-
NIST seeks public comments on updated smart-grid cybersecurity guidelines
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is requesting public comments on the first revision to its guidelines for secure implementation of “smart grid” technology. The draft document, NIST Interagency Report (IR) 7628 Revision 1: Guidelines for Smart Grid Cybersecurity, is the first update to NISTIR 7628 since its initial publication in September 2010.
-
-
New method to help coastal communities adapt to sea-level rise
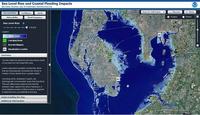
Future sea-level rise seems inevitable, although the rates and geographical patterns of change remain uncertain. Given the large and growing populations and economic activity in coastal zones, as well as the importance of coastal ecosystems, the potential impacts of sea-level change are far-reaching. Current methods to assess the potential impact of sea-level rise have varied significantly and hindered the development of useful scenarios and, in turn, suitable adaption policies and planning.
-
-
NIST releases Preliminary Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on Tuesday released its Preliminary Cybersecurity Framework to help critical infrastructure owners and operators reduce cybersecurity risks in industries such as power generation, transportation, and telecommunications. In the coming days, NIST will open a 45-day public comment period on the Preliminary Framework and plans to release the official framework in February 2014.
-
-
$32 million NSF grants for improving prediction of, response to natural disasters
With Sandy’s one-year anniversary – 29 October – next week, how do scientists better predict and respond to natural hazards such as hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, and wildfires? To find answers, the National Science Foundation (NSF) recently awarded twelve new research grants totaling $32 million. The awards will advance understanding of natural hazards and of technological hazards linked with natural phenomena, as scientists study ways of predicting and responding to hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, wildfires.
-
-
Cyber Grand Challenge for automated network security-correcting systems
What if computers had a “check engine” light that could indicate new, novel security problems? What if computers could go one step further and heal security problems before they happen? To find out, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) intends to hold the Cyber Grand Challenge (CGC) — the first-ever tournament for fully automatic network defense systems. The Challenge will see teams creating automated systems that would compete against each other to evaluate software, test for vulnerabilities, generate security patches, and apply them to protected computers on a network. The winning team in the CGC finals would receive a cash prize of $2 million, with second place earning $1 million and third place taking home $750,000.
-
-
Quake-triggered landslides a significant hazard for Seattle

Seattle is prone to strong shaking as it sits atop the Seattle Basin — a deep sedimentary basin that amplifies ground motion and generates strong seismic waves that tend to increase the duration of the shaking. A new study suggests the next big quake on the Seattle fault may cause devastating damage from landslides, greater than previously thought and beyond the areas currently defined as prone to landslides.
-
-
The only effective asteroid defense: early detection – and evacuation of impact area

For the threat of meteor strikes large or small, early detection is key, and evacuation may be the only defense needed within the next 1,000 years, according to an asteroid impact expert. He says that the best investment in asteroid defense is not in weapons to deflect them, but in telescopes and surveys to find them.
-
-
Weatherizing U.S. homes to uniform standard to save $33 billion a year
The U.S. residential sector — 113 million homes — uses about 23 percent of total U.S. source energy annually (source energy includes site energy, the energy consumed by buildings for heating and electricity, as well as the raw energy required to transmit, deliver and produce it). A new study finds that upgrading buildings’ airtightness to a uniform level could achieve as much as $33 billion in annual energy savings.
-
-
Geologists: Sandy could happen again
Sandy’s storm surge hit the coast at high tide, but storm and tidal conditions were not the only cause of the devastation. Seawaters off New York’s coast have risen sixteen inches since 1778, the year of New York City’s first major recorded storm. Geologists say that due to rising sea levels, smaller storms could produce significant flooding.
-
-
New barrier system to protect Venice from rising seas
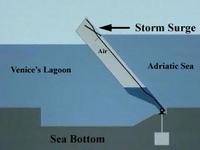
The City of Venice, Italy has carried out the first test of its $7.3 billion barrier system designed to protect the city from rising sea levels. The system, known as MOSE (MOdulo Sperimentale Elettromeccanico), consists of seventy-eight mobile barriers divided into four sections at the three inlets to the Venice lagoon.
-
-
Using hills to shelter buildings from tornadoes
Researchers have demonstrated the influence of hills on tornadoes. The researchers’ models revealed that the height of a hill and the size of a tornado’s vortex have a significant effect on the tornado’s destructive power. The findings could be used to identify safer areas for construction.
-
-
U.S. formulates strategy for a new Arctic landscape
U.S. national security officials have become increasingly concerned about the national security implications of an ice-free Arctic. The Arctic will become ice-free during the summer by mid-decade. In a strategy document, the Pentagon says: “Melting sea ice in the Arctic may lead to new opportunities for shipping, tourism, and resource exploration, but the increase in human activity may require a significant increase in operational capabilities in the region in order to safeguard lawful trade and travel and to prevent exploitation of new routes for smuggling and trafficking.”
-
-
Canadian city developed mathematical formula to evaluate risk
The City of Hamilton, Ontario has ranked Terrorism fourth on its list of top ten emergency risks, below Hazardous Materials and Explosions, Energy Supply Emergencies, and Epidemics/Pandemics.The city’s ranking of top 10 emergencies for which it plans is not a mere judgment call: The city’s emergency management office uses a mathematical equation to rate the risks to the city and its population.
-
-
Maryland preparing for sea level rise
Maryland has 3,100 miles of tidal shoreline. A scientific report recommends that it would prudent for the state to prepare for a sea level rise of 1.4 feet by 2050.Maryland’s CoastSmart Communities Initiative (CCI) provides grant funding for coastal communities which want to reduce their vulnerabilities to the effects of coastal hazards and sea level rise by becoming ready, adaptive, and resilient.
-
-
Maryland preparing for sea level rise
Maryland has 3,100 miles of tidal shoreline. A scientific report recommends that it would prudent for the state to prepare for a sea level rise of 1.4 feet by 2050.Maryland’s CoastSmart Communities Initiative (CCI) provides grant funding for coastal communities which want to reduce their vulnerabilities to the effects of coastal hazards and sea level rise by becoming ready, adaptive, and resilient.
-
More headlines
The long view
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Using Drone Swarms to Fight Forest Fires
Forest fires are becoming increasingly catastrophic across the world, accelerated by climate change. Researchers are using multiple swarms of drones to tackle natural disasters like forest fires.
