-
NSA’s bulk metadata collection program ends
The NSA on Sunday ended its controversial surveillance program, initiated by the George W. Bush administration in 2006, which collected the metadata of all communications in the United States. The creation of the bulk collection program was the result of criticism by the 9/11 Commission, and many security experts, who argued that the information about the nineteen 9/11 terrorists was available, but that law enforcement and intelligence agencies lacked structure and procedure which would have allowed them to “connect the dots.”
-
-
Israel-Russia communication: Straying Russian plane avoid being shot down

Israel defense minister, Moshe Ya’alon, on Sunday told reporters that a Russian jet recently entered Israeli airspace but was not shot down because Israel and Russia had established an effective open communication system between the two countries. Ya’alon said the plane, by mistake, entered about one mile into Israeli airspace and immediately turned around back to Syria when the Russians were notified.
-
-
Turkey’s, Russia’s official versions of jet shoot down scientifically impossible: Physicists
Two astrophysicists show that the official versions of both Turkey and Russia about the circumstances surrounding the shooting down of a Russian fighter jet over Turkey should be taken with a grain of salt. Turkey’s insists that the Russian jet flew over Turkish territory for 17 seconds, but this is contradicted by the video of the shooting provided by the Turkish military. Russia’s claims that the jet made a 90-dgree turn in order to avoid Turkish airspace does “not correspond to the laws of mechanics.”
-
-
New technique can tell whether a fingerprint belongs to a male or female
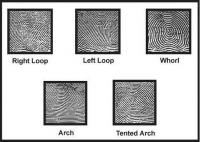
Culprits beware: researchers are taking crime scene fingerprint identification to a new level. They have discovered a straightforward concept for identifying whether a culprit is male or female. It is based on the content in fingerprints — specifically amino acids. Amino acid levels in the sweat of females are about twice as high as in males. There is also a slightly different distribution, due mostly to hormonal differences. The same is true for amino acids left behind in fingerprints.
-
-
New sensors detect cable fire before it starts burning
Fires are frequently caused by smoldering cables. New sensors now help detect such smoldering fires at an early stage by analyzing the plastic vapors released by overheated insulating cables. Scientists have developed these hybrid sensors that combine measurement processes with data evaluation. These detect the gases released from the plastic coating due to heating and reliably identify and analyze the gas mixture and its concentration.
-
-
NYPD commissioner to Congress: Do not allow people on terror watch list to buy guns
NYPD Commissioner Bill Bratton the other day called on Congress today to “start getting serious” about fixing the loophole which allows individuals on the U.S. terror watch list legally to purchase firearms in the United States. Bratton said: “If Congress really wants to do something instead of just talking about something, help us out with that terrorist watch list, those thousands of people that can purchase firearms in this country. I’m more worried about them than I am about Syrian refugees.”
-
-
N.Y. State Police app helps citizens report suspicious activity
The New York State Police is urging citizens to download a new digital app which allows citizens to capture and report suspicious activity with their smart phones. The app is part of the “See Something, Send Something” campaign which aims to turn willing citizens into the eyes and ears of law enforcement. For example, if a citizen notices an unattended package at a train station of an airport, they could use the app to alert law enforcement.
-
-
Tech companies: weakening encryption would only help the bad guys
Leading technology companies — Apple, Microsoft, Google, Samsung, Twitter, Facebook, and fifty-six other technology companies — have joined forces to campaign against weakening end-to-end encryption, insisting that any weakening of encryption would be “exploited by the bad guys.” Apple’s chief executive Tim Cook recently asserted that “any backdoor is a backdoor for everyone.”
-
-
After Paris, it’s traditional detective work that will keep us safe, not mass surveillance
Before the dust has even settled from the attacks on Paris, familiar calls for greater surveillance powers are surfacing. The desire for greater security is understandable, but that doesn’t mean we should suspend our judgement on the measures proposed to bring it about. It’s widely accepted that intelligence work is the most effective form of counter-terrorism, and that the best intelligence comes from community engagement, not coercion. So we must be wary of the evangelism of those pushing technological solutions to security problems, and the political clamor for mass surveillance.
