-
Last year’s east coast earthquake has the region preparing for another one
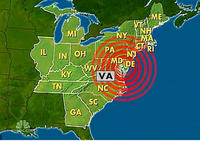
Last year an earthquake that was centered in Virginia shook up the entire east coast, surprising everyone; it did not result in any deaths and was considered relatively light compared to many tremors on the West Coast, but it was bad enough to force some states to prepare themselves in case of another quake
-
-
Activists in arms over plans to ship plutonium to New Mexico
A proposal to ship tons of plutonium to New Mexico, including cores of nuclear warheads which would be dismantled at a structurally questionable lab on top of an earthquake fault zone, has activists and nuclear watchdogs up in arms
-
-
Los Alamos lab responds to radiological incident

The Los Alamos National Laboratory said it is investigating the inadvertent spread of Technetium 99 by employees and contractors at the Lujan Neutron Scattering Center at the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center (LANSCE), a multidisciplinary accelerator facility used for both civilian and national security research; multiple tests indicate no health risks to public or employees
-
-
Near-instantaneous DNA analysis
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an indispensible technique allowing researchers and clinicians to produce millions of copies from a single piece of DNA or RNA for use in genome sequencing, gene analysis, inheritable disease diagnosis, paternity testing, forensic identification, and the detection of infectious diseases; PCR for point-of-care, emergency-response, or widespread monitoring applications needs to be very fast — on the order of a few minutes; this has now been achieved
-
-
One solution to the aging U.S. grid: microgrids
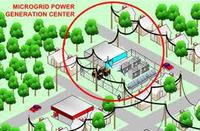
Most Americans do not have to think much about energy reliability; they plug in a computer and it powers up; they flip a switch and the lights come on; while very reliable today, the U.S. electricity grid is old and has gone at least five decades without a significant technological upgrade. The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory is working with industry on one solution to help maintain a secure, reliable flow of energy: microgrids
-
-
Cooling coal emissions would clean air, lower health, climate-change costs

In the United States there are about 1,400 electric-generating unit powered by coal, operated at about 600 power plants; the estimated health costs of burning coal in the United States are in the range of $150 billion to $380 billion, including 18,000-46,000 premature deaths, 540,000 asthma attacks, 13,000 emergency room visits, and two million missed work or school days each year; scientists estimate that implementing large-scale cryogenic systems into coal-fired plants would reduce overall costs to society by 38 percent through the sharp reduction of associated health-care and climate-change costs
-
-
Maldives to build floating islands to save country from rising sea levels
The Maldives Islands, a low-lying chain of twenty-six atolls in the Indian Ocean, are sinking; more precisely: due to global warming, the sea level is rising over the islands, most of which sit lower than three feet above the rising water; the Maldives government has embarked on an ambitious project: build floating islands, anchor them to the ocean floor, then relocate most of the population of 300,000 – and some of the tourist attractions – to them
-
-
New hurricane simulator to help find way to minimize storms’ destruction
Hurricanes in Miami can range from just rain and light wind to shredded houses, overturned cars, massive flooding, and death. Now, almost twenty years after Hurricane Andrew, Florida International University is using a new simulator to find ways to prevent the massive damage a hurricane can create
-
-
Decline and fall: all built structures are destined to break down or fail
A series of infrastructure-related accidents in Ontario this summer has caused people to ask: Just how safe are the structures that we build? The answer a materials science and engineering professor offers may not be reassuring: “Nature always looks for ways to use energy in a favorable state — gravity always pushing things downwards is an example. Any built structure naturally goes against nature. Therefore, all structures will eventually be broken or destroyed — given the right amount of time, they will break down or fail.”
-
-
U.S. risks losing out to Asia in medical research
Medical research saves lives, suffering, and dollars — while also creating jobs and economic activity; the United States has long led the world, with hundreds of thousands of jobs and marketable discoveries generated by government research funding every year; this is now changing: strong, sustained growth in research spending in Asian nations contrasts with U.S. cuts and short-term approach, and a brain drain could result
-
-
Electric plants challenged by high temperatures, drought
The hottest July on record since 1895, along with the most wide-spread drought in the country since 1956, have nuclear plants struggling with finding enough water — cool water — to keep key parts of the plants cool; if the water gets too warm, operators have to dial back production — for reactor safety, and also to regulate the temperature of discharge water, which affects aquatic life
-
-
Glass offers a better way of storing U.K. nuclear waste

Researchers have shown, for the first time, that a method of storing nuclear waste normally used only for High Level Waste (HLW) could provide a safer, more efficient, and potentially cheaper solution for the storage and ultimate disposal of Intermediate Level Waste (ILW)
-
-
No-till could help stabilize crop yields despite climate change
Reducing tillage for some Central Great Plains crops could help conserve water and reduce losses caused by climate change, according to studies at the U.S. Department of Agriculture
-
-
New camouflage makeup shields soldiers from searing heat of bomb blasts
The new camouflage makeup protects the face and hands for up to fifteen seconds before its own temperature rises to the point where a first-degree burn, which is a mild burn, might occur; in some tests, the new face paint can protect for up to sixty seconds, which could be important in giving soldiers time to move away from blast-related fires and also for use by civilian firefighters
-
-
ONR’s augmented-reality project progresses

The Office of Naval Research (ONR) yesterday demonstrated the next phase of an augmented-reality project which will change the way soldiers view operational environments — literally
-
More headlines
The long view
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Vulnerable to Road Object Spoofing and Vanishing Attacks
Researchers have demonstrated the potentially hazardous vulnerabilities associated with the technology called LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, many autonomous vehicles use to navigate streets, roads and highways. The researchers have shown how to use lasers to fool LiDAR into “seeing” objects that are not present and missing those that are – deficiencies that can cause unwarranted and unsafe braking or collisions.
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
Prototype Self-Service Screening System Unveiled
TSA and DHS S&T unveiled a prototype checkpoint technology, the self-service screening system, at Harry Reid International Airport (LAS) in Las Vegas, NV. The aim is to provide a near self-sufficient passenger screening process while enabling passengers to directly receive on-person alarm information and allow for the passenger self-resolution of those alarms.
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Testing Cutting-Edge Counter-Drone Technology
Drones have many positive applications, bad actors can use them for nefarious purposes. Two recent field demonstrations brought government, academia, and industry together to evaluate innovative counter-unmanned aircraft systems.
Strengthening the Grid’s ‘Backbone’ with Hydropower
Argonne-led studies investigate how hydropower could help add more clean energy to the grid, how it generates value as grids add more renewable energy, and how liner technology can improve hydropower efficiency.
