-
Transporting diluted bitumen through pipelines does not increase likelihood of release
Scientific study has found that the thick Canadian crude oil, known asdiluted bitumen, whichwould be shipped to the U.S. through the Keystone XL pipleline is no more dangerous than transporting other types of crude oil.
-
-
Environmentalists begin a summer of protest against Keystone project
A coalition of environmentalist groups calling itself “fearless summer” launched what it said would be a series of protests against the Keystone XLL pipeline project. Near the city of Seminole, Oklahoma, members of the group shackled themselves to industrial equipment and disruoted work at Keystone-related construction site. Ten were arrested.
-
-
Policy, regulatory issues hobble hydropower as wind-power backup

Theoretically, hydropower can step in when wind turbines go still, but barriers to this non-polluting resource serving as a backup are largely policy- and regulation-based, according to researchers.
-
-
Methane, ethane, and propane found in water wells near shale gas sites
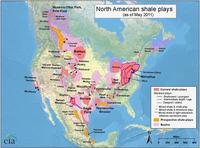
Homeowners living within one kilometer of shale gas wells appear to be at higher risk of having their drinking water contaminated by stray gases, according to a new study. Scientists analyzed 141 drinking water samples from private water wells across northeastern Pennsylvania’s gas-rich Marcellus shale basin. Their study documented not only higher methane concentrations in drinking water within a kilometer of shale gas drilling — which past studies have shown — but higher ethane and propane concentrations as well.
-
-
An environmentally friendly battery made from wood
Taking inspiration from trees, scientists have developed a battery made from a sliver of wood coated with tin that shows promise for becoming a tiny, long-lasting, efficient and environmentally friendly energy source. Their report on the device — 1,000 times thinner than a sheet of paper — appears in the journal Nano Letters.
-
-
Shale oil and shale gas resources globally abundant: report
Estimated shale oil and shale gas resources in the United States and in 137 shale formations in forty-one other countries represent 10 percent of the world’s crude oil and 32 percent of the world’s natural gas technically recoverable resources, or those that can be produced using current technology. A new report estimates technically recoverable 345 billion barrels of world shale oil and 7,299 trillion cubic feet of world shale gas.
-
-
Natural gas from fracking, coal have similar energy return on investment (EROI)
The value of a fuel’s long-term usefulness and viability is judged through its energy return on investment, that is, the comparison between the eventual fuel and the energy invested to create it. A new study finds that shale gas has a return value which is close to coal.
-
-
Risk assessment of shale gas fracking to biodiversity

Fracking, the controversial method of mining shale gas, is widespread across Pennsylvania, covering up to 280,000 km² of the Appalachian Basin. New research explores the risks posed to biodiversity including pollution from toxic chemicals, the building of well pads and pipelines, and changes to wetlands.
-
-
Increased U.S. crude oil production leads to dramatic fall in oil imports
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) issued its Annual Energy Outlook 2013 (AEO2013), which shows that under the assumption of crude oil production of about ten million bbl/d between 2020 and 2040 – which means total U.S. liquid fuels production (which includes crude oil, natural gas liquids (NGL), refinery gains, biofuels, and other liquid fuels) of more than eighteen million bbl/d in 2040 – net import of oil drops to 7 percent or less of total demand compared to 40 percent in 2012.
-
-
Environmental group sues State Department for Keystone XL-related files
The Sierra Club has announced it is suing the State Department for files related to an environmental review draft of the Keystone XL pipeline. The group tried to gain access to the files through the Freedom of Information Act, but the request was denied, so the group filed the suit on Monday in the U.S. District Court in the Northern District of California.
-
-
Understanding next-generation nuclear fuel
The long search for the location of a rare element within nuclear fuel particles has ended. Researchers have finally pinpointed where silver congregates inside irradiated particles of a new type of nuclear fuel. The finding will help scientists better understand how select fission products such as silver can escape from tristructural isotropic (TRISO) fuel. This specialized fuel could run high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) that have numerous enhanced safety features.
-
-
Making jet fuel from switchgrass

The Energy Department’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) is partnering with Cobalt Technologies, U.S. Navy, and Show Me Energy Cooperative to demonstrate that jet fuel can be made economically and in large quantities from a renewable biomass feedstock such as switch grass. The project could spur jobs in rural America, lead to less reliance of foreign oil.
-
-
U.S. unlikely to meet its biofuel goals

The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 (EISA) mandates that by 2022 the United States derive fifteen billion gallons per year of ethanol from corn to blend with conventional motor fuels. A new study says that if the climate continues to evolve as predicted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the United States stands little to no chance of satisfying its biofuel goals.
-
-
Health impact of Chernobyl accident overestimated: study

The impact of the Chernobyl nuclear accident has been seriously overestimated, while unfounded statements presented as scientific facts have been used to strangle the nuclear industry, according to Russian researchers.
-
-
California Democratic lawmakers want a go-slow approach to fracking
California may be on the verge of an oil rush. It is estimated that hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, at the Monterey Shale formation may tap reserves of fifteen billion barrels of oil. Democratic lawmakers do not see it that way, and have proposed numerous anti-fracking bills aiming to control the use of the controversial technology. Ten bills have been tabled so far, and more are on the way.
-
More headlines
The long view
Strengthening the Grid’s ‘Backbone’ with Hydropower
Argonne-led studies investigate how hydropower could help add more clean energy to the grid, how it generates value as grids add more renewable energy, and how liner technology can improve hydropower efficiency.
LNG Exports Have Had No Impact on Domestic Energy Costs: Analysis
U.S. liquified natural gas (LNG) exports have not had any sustained and significant direct impact on U.S. natural gas prices and have, in fact, spurred production and productivity gains, which contribute to downward pressure on domestic prices.
