-
The irreducible elements of a Freeze Plus interim agreement with Iran
Iran and the P5+1 are set to resume talks on Iran’s nuclear program tomorrow, Thursday, 7 November in Geneva.The Institute for Science and International Security (ISIS) has developed a list of what it calls “irreducible elements” which a negotiated interim agreement should aim to achieve. These four elements are: Stopping the advance of Iran’s centrifuge and Arak reactor programs; extending breakout times; capping the Iranian centrifuge program and ensuring that it will not expand beyond this cap (in terms of enrichment output) during the next 5-15 years; and increasing the chance of finding a secret centrifuge or plutonium separation plant.
-
-
Where should U.S. radioactive waste be buried?
In the United States, about 70,000 metric tons of spent commercial nuclear fuel are located at more than seventy sites in thirty-five states. Shales and other clay-rich (argillaceous) rocks have never been seriously considered for holding America’s spent nuclear fuel, but it is different overseas. France, Switzerland, and Belgium are planning to put waste in tunnels mined out of shale formations, and Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom are evaluating the idea.
-
-
Where should U.S. radioactive waste be buried?
In the United States, about 70,000 metric tons of spent commercial nuclear fuel are located at more than seventy sites in thirty-five states. Shales and other clay-rich (argillaceous) rocks have never been seriously considered for holding America’s spent nuclear fuel, but it is different overseas. France, Switzerland, and Belgium are planning to put waste in tunnels mined out of shale formations, and Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom are evaluating the idea.
-
-
Sharp increase in radioactive water leaks at Fukushima
Tokyo Electric Power(TEPCO) has reported a rise in groundwater radiation levels, saying a tank at the firm’s Fukushima plant leaked 300 metric tons of toxic water in August 2013. Water samples from wells, taken in mid-October, show a record-high concentration of beta-ray emitting substances, and a sharp increase in the presence of radioactive tritium. Japanese prime ministerShinzo Abe, in a tacit admission that Japan cannot effectively handle the continuing radiation leaks from the stricken plant, said Japan would be interested in receiving foreign help to contain widening radioactive water leaks at Fukushima.
-
-
Bolstering the safety, security of U.S. nuclear weapons
To improve the safety and security of nuclear weapons, specialists must weigh the risks and benefits of making intrinsic changes to the warheads (possibly degrading their performance) or pursuing external changes such as better access controls, according to experts. While improvements such as use of shock- and fire-resistant chemical explosives in the warheads could further decrease the risk of an accidental nuclear detonation or dispersal of plutonium, most of the experts who participated in a workshop on the issue were not greatly concerned about the safety level of the current U.S. nuclear arsenal.
-
-
Compound derived from vegetables offers shield from lethal radiation doses

Researchers say a compound derived from cruciferous vegetable such as cabbage, cauliflower, and broccoli protected rats and mice from lethal doses of radiation. The compound, known as DIM could protect normal tissues in patients receiving radiation therapy for cancer, but could also protect individuals from the lethal consequences of a nuclear disaster.
-
-
Arktis closes $2 million financing round
Zürich, Switzerland-based Arktis Radiation Detectors Ltd., developer of a proprietary fast neutron detection technology which offers an innovative detection method for discovering well-shielded nuclear materials, successfully closed a round of financing worth $2 million.
-
-
$5 million NSF grant focuses on nuclear threat inspection
Penn State University has received a 5-year grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and DHS for nuclear threat inspection, as part of a team led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and including Georgia Tech. The grant will help develop new systems and sensors that will help detect nuclear weapons, special nuclear materials, radiation dispersal devices, and related threats.
-
-
Preventing nuclear terrorism

Nuclear terrorism remains a real and urgent threat. Despite an array of mechanisms established to combat this threat, several serious problems persist, requiring relentless attention and actions by the United States, Russia, and other responsible nations. These problems include continuing nuclear security vulnerabilities in a number of countries and the continued incidents of illicit trafficking in nuclear materials, radioactive sources, and the various components.
-
-
Iran indicates willingness to rethink nuclear program in exchange for sanction relief
As part of a series of steps designed to present post-election Iran as more pragmatic, President Hassan Rouhani and his advisers indicated they would be willing to consider curbs on Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for relief from the crippling economic sanctions imposed on Iran. Some Western experts say that all these steps are more than mere cosmetic changes, while skeptics note that Obama has reached out to Iran before, with no results. Veterans of past nuclear negotiations with Iran also noted that it is likely that Rouhani’s team may not yet fully understand the kinds of concessions that the Islamic republic would be required to make to have the most painful economic sanctions lifted.
-
-
Fukushima radioactive plume to reach U.S. next year
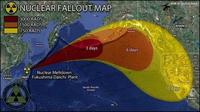
The radioactive ocean plume from the 2011 Fukushima nuclear plant disaster will reach the shores of the United States within three years from the date of the incident, but is likely to be harmless, according to a new study. While atmospheric radiation was detected on the U.S. west coast within days of the incident, the radioactive particles in the ocean plume take considerably longer to travel the same distance.
-
-
3D Earth model accurately pinpoints source of earthquakes, explosions
During the cold war, U.S. and international monitoring agencies could spot nuclear tests and focused on measuring their sizes. Today, they are looking around the globe to pinpoint much smaller explosives tests. Researchers are working on developing a 3-D model of the Earth’s mantle and crust called SALSA3D. The purpose of this model is to assist the U.S. Air Force and the international Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) in Vienna, Austria, more accurately locate all types of explosions.
-
-
Detecting radioactive material smuggled in containers

Nearly 90 percent of imported and exported goods travel the globe in shipping containers. Roughly 500 million containers travel the sea each year. A Sandia National Laboratories team completed acceptance testing on an enormous mobile scanner — the Mobile Radiation Detection and Identification System (MRDIS) — which makes smuggling radiological materials in containers more difficult.
-
-
U.S. nuclear facilities vulnerable to terrorist attack: study

Some U.S. nuclear facilities are inadequately protected against theft of weapons-grade materials and sabotage by terrorists. Terrorist attacks on vulnerable nuclear facilities could trigger a meltdown or lead to a diversion of bomb-grade uranium. The danger is far from hypothetical since the 9/11 hijackers are known to have considered flying a passenger jet into a U.S. nuclear reactor before they settled on the World Trade Center as their main terror target.
-
-
Nuclear academics, professionals meet for 6th annual ATR NSUF Users Week
The sixth annual Advanced Test Reactor National Scientific User Facility (ATR NSUF) Users Week was held 10-14 June at University Place, the satellite campus for Idaho State University and University of Idaho in Idaho Falls. This nuclear research-themed week was the user facility’s opportunity to update the user community on nuclear energy issues and tools, conduct a research forum where users can come and present their research, run specialized workshops, and build collaboration among academic, industry and government institutions.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
