-
Smart sensor detects single molecule in chemical compounds
Researchers have developed a smart sensor that can detect single molecules in chemical and biological compounds — a highly valued function in medicine, security, and defense. The researcher used a chemical and biochemical sensing technique called surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), which is used to understand more about the make-up of materials.
-
-
U.K. plans to boost counterterrorism, aviation security significantly

The U.K. government will substantially increase efforts to counter the threat from ISIS. In the five-year defense and security review, to be unveiled next week, the government details plans to increase the staff of MI5, MI6, and GCHQ by 1,900 officers; at least a double the funding for aviation security around the world; and deploy additional aviation security officers to assess security at overseas airports.
-
-
U.S. to unveil drone registry plan in response to safety, security concerns
As part of the U.S. aviation authorities’ effort to tackle the growing safety and security problems posed by drones, U.S. drone will soon be required to register their aircraft with the Department of Transportation. The register, to be made public on Monday, comes in response to a surge in incidents in which drones have flown near airports and crowded public venues.
-
-
Expert passport officers better than face recognition technology in detecting fraud
Face-matching experts at the Australian Passport Office are 20 percent more accurate than average people at detecting fraud using automatic face recognition software, new research shows. The study is the first to test how well people perform on this difficult but common operational task carried out by passport officers. “Our research shows that accuracy can be significantly improved by recruiting staff who are naturally good at face recognition - the so-called “super-recognizers” — and then giving them in-depth training in the use of the software,” said the study lead author.
-
-
FAA expands efforts to tackle risk of drones near busy airports
A steep increase in reports of small unmanned aircraft in close proximity to runways is presenting a new challenge for the FAA. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has entered into a Pathfinder agreement with CACI International Inc. to evaluate how the company’s technology can help detect Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) in the vicinity of airports.
-
-
Airport X-ray screening systems comply with health and safety radiation exposure standard
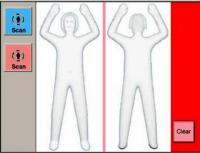
Machines that use advanced X-ray imaging technology to screen airport passengers comply with radiation exposure limits set by the American National Standards Institute/Health Physics Society (ANSI/HPS), says a new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The report also finds that the machines adhere to the recommended safety mechanisms described in the ANSI/HPS standards to prevent overexposure to radiation in the event of a mechanical failure or deliberate tampering.
-
-
TSA agents find record number of guns in carry-on luggage at airports
TSA agents discovered 67 guns in carry-on luggage during the week which ended 17 September. The tally for the week broke an earlier record of 65 firearms found during one week in May 2013. TSAofficers found nearly 1,900 firearms in carry-on luggage between 1 January and 31 August 2015. This year is thus on track to see a 28 percent spike in the number of firearms found compared to the 2,212 guns — an average of about 40 a week — discovered by TSA agents in 2014.
-
-
Residents of 4 states may need more than a driver license to board domestic flights
Residents of four states — New York, New Hampshire, Minnesota, and Louisiana – may soon need more than their driver’s licenses as a means of identification when boarding an aircraft for a domestic flight, DHS says. These states’ licenses do not meet the standards stipulated by DHS under the latest phase of the federal Real ID Act of 2005. Residents from these four states will have to present their passports with them, or some other means of DHS-approved identification, before being allowed on board.
-
-
Bringing contactless fingerprint technology to market

Quickly moving through security checkpoints by showing your hand to a scanner seems straight out of science fiction, but work is being done to bring fast, touchless fingerprint readers out of the lab and into the marketplace. The touchless technology offers speed and a hygienic alternative to conventional fingerprint readers.
-
-
TSA deploys AtHoc crisis communication solution in 200 airports
TSA joins the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) in deploying AtHoc to improve crisis communication in 200 U.S. airports. TSA’s Alert Warning System (AWS), based on AtHoc, will enable real-time accountability of TSA staff during routine, emergency, and critical events.
-
-
Airport body scanners fail to provide promised security
Since 2008, the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) has spent $160 million on scanners to identify passengers which may be carrying weapons. These scanners, however, do not perform as well as was originally believed.Independent audits have found that the system provides weak protection against determined adversaries.A display of the mock weapons and explosives whichthat investigators were able to get through the scanners included various size folding knives, a kitchen knife, explosive-less hand grenades, a handled awl, a lighter, handguns, ammunition, a shotgun shell, various bludgeons, and a nunchaku.
-
-
U.S., Canada, Mexico create North American Trusted Traveler network

DHS said it has joined Public Safety Canada and the Secretariat of Governance of Mexico in outlining the first steps toward the creation of a North American Trusted Traveler network. The new agreement, signed on 10 July 2015, will make it easier for eligible travelers in the United States, Mexico, and Canada to apply for expedited screening programs. Eligible travelers will be able to apply for each program beginning in 2016.
-
-
D.C. security gaps exposed by gyrocopter landing on Capitol grounds: Senate panel
A Senate committee has concluded that the Florida man who flew a one-man gyrocopter and landed it on the U.S. Capitol grounds, had exposed security gaps and inadequate coordination among the agencies charged with protecting the Capitol, the White House, and other Washington landmarks. In addition to calling for better coordination among the different agencies responsible for securing important sites in Washington, D.C., the committee strongly recommends seeking new “technological solutions” to spot similar flights in the future, suggesting that Congress should also consider increasing penalties for those who breach the restricted airspace.
-
-
New air traffic management system to make drone air traffic safer

Researchers are now working on a new, low-altitude traffic management system to keep fast-moving flyers safer as they cruise through increasingly crowded skies. A handful of organizations are participating in the first phase of the NASA Ames Unmanned Aerial Systems Traffic Management project to enable safer use of low-altitude airspace, of 500 feet and below, where autonomous aerial vehicles, helicopters, gliders, and other general aircraft are operating.
-
-
Bomb-proof lining contains explosion in aircraft’s luggage hold
A bomb-proof lining developed by an international team of scientists has successfully contained blasts in a series of controlled explosions in the luggage hold of a Boeing 747 and an Airbus 321. The Fly-Bag, which lines an aircraft’s luggage hold with multiple layers of novel fabrics and composites, was tested last week under increasing explosive charges on disused planes. The tests, using this technology, have demonstrated that a plane’s luggage hold may be able to contain the force of an explosion should a device concealed within a passenger’s luggage be detonated during a flight.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
