-
Universal Detection developing smartphone radiation scanner for food
In the wake of Japan’s nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi atomic energy plant, concerns over contaminated food supplies have swept the nation, sparking Universal Detection Technology to develop a smartphone radiation detector specifically designed for comestibles
-
-
Anthrax-decontamination foam used in meth lab cleanup
The meth cleanup problem in the United States is a big one; the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration lists thousands of locations where law enforcement agencies have found chemicals or paraphernalia indicating the presence of either clandestine drug laboratories or dumpsites; Sandia’s decontamination foam, originally developed to deal with anthrax, is now also a meth eraser
-
-
Cell phone-based sensor detects E. coli
Researchers have developed a new cell phone-based fluorescent imaging and sensing platform that can detect the presence of the bacterium Escherichia coli in food and water
-
-
Thwarting the botulinum neurotoxin
The botulinum neurotoxin is the most poisonous substance known to man, causing botulism; it can be used by terrorists for deadly attacks; the toxin paralyzes muscle cells by disrupting their connections with the nerves that tell them how and when to move
-
-
New app to help fight nonnative species invasion of U.S.
Nonnative species invading the United States — animals, pathogens, and plants — deplete water supplies, poison wildlife and livestock, and damage property in urban and rural areas at a cost of about $138 billion annually; the U.S. Forest Service funded the development of an iPhone application that helps people identify harmful, non-native plants
-
-
Middle school robotics team develops solution to food poisoning

A group of eight middle school students in California has developed an electrolyzed water vending machine that can cheaply and effectively reduce food contamination
-
-
Drug-resistant MRSA in livestock now infects humans
A novel form of MRSA, a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus called ST398, can now be found in pigs, turkeys, cattle, and other livestock and has been detected in 47 percent of meat samples in the United States; the figures illustrate a very close link between antibiotic use on the farm and potentially lethal human infections
-
-
Kansas fights to keep bio lab project alive

Still reeling from the shock of finding out that the administration’s budget proposal does not contain any construction funds for the $650 million Bio Lab Level 4 facility in their state, Kansas political and business leaders vowed to fight to keep the project alive, including looking for alternative funding sources; the bio lab was considered the anchor of what is called an Animal Health Corridor stretching from Kansas State University in Manhattan, Kansas, to the University of Missouri in Columbia, Missouri
-
-
Antibiotic alternative to overcome drug-resisting infections
About 700 million people have symptomatic group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections around the world each year, and the infection can be fatal; researchers have found a potential alternative to conventional antibiotics that could fight infection with a reduced risk of antibiotic resistance
-
-
U.S. extends zero tolerance policy to six additional E.Coli serogroups
The U.S. Department of Agriculture has taken additional steps to fight E. coli in the food supply; the new policy adds six E. coli serogroups to the list of sergroups which are not allowed to be present in raw ground beef or the meat used to make raw ground beef; the beef industry says it will be too expensive to implement, and U.S. trading partners said preventing their beef from entering the U.S. unless tested for the six serogroups would violate existing trade agreement
-
-
Using ozone to kill prions dead
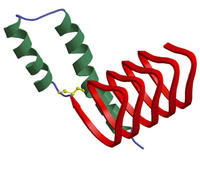
Prions are among the worst infectious-disease agents; these proteins are resistant to a wide variety of extreme disinfectant procedures; they have been identified as the culprits behind mad cow disease and chronic wasting disease in animals and humans, and are also implicated in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other prion-related disorders
-
-
Food safety business plan competition
Two Michigan-based organizations announce a business plan competition for ventures in the food safety area; entrepreneurs with new food safety business concepts will compete for $10,000 prize
-
-
Kansas biolab project on life support

In 2008, DHS chose Manhattan, Kansas, as the location for a new, $650 million BioLab Level 4; the new lab was planned as a replacement for the aging Plum Island facility; critics argued that the lab’s location — in the middle of Tornado Alley and at the center a region which is home to a large portion of the U.S. beef industry – was not ideal for a facility doing research on deadly animal and human pathogens; it now appears that budgetary considerations have doomed to project
-
-
Discovery paves way for salmonella vaccine
More than 1.4 million cases of salmonella occur annually in the United States, at an estimated cost of $3 billion and the loss of 580 lives; around the world, this increasingly antibiotic-resistant food-borne bacteria that kills hundreds of thousands of people worldwide each year; , immunologists have taken an important step toward an effective vaccine against salmonella
-
-
Georgia Tech’s software for rapid analysis of food-borne pathogens
A team of Goergia Tech bioinformatics graduate students, led by a biology professor, worked in close collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to create an integrated suite of computational tools for the analysis of microbial genome sequences
-
More headlines
The long view
Ransomware Attacks: Death Threats, Endangered Patients and Millions of Dollars in Damages
A ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a company that processes 15 billion health care transactions annually and deals with 1 in 3 patient records in the United States, is continuing to cause massive disruptions nearly three weeks later. The incident, which started on February 21, has been called the “most significant cyberattack on the U.S. health care system” by the American Hospital Association. It is just the latest example of an increasing trend.
