-
Calif.’s earthquake early warning system bill approved
California’s earthquake early warning system, State Senate Bill 135, was approved by Governor Jerry Brown. The bill requires the Office of Emergency Services (OES) to develop a comprehensive statewide earthquake early warning system to alert Californians in advance of shaking from an earthquake.
-
-
Improving earthquake early warning systems
Earthquake early warning systems may provide the public with crucial seconds to prepare for severe shaking. For California, a new study suggests upgrading current technology and relocating some seismic stations would improve the warning time, particularly in areas poorly served by the existing network — south of San Francisco Bay Area to north Los Angeles and north of the San Francisco Bay Area.
-
-
Helping first responders identify chemical, biological, and radiological agents
The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has expanded the reach and capabilities of its rapid urban plume modeling and hazard assessment system, CT-Analyst, by providing a commercial license to Valencia, California-based Safe Environment Engineering (SEE) for the fields of use of public safety, industrial safety and monitoring, and environmental monitoring. CT Analyst is a tool designed to provide first responders with fast and accurate predictions of chemical, biological, and radiological agent airborne transport in urban environments. CT Analyst will be integrated into the existing product line of SEE’s Lifeline MultiMeterViewer software suite.
-
-
Arkansas deploys first statewide SmartPrepare system
Arkansas uses citizen-supplied data for more efficient emergency planning and response. The service allows citizens to create secure profiles online which contain vital details about their household. Public safety officials can use the data to gain greater insight into their communities and identify potential challenges in order to prepare more effectively for disasters, allocate resources, and expedite emergency response and recovery efforts during events.
-
-
U.S. nation-wide quake early-warning system
The United States is likely to be struck by a major earthquake within the next twenty years. Scientists say that instead of waiting to experience a devastating earthquake and then invest in preventative measures for subsequent earthquakes, the country should be proactive and take action before the event. Investing in a nationwide earthquake warning system will save lives, prevent destruction of key infrastructure, and reduce the size of the economic loss that may result from an earthquake.
-
-
Building disaster-relief phone apps on the fly
Researchers combine powerful new Web standards with the intuitive, graphical MIT App Inventor to aid relief workers with little programming expertise.
-
-
California mulls costly earthquake early-warning system
The price of an early warning system which would alert California officials about an earthquake within sixty seconds before a major temblor strikes would be $80 million. The California legislature passed a bill on 13 September, requiring the state to develop the earthquake warning system, but it is unclear whether Governor Jerry Brown will sign the bill.
-
-
NASA, DHS to demonstrate disaster rescue tool
NASA and DHS are collaborating on a new radar device which detects heartbeats of victims trapped in wreckage. The device, known as the Finding Individuals for Disaster and Emergency Response (FINDER), can locate individuals buried under as much as thirty feet of crushed materials, hidden behind twenty feet of solid concrete, or from a distance of 100 feet in open spaces.
-
-
Training volcano scientists saves lives

Scientists and technicians who work at volcano observatories in nine countries are visiting Mount St. Helens and the U.S. Geological Survey Volcano Science Center’s Cascades Volcano Observatory this week to learn techniques for monitoring active volcanoes. The International Training Program in Volcano Hazards Monitoring is designed to assist other nations in attaining self-sufficiency in monitoring volcanoes and reducing the risks from eruptions.
-
-
U.S. Emergency Alerting System (EAS) vulnerable to hacking
The U.S. Emergency Alerting System (EAS) is designed to allow for quick alerts during an emergency. Researchers uncovered vulnerabilities in the digital alerting systems, vulnerabilities which allow an attacker remotely to log in over the Internet and manipulate any system function. The attacker could disrupt a TV or radio station’s ability to transmit and could disseminate false emergency information.
-
-
Gauging how residents in storm-prone regions react in the event of an imminent storm

StormView software program gauges how residents of hurricane-prone regions react to warnings and prepare for storms. The program is designed to be as realistic as possible in order accurately to assess how people would react in the event of an imminent storm.
-
-
New technologies help in tornado prediction

Scientists are working to increase tornado warning times. A new method, known as “warn-on forecasts,” will issue warnings based on forecasts rather than on observations. These warnings could increase the warning time to one -to-six hours before a tornado touches down. Another methodology being developed would give meteorologists the ability to tell people how strong the tornado will be before it hits the ground.
-
-
GPS technology offers 3-minute tsunami alerts
Researchers show that by using global positioning systems (GPS) to measure ground deformation caused by a large underwater earthquake, they can provide accurate warning of the resulting tsunami in just a few minutes after the earthquake onset.
-
-
Japan has an earthquake early-warning system, but California is yet to deploy one
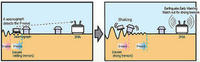
The 2011 Fukushima earthquake claimed many lives, but at least some lives were saved by an early warning system designed ten years ago at Caltech and deployed in Japan in 2007. The system gives people about a minute to prepare for the impending tremor. California is yet to deploy the system.
-
-
EU considers far-reaching Internet security initiative
Cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly more daunting challenge as governments try to prevent attacks against critical infrastructure on which the well-being of countries depends, now, several European countries are trying to come together in an effort to defend themselves against a cyber attack, but critics say the project, called CleanIT, goes too far
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
