-
U.S. first nuke in thirty years mired in costly legal wrangling
The U.S. first nuclear construction project in thirty years is the center of a $900 million lawsuit pitting Westinghouse Electric Co. against Georgia Power. The $14 billion project is about twenty months behind schedule and $900 million over budget, and each side blames the other for the delays and cost overruns.
-
-
Irish heritage groups sues U.K. over nuclear power plant
An Taisce, an Irish charity group promoting the preservation of Ireland’s heritage, is taking the British government to the High Court in London in December seeking a judicial review of the legality of British energy minister Ed Davey’s decision to approve the construction of a nuclear power plant just 150 miles from the Irish coast without consulting the Irish public.
-
-
Better protective shield material for nuclear waste
The integrity and survivability of a nuclear waste package is critically important in the transport of nuclear fuel and high-level waste. Research are working on developing an outer shield material for use in packaging which is resistant to corrosion, radiation, diffusion, and thermal cycling processes that affect fuel packages during long-term storage. The material will also need to be wear-tolerant and mechanically robust so that it can survive repeated handling and transportation.
-
-
U.S. nuclear power industry facing growing challenges
The U.S. nuclear industry is scaling back expectations on the future of the industry, expectations which only a few were soaring. The availability of cheaper energy alternatives, a growing trend toward energy conservation, and renewed safety and health worries as a result of the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plantaccident, are all reasons for why active nuclear plants are being forced to close, and why fewer energy companies are investing in new nuclear plants or upgrading existing ones.
-
-
Debate heats up over N.Y.’s Indian Point nuke license renewal
Indian Point nuclear power plant, located twenty-four miles north of New York City, provides 25 percent of the power used in New York City and Westchester County. The plant’s two reactors were built four decades ago, and the plant operator is seeking a 20-year license renewal for them, or they will have to be shut down. Opponents of the license renewal point to the risk inherent in operating aging reactors – and to a recently discovered risk: Indian Point is located near two active seismic areas — the Ramapo Fault Plain and the Peekskill-Stamford line.
-
-
Costly DOE uranium processing facility questioned

The cost of a proposed Department of Energy’s uranium processing facility for nuclear weapons at theY-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tennessee has increase nineteen times – from the original estimate of $600 million to $11.6 billion. If these estimates are accurate, the processing facility would entail one the largest investments in the U.S. nuclear weapons infrastructure since the Manhattan Project.
-
-
$5 million NSF grant focuses on nuclear threat inspection
Penn State University has received a 5-year grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and DHS for nuclear threat inspection, as part of a team led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and including Georgia Tech. The grant will help develop new systems and sensors that will help detect nuclear weapons, special nuclear materials, radiation dispersal devices, and related threats.
-
-
Jellyfish attack shuts down Swedish nuke
The Oskarshamn nuclear plant in southeastern Sweden, one of the world’s largest nuclear power plants, was forced to shut down when it was attacked by a large cluster of jellyfish. On Sunday, operators of the plant had to scramble reactor number three after a cluster of jellyfish, weighing several tons, clogged the cooling pipes which carry water to keep the core of the reactor cool.
-
-
Alabama State launches Nuclear Academy
A new academy at Alabama State University (ASU) will enhance security at nuclear, electric, and green-energy power installations across the United States and abroad. The new academy will provide comprehensive training for current and future security professionals who will offer infrastructure protection services to nuclear, electric and green-energy power installations.
-
-
Robust fourth-generation nuclear fuel withstands high-temperature accident conditions

A safer and more efficient nuclear fuel is on the horizon. A team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Idaho National Laboratory (INL) and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) have reached a new milestone with tristructural-isotropic (TRISO) fuel, showing that this fourth-generation reactor fuel might be even more robust than previously thought.
-
-
U.S. nuclear power industry facing dire prospects
The U.S. nuclear industry is facing several daunting challenges, with industry experts concluding that it may well be an energy source of the past. New construction of nuclear plants has come to a halt, older nuclear plants are closing, and plant expansions are put on hold. The main culprits: the price of natural gas is dropping fast because of new resources becoming available as a result of fracking, and wind and solar are making steady, if slow, gains.
-
-
Improving nuclear waste repositories
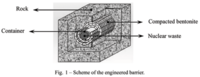
How fast will iodine-129 released from spent nuclear fuel move through a deep, clay-based geological repository? Understanding this process is crucial. Countries worldwide consider underground clay formations for nuclear waste disposal because clay offers low permeability and high radionuclide retention. Even when a repository is not sited in clay, engineered barriers often include a compacted buffer of bentonite, a common type of clay, to improve waste isolation.
-
-
Children living close to nuclear power plants do not have higher risk of developing leukemia

Young children who live near nuclear power plants do not have a greater risk of developing childhood leukemia or non-Hodgkin Lymphoma according to new research. Researchers conducted a study of almost 10,000 children under five years of age who were diagnosed with leukemia or similar cancers in Britain between 1962 and 2007. The scientists measured the distance from the nearest nuclear power plant both at birth and when diagnosed with childhood leukemia or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and found that there was no apparent extra risk living near a nuclear power plant.
-
-
Shale gas threatens U.S. nuclear power industry
The U.S. nuclear industry is facing a new enemy, and it is not anti-nuclear peacenicks. It is the shale gas boom, which on Tuesday claimed yet another victim when Entergy Corporation said it would close its Vermont Yankee reactor ahead of schedule. It is the fourth U.S nuclear plant to be closed this year, as utilities have concluded that investing in refurbishing older reactors is no longer economically viable.
-
-
Fukushima radioactive plume to reach U.S. next year
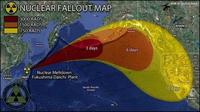
The radioactive ocean plume from the 2011 Fukushima nuclear plant disaster will reach the shores of the United States within three years from the date of the incident, but is likely to be harmless, according to a new study. While atmospheric radiation was detected on the U.S. west coast within days of the incident, the radioactive particles in the ocean plume take considerably longer to travel the same distance.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
