-
Extracting maximum energy from currents

In the long sprint to find new sources of clean, low-cost power, slow and steady may win the race — the slow-moving water of currents and tides, that is. Just as wind turbines tap into the energy of flowing air to generate electricity, hydrokinetic devices produce power from moving masses of water.
-
-
World's first grid-scale isothermal compressed air energy storage system
A New Hampshire company has completed construction and begun startup of the world’s first megawatt-scale isothermal compressed air energy storage (ICAES) system. The system stores and returns megawatts of electricity to provide long-term grid stability and support integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Unlike chemical battery systems, ICAES performance does not degrade over its lifetime or need frequent replacement. No hazardous materials are used.
-
-
History of explosives highlighted in museum exhibit
For more than seventy years, Los Alamos National Laboratory has been a frontrunner in explosives research, development, and applications. To highlight the Laboratory’s work in the field of explosives, the Bradbury Science Museum is opening a new exhibit, titled “The Science of Explosives.”
-
-
Unified military intelligence picture dispels the fog of war
Military operations depend upon the unimpeded flow of accurate and relevant information to support timely decisions related to battle planning and execution. To address these needs, numerous intelligence systems and technologies have been developed over the past twenty years, but each of these typically provides only a partial picture of the battlefield, and integrating the information has proven to be burdensome and inefficient. DARPA’s Insight program aims to bring real-time, integrated, multi-source intelligence to the battlefield.
-
-
Bomb-detecting lasers to improve security checkpoints

Research has put the possibility of bomb-detecting lasers at security checkpoints within reach by developing a laser that can detect micro traces of explosive chemicals on clothing and luggage. The laser not only detects the explosive material, but it also provides an image of the chemical’s exact location, even if it’s merely a minute trace on a zipper.
-
-
Flexible vehicle-arrest system stops cars involved in crime, terrorism

Researchers have developed a mathematical model that could help engineers design a flexible vehicle-arrest system for stopping cars involved in criminal activity or terrorism, such as suspect car bombers attempting break through a check point, without wrecking the car or killing the occupants.
-
-
New detectors for chemical, biological threats
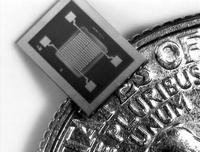
In the late 1990s, Sandia scientists developed a simple-to-use handheld chemical detector for the military, the MicroChemLab. Ever since, Sandia has improved such microfluidics- and microelectromechanical (MEMS) systems-based instruments that identify chemicals based on gas chromatography, or GC, and resonator-style instruments such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) detectors. The lab’s researchers are building on this sensor work to invent tiny detectors that can sniff out everything from explosives and biotoxins to smuggled humans.
-
-
Top Five most awesome robots
In the last decade, robots have often been employed on the battlefields of Iraq and Afghanistan, usually to seek out hidden bombs. More and more of these the robots are now being adopted by first response agencies to help in search-and-rescue operations in the wake of disasters. The growing interest in – and usefulness of — robotics have also inspired a series of competitions and challenges, some of which are directed at high-school and college students, to encourage budding scientists to go into the field of robotics.
-
-
3D Earth model accurately pinpoints source of earthquakes, explosions
During the cold war, U.S. and international monitoring agencies could spot nuclear tests and focused on measuring their sizes. Today, they are looking around the globe to pinpoint much smaller explosives tests. Researchers are working on developing a 3-D model of the Earth’s mantle and crust called SALSA3D. The purpose of this model is to assist the U.S. Air Force and the international Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) in Vienna, Austria, more accurately locate all types of explosions.
-
-
New technology improves IED detection

Improvised explosive devices, or IEDs, are homemade bombs that can both injure and kill civilians and service members. One solution to the problem of IEDs is to find them before they explode by detecting the chemicals used in the explosives. Scientists at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) have developed a technology, using silicon to fabricate a sensor that may revolutionize the way trace chemical detection is conducted
-
-
Unmanned undersea platform network to help better deploy naval capabilities
Today’s naval forces rely primarily on highly capable multifunctional manned platforms, such as ships and submarines. Even the most advanced vessel, however, can only be in one place at a time, making the ability to respond increasingly dependent on being ready at the right place at the right time. New Hydra program aims to make it easier, faster, and cheaper to deploy crucial capabilities worldwide.
-
-
World's smallest drone may be a search-and-rescue tool
Researchers have designed, built, and tested the world’s smallest open source autopilot for small unmanned aircraft. A smaller and lighter autopilot — it weighs only 1.9 grams — allows these small flying robots to fly longer, fit into narrower spaces, or carry more payloads such as cameras. This makes them more suitable to be used, for example, rescue operations.
-
-
A flying car is developed for the U.S. military

