-
WhatsApp to add encryption to voice chats

Reports say that WhatsApp is planning to add encrypted video chats to its app in order to make it impossible for, so that nobody could snoop on its users. Adding encrypted voice chats will mean that all of the messages that pass through WhatsApp will be secure. Text messages are already encrypted.
-
-
How organizations can secure their teleworkers, data
As the number of employees who telework trends upward — and new kinds of devices are used in telework — the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) says it is updating its guidance to include the latest technology available to strengthen an organization’s remote-access data security.
-
-
Social media used to assess damage caused by natural disasters
A new study concludes that it is possible to determine the damage caused by a natural disaster in just a few hours by using data from social networks. “Twitter, the social network which we have analyzed, is useful for the management, real-time monitoring and even prediction of the economic impact that disasters like Hurricane Sandy can have,” says one of the researchers.
-
-
U.S. files case against Iranian government hackers behind attack on N.Y. dam

In 2013 hackers infiltrated the operations center for the Bowman Avenue Dam, a small dam on Blind Brook in Rye Brook, New York. DHS, in a classified report, later identified the attackers r identified the attackers as the same Iranian group responsible for attacks on PNC Financial Services Group, SunTrust, and Capital One Financial. Now the Department of Justice is set to file an indictment against the Iranian hackers behind the intrusion.
-
-
Doodling trumps text passwords for smartphone security
Someday soon, you may be able to log into your smartphone with sweeping gestures or doodling, using one or more fingers. Researchers have performed the first study of free-form gesture passwords for smartphones in the field. Free-form gesture passwords allow people to draw a password of any shape with any number of fingers.
-
-
Snowden dismisses FBI's claim it cannot unlock San Bernardino killers’ iPhone

Edward Snowden has joined the debate over the FBI’s attempt to force Apple to help it unlock the iPhone 5C used by one of the San Bernardino terrorists. The FBI says that only Apple can deactivate certain passcode protections on the iPhone — for example, the 10-attempt limit, which makes the phone permanently inaccessible after ten attempts to guess the password —which would allow law enforcement to guess the passcode by using brute-force.
-
-
ISIS hackers post N.J. police officers’ details online, calling on followers to attack them

ISIS hackers have posted the personal details of U.S. officials online, encouraging the group’s supporters to carry out “lone wolf” attacks against them. The Caliphate Cyber Army (CCA), formerly known as the Islamic Cyber Army, posted the personal details of fifty-five New Jersey police officers last week after hacking into the Web site of the New Jersey Transit police.
-
-
Calif. terrorists’ iPhone may have been used to introduce malware into data networks: DA

San Bernardino County District Attorney Michael Ramos has advanced what experts describe as an unusual reason for forcing Apple to allow the FBI to break the password of the iPhone used by the two terrorists as part of the agency’s investigation of the attack. Ramos says the phone might have been “used as a weapon” to introduce malicious software to county computer systems.
-
-
New vulnerability discovered in Open SSL, a common encryption protection package

One of the world’s most common security software packages — used as the basis of protection for many Web browsers — has been found to be vulnerable to a specific form of attack, according to new research. Researchers have discovered that OpenSSL is vulnerable to a type of attack known as a “side channel attack.”
-
-
Web security protocol TLS compromised
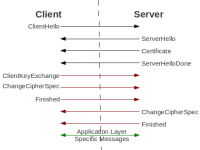
In one third of all servers, the security protocol TLS and encrypted data transfer can be compromised. All types of online communication that deal with sensitive data are affected. The researchers discovered the flaw by launching a DROWN (Decrypting RSA with Obsolete and Weakened eNcryption) attack – which they will demonstrate and discuss at a forthcoming security conference in Germany.
-
-
French law would penalize encrypted phone makers who refuse to help police probes
French lawmakers on Thursday voted for a measure which would impose penalties on manufacturers of smartphone who refuse to cooperate with law enforcement in inquiries of terrorism cases. The measure stipulates that a private manufacturer of smartphones, which refuses to hand over encrypted data to an investigating authority, would face up to five years in jail and a 350,000 euro ($380,000) fine.
-
-
App warns users when they are about to give away sensitive information online
Researchers are seeing potential in a software application which could effectively warn users when they are about to give away sensitive personal information online. The eye tracker detects where a user’s eyes are at the computer screen and records how long they gazed at that spot. The app uses these two functions to find when a user’s eyes remain on a request for sensitive personal information.
-
-
Smartphones now account for 60% of infections in the mobile network
Nokia Security Center Berlin the other day released research findings showing that in the mobile networks, smartphones pulled ahead of Windows-based computers and laptops, now accounting for 60 percent of the malware activity observed in the mobile space. The Nokia Threat Intelligence Report also reveals an increase in iOS-based malware, growing sophistication of Android malware and the rising threat of mobile ransomware.
-
-
Three “twisted” photons in 3 dimensions for quantum encryption
Researchers have achieved a new milestone in quantum physics: they were able to entangle three particles of light in a high-dimensional quantum property related to the “twist” of their wave-front structure. Multi-photon entangled states such as these have applications ranging from quantum computing to quantum encryption. Along these lines, the authors of this study have developed a new type of quantum cryptographic protocol using their state that allows different layers of information to be shared asymmetrically among multiple parties with unconditional security.
-
-
FBI cannot force Apple to unlock iPhone in drug case: Judge
Magistrate Judge James Orenstein in Brooklyn on Monday ruled that the U.S. government cannot force Apple to unlock an iPhone in a New York drug case. The ruling strengthens the company’s arguments in its landmark legal confrontation with the Justice Department over encryption and privacy. The government sought access to the drug dealer’s phone months before a California judge ordered Apple to give access to the San Bernardino terrorist’s handset.
-
More headlines
The long view
States Rush to Combat AI Threat to Elections
This year’s presidential election will be the first since generative AI became widely available. That’s raising fears that millions of voters could be deceived by a barrage of political deepfakes. Congress has done little to address the issue, but states are moving aggressively to respond — though questions remain about how effective any new measures to combat AI-created disinformation will be.
Ransomware Attacks: Death Threats, Endangered Patients and Millions of Dollars in Damages
A ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a company that processes 15 billion health care transactions annually and deals with 1 in 3 patient records in the United States, is continuing to cause massive disruptions nearly three weeks later. The incident, which started on February 21, has been called the “most significant cyberattack on the U.S. health care system” by the American Hospital Association. It is just the latest example of an increasing trend.
Chinese Government Hackers Targeted Critics of China, U.S. Businesses and Politicians
An indictment was unsealed Monday charging seven nationals of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) with conspiracy to commit computer intrusions and conspiracy to commit wire fraud for their involvement in a PRC-based hacking group that spent approximately 14 years targeting U.S. and foreign critics, businesses, and political officials in furtherance of the PRC’s economic espionage and foreign intelligence objectives.
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Vulnerable to Road Object Spoofing and Vanishing Attacks
Researchers have demonstrated the potentially hazardous vulnerabilities associated with the technology called LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, many autonomous vehicles use to navigate streets, roads and highways. The researchers have shown how to use lasers to fool LiDAR into “seeing” objects that are not present and missing those that are – deficiencies that can cause unwarranted and unsafe braking or collisions.
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
