-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
-
Helping first responders identify chemical, biological, and radiological agents
The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has expanded the reach and capabilities of its rapid urban plume modeling and hazard assessment system, CT-Analyst, by providing a commercial license to Valencia, California-based Safe Environment Engineering (SEE) for the fields of use of public safety, industrial safety and monitoring, and environmental monitoring. CT Analyst is a tool designed to provide first responders with fast and accurate predictions of chemical, biological, and radiological agent airborne transport in urban environments. CT Analyst will be integrated into the existing product line of SEE’s Lifeline MultiMeterViewer software suite.
-
-
Arkansas deploys first statewide SmartPrepare system
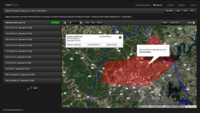
Arkansas uses citizen-supplied data for more efficient emergency planning and response. The service allows citizens to create secure profiles online which contain vital details about their household. Public safety officials can use the data to gain greater insight into their communities and identify potential challenges in order to prepare more effectively for disasters, allocate resources, and expedite emergency response and recovery efforts during events.
-
-
Dolphin-inspired radar system detects hidden surveillance, explosive devices

Scientists, inspired by the way dolphins hunt using bubble nets, have developed a new kind of radar that can detect hidden surveillance equipment and explosives. The twin inverted pulse radar (TWIPR) is able to distinguish true targets, such as certain types of electronic circuits that may be used in explosive or espionage devices, from clutter (for example, other metallic items like pipes, drinks cans, or nails) which may be mistaken for a genuine target by traditional radar and metal detectors.
-
-
Hazmat Challenge tests skills of hazmat response teams from three states

Twelve hazardous materials response teams from New Mexico, Missouri, and Oklahoma will test their skills at the 17th annual Hazmat Challenge, which will be held 30 July through 2 August at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
-
-
Responding to public health emergencies

Over the past decade, community engagement has become a central tenet of U.S. federal approach to public health emergency preparedness. Little is known, however, about how the vision of a ready, aware, and involved populace has translated into local practice.
-
-
Automakers help Detroit emergency services
General Motors, Ford Motors, and the Chrysler Group joined Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan, Quicken Loans, and several other businesses in the Detroit area to donate $8 million for new ambulances and police cars, on the same day that emergency manager Kevyn Orr started his job.
-
-
Napa Valley hospital employees fearful of new, wearable security system
Employees at a Napa Valley, California hospital are required to carry an alarm device on a lanyard around their necks; the alarm device is about the size of a smart phone and can send and receive signals during an emergency; after incidents in which psychiatric patients tried to choke employees by grabbing and twisting the lanyards, employees want other options for carrying the alarm device
-
-
Handheld plasma flashlight rids skin of pathogens
Scientists develop a handheld, battery-powered plasma-producing device that can rid skin of bacteria in an instant; the device could be used in ambulance emergency calls, natural disaster sites, military combat operations, and many other instances where treatment is required in remote locations
-
-
County experiments with new medical emergency dispatch protocol

In an effort to reduce costs and free up valuable resources, Kings County, Seattle is experimenting with a new 911 emergency call system that prioritizes emergency calls over nonemergency calls; under the new system, when residents call 911 with a serious medical emergency, the system will dispatch a fire truck or ambulance
-
-
The Red Cross, emergency response, and Twitter
Social media has become such an integral part of our lives that emergency responders are now turning to Twitter and Facebook to gain valuable information during natural disasters or crises
-
-
Infant survivor of Indiana tornadoes dies, death toll rises to 39
The fifteen-month old infant survivor of the twisters that struck Kentucky and Indiana, who had come to represent a symbol of hope, has died; the death toll is now thirty-nine
-
-
New York overhauls emergency response capabilities post-Irene

Last week New York Governor Andrew Cuomo proposed a series of major initiatives to bolster the state’s emergency response capabilities; the proposals specifically incorporate lessons learned from the state’s response to Hurricane Irene and Tropical Storm Lee
-
-
London holds massive Olympic security drill

Last week, in preparation for the London 2012 Olympic Games, more than 2,500 government officials, local police, and emergency responders participated in a two-day long emergency drill that simulated a terrorist attack on the city’s transportation network
-
-
Study finds disaster survivors more prone to fatal mistakes
A new study concludes that survivors of traumatic natural disasters may suffer from a decline in mental capabilities causing them to make grave errors in their daily lives
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
