promotion Program was a critical step to enable us to embark upon the commercialization of Vecmap,” said Guy Hendrickx, CEO of Avia-GIS.
