Invisibility cloaksNew invisibility cloak conceals objects from human view
For the first time, scientists have devised an invisibility cloak material that hides objects from detection using light that is visible to humans; the new “carpet cloak” works by concealing an object under layers of silicon oxide and silicon nitride etched in a special pattern, and bending light waves away from the bump that the object makes, so that the cloak appears flat and smooth like a normal mirror
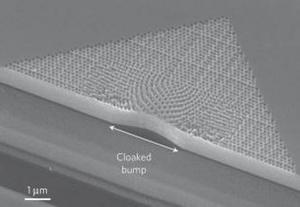
Change in weave pattern shows light bending around object // Source: nanometer.ru
For the first time, scientists have devised an invisibility cloak material that hides objects from detection using light that is visible to humans. The new device is a leap forward in cloaking materials, according to a report in the American Chemical Society (ACS) journal Nano Letters.
The American Chemical Society reports that Xiang Zhang and colleagues note that invisibility cloaks, which route electromagnetic waves around an object to make it undetectable, “are still in their infancy.” Most cloaks are made of materials that can only hide things using microwave or infrared waves, which are just below the threshold of human vision. To remedy this, the researchers built a reflective “carpet cloak” out of layers of silicon oxide and silicon nitride etched in a special pattern. The carpet cloak works by concealing an object under the layers, and bending light waves away from the bump that the object makes, so that the cloak appears flat and smooth like a normal mirror.
Although the study cloaked a microscopic object roughly the diameter of a red blood cell, the device demonstrates that it may be “capable of cloaking any object underneath a reflective carpet layer. In contrast to the previous demonstrations that were limited to infrared light, this work makes actual invisibility for the light seen by the human eye possible,” the scientists write.
The research was funded by the U.S. Army Research Office, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program.
— Read more in Majid Gharghi et al., “A Carpet Cloak for Visible Light,” Nano Letters, 11, no. 7 (27 May 2011): 2825–28 (DOI: 10.1021/nl201189z)