-
-
ISIS “trying to obtain chemical, nuclear weapons”: U.K. government
British prime minister David Cameron said yesterday that the government security review has warned that ISIS and al-Qaeda are trying to get their hands on chemical and nuclear weapons. Cameroon referred to the security review in a speech in which he called on Members of Parliament to approve U.K. air strikes in Syria within a week. The British government pledged allocation additional resources for new equipment and the creation of within the Army of two new rapid response “strike brigades” of 5,000 soldiers each. The number of civilian jobs in the Ministry of defense, though, will be heavily reduced.
-
-
Smart sensor detects single molecule in chemical compounds
Researchers have developed a smart sensor that can detect single molecules in chemical and biological compounds — a highly valued function in medicine, security, and defense. The researcher used a chemical and biochemical sensing technique called surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), which is used to understand more about the make-up of materials.
-
-
Telegram IM app recalibrates policies after Paris attacks
Pavel Durov, the creator of the popular instant messaging app Telegram, has said that following the Paris terrorist attacks, his company has blocked dozens of accounts associated with the jihadist Islamic State group. As is the case with other technology companies, Telegram is trying to negotiate the balance between privacy and security: the same privacy-enhancing technology which keeps customers’ communication private, also helps terrorists communicate with each other and plot attacks safe from monitoring and surveillance by intelligence agencies and law enforcement.
-
-
Demonstrating technologies for disaster response
Radiological incidents such as Chernobyl and Fukushima illustrate the need for effective coordination of federal, state, and local agencies in response efforts. Earlier this year, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate’s (S&T) National Urban Security Technology Laboratory (NUSTL) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) demonstrated new technology developments at the Columbus, Ohio, Battelle Memorial Institute facility that will enable more effective radiological decontamination.
-
-
2 dead, 7 arrested in French police raid on apartment building in search of attacks’ mastermind
About 200 members of the special units of the French police early Wednesday morning (Paris time) swooped on the Parisian banlieue, or suburb, of Saint-Denis – where the Stade de France, one of the sites of Friday’s terrorist attacks, is located – and arrested seven people. Two people were killed. One of the dead was a young woman who blew herself up with a suicide vest. French Prosecutor Francois Molins told reporters that the operation was a result of a credible tip — in all likelihood, a police informer who resides in the neighborhood — suggesting Abdelhamid Abbaaoud, a 27-year-old Belgian of Moroccan origin, was holed up in an apartment in a residential building.
-
-
Paris terrorist attacks reignite debate over end-to-end encryption, back doors
The exact way the terrorists who attacked France last Friday communicated with each other, and their handlers, in the run-up to the attack is not yet clear, but the attack has prompted law enforcement and intelligence agencies in Europe and the United States to renew their call to regulate the use of new encryption technologies which allow users to “go dark” and make it difficult, if not altogether impossible, to retrieve the contents of communication.
-
More headlines
The long view
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
By Trina West
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
Using Drone Swarms to Fight Forest Fires
Forest fires are becoming increasingly catastrophic across the world, accelerated by climate change. Researchers are using multiple swarms of drones to tackle natural disasters like forest fires.
Testing Cutting-Edge Counter-Drone Technology
Drones have many positive applications, bad actors can use them for nefarious purposes. Two recent field demonstrations brought government, academia, and industry together to evaluate innovative counter-unmanned aircraft systems.
European Arms Imports Nearly Double, U.S. and French Exports Rise, and Russian Exports Fall Sharply
States in Europe almost doubled their imports of major arms (+94 per cent) between 2014–18 and 2019–23. The United States increased its arms exports by 17 per cent between 2014–18 and 2019–23, while Russia’s arms exports halved. Russia was for the first time the third largest arms exporter, falling just behind France.
How Climate Change Will Affect Conflict and U.S. Military Operations
By Doug Irving
“People talk about climate change as a threat multiplier,” said Karen Sudkamp, an associate director of the Infrastructure, Immigration, and Security Operations Program within the RAND Homeland Security Research Division. “But at what point do we need to start talking about the threat multiplier actually becoming a significant threat all its own?”
The Tech Apocalypse Panic is Driven by AI Boosters, Military Tacticians, and Movies
By Matthew Guariglia
From popular films like a War Games or The Terminator to a U.S. State Department-commissioned report on the security risk of weaponized AI, there has been a tremendous amount of hand wringing and nervousness about how so-called artificial intelligence might end up destroying the world. There is one easy way to avoid a lot of this and prevent a self-inflicted doomsday: don’t give computers the capability to launch devastating weapons.