Flying cars would enhance the mobility of soldiers. Transportation will no longer be restricted to trafficable terrain that makes movement predictable and easy to track, and a flying car will enhance capabilities for resupply operations, fire-team insertion and extraction, and medical evacuation — reducing timelines and increasing the probability of survival.
-
-
Collaboration with industry leads to improved forensics
Three-dimensional (3D) scanners used at crime scenes for forensic investigations are not just the stuff of prime time television. Investigators and crime laboratories are using 3D laser scanning measurement systems to measure and model, in 3D simulations, the critical aspects of crime scenes. A 2009 National Academy of Sciences (NAS) report, however, questioned the reliability of some forensic sciences, including the use of 3D scanning technique. Furthermore, pressure began building in the forensics community to have crime laboratories and stand-alone crime scene units in the United States adhere to specific standards in their services, which require traceability to the SI [the SI in SI traceability refers to the International System of Units (Système International d’unités)].
-
-
Secure, private Internet and cloud to soldiers, marines at the tactical edge
Squads of soldiers or marines on patrol in remote forward locations often do not have the luxury of quickly sharing current intelligence information and imagery on their mobile devices, because they cannot access a central server. Troops frequently have to wait until they are back at camp to download the latest updates. In the meantime, mission opportunities may erode because the information needed at the tactical edge isn’t immediately available. DARPA’s Content-Based Mobile Edge Networking (CBMEN) program aims to provide an alternative approach to the top down focus of most military networks by starting the content sharing at the individual soldier or marine level.
-
More headlines
The long view
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Vulnerable to Road Object Spoofing and Vanishing Attacks
Researchers have demonstrated the potentially hazardous vulnerabilities associated with the technology called LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, many autonomous vehicles use to navigate streets, roads and highways. The researchers have shown how to use lasers to fool LiDAR into “seeing” objects that are not present and missing those that are – deficiencies that can cause unwarranted and unsafe braking or collisions.
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
By Trina West
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
Prototype Self-Service Screening System Unveiled
TSA and DHS S&T unveiled a prototype checkpoint technology, the self-service screening system, at Harry Reid International Airport (LAS) in Las Vegas, NV. The aim is to provide a near self-sufficient passenger screening process while enabling passengers to directly receive on-person alarm information and allow for the passenger self-resolution of those alarms.
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
By Zulfikar Abbany, Julia Vergin, and Katja Sterzik
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Testing Cutting-Edge Counter-Drone Technology
Drones have many positive applications, bad actors can use them for nefarious purposes. Two recent field demonstrations brought government, academia, and industry together to evaluate innovative counter-unmanned aircraft systems.
Strengthening the Grid’s ‘Backbone’ with Hydropower
By Michael Matz
Argonne-led studies investigate how hydropower could help add more clean energy to the grid, how it generates value as grids add more renewable energy, and how liner technology can improve hydropower efficiency.
The Tech Apocalypse Panic is Driven by AI Boosters, Military Tacticians, and Movies
By Matthew Guariglia
From popular films like a War Games or The Terminator to a U.S. State Department-commissioned report on the security risk of weaponized AI, there has been a tremendous amount of hand wringing and nervousness about how so-called artificial intelligence might end up destroying the world. There is one easy way to avoid a lot of this and prevent a self-inflicted doomsday: don’t give computers the capability to launch devastating weapons.
The Tech Apocalypse Panic is Driven by AI Boosters, Military Tacticians, and Movies
By Matthew Guariglia
From popular films like a War Games or The Terminator to a U.S. State Department-commissioned report on the security risk of weaponized AI, there has been a tremendous amount of hand wringing and nervousness about how so-called artificial intelligence might end up destroying the world. There is one easy way to avoid a lot of this and prevent a self-inflicted doomsday: don’t give computers the capability to launch devastating weapons.
