-
Hackers well-versed in Wall Street vernacular hack publicly traded companies
Security firm FireEye’s recent reporton a group of hackers who have been infiltrating e-mail correspondence from more than 100 organizations, differs from the company’s previous reportson cyber criminals operating from China or Russia. This time, the hackers are based in North America or Western Europe, and are well-versed in Wall Street vernacular. The hackers, who FireEye named “FIN4” because they are one of many groups that hack for financial gain, targeted mostly publicly traded healthcare or pharmaceutical companies, along with their advisory firms, in pursuit of information that could affect global financial markets.
-
-
Online tools help users adopt better privacy practices
Research shows a growing concern for online privacy, but Internet users give up personal information every day in exchange for the convenience and functionality of a variety of online services. Online privacy is distinct from online security, which encompasses efforts to mitigate the theft of personal information. Most violations of online privacy are not illegal but rather the results of tacit consumer consent. The new Privacy Helper mobile app teaches users about the features on their phones that can affect privacy. The key to Privacy Helper, its developers say, is its flexibility in giving users better control over how they share personal information.
-
-
Southeastern Louisiana has a problem: "The sea is rising and the land is sinking"
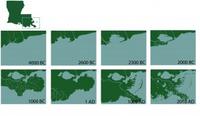
Southeastern Louisiana is drowning at the rate of one football field per hour, totaling up to sixteen square miles annually. In just eighty years, sea level rise, fossil fuel extraction, and having too few wetlands separating the Gulf from the flood protection levee systems have caused some 2,000 square miles of Louisiana’s coastal landscape to sink into the Gulf of Mexico. The issues facing Louisiana’s southeastern coast pose a threat to American energy and economic stability. A $50 billion, 50-year coastal restoration plan, formulated in 2007, is yet to be accepted and funded, but experts note that if sea-level rise is as bad as the worst case scenario, several projects at the heart of the restoration plan would become infective.
-
-
A solution to the U.S. water problem: People who use more water, pay more
Approximately one-third of the United States is in at least a moderate state of drought. Exacerbating the drought is a rapidly increasing population. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates the country’s population will balloon from nearly 310 million in 2010 to more than 420 million in 2060. Experts say that current levels of water consumption cannot continue. One expert says that seasonally adjusted increasing block rates could be the answer. In short, people who use more water, pay more.
-
-
Egypt thwarts terrorist attack on Israeli gas platforms in the Mediterranean Sea

Egypt said it had thwarted an attempt by Islamic State (ISIS)-affiliated Egyptian terrorists on 12 November to attack Israeli energy platforms in the Mediterranean Sea. The terrorists, members of the Ansar Bayt al-Maqdis terror group which operates in the Sinai Peninsula, commandeered an Egyptian navy missile boat for the planned attack. Other Egyptian navy vessels gave chase and stopped the commandeered missile boat, killing eight aboard in a heavy exchange of fire. In addition to attacking Israeli gas platform, the terrorists planned to attack Israeli ships.
-
-
Impasse in Congress over terrorism insurance (TRIA) renewal

The Terrorism Risk Insurance Act(TRIA) is expected to expire by 31 December unless Congress renews the legislation or places a temporary extension. The legislation, initially established in November 2002 as a federal backstop to protect insurers in the event an act of terrorism results in losses above $100 million, has been extended and reauthorized. The insurance industry supports the reauthorization approved by the Senate, and opposes a short-term extension. Some insurance companies have noted on their contracts that policyholders could lose terrorism coverage if TRIA is not renewed.
-
-
Here’s how to fix America’s crumbling bridges

There are about 600,000 bridges in the United States, and about one in four is classified as functionally obsolete or structurally deficient. This doesn’t mean they’re in danger of imminent collapse; they may be simply too narrow or built for lighter traffic than today’s standards. Bridges that can’t support heavy trucks have weight restrictions posted. There are plenty of repairs that need to be done. With government funding for infrastructure projects being so tight, an alternative has arisen in what are called public-private partnerships, often abbreviated PPP or P3. In this arrangement, private investors assume the responsibility for financing and building a bridge or highway, and the investors are granted the right to collect tolls for what may be decades. The investors naturally believe they will realize a good return on their investment, even after they pay the public partner a sizable sum upfront for the concession. This upfront payment can be in the billions of dollars, which can be very tempting for a state or municipality struggling to balance its budget.
-
-
Internet security market to reach $42.8 billion globally by 2020
According to a new report by Allied Market Research, the global Internet security market is expected to reach $42.8 billion by 2020, registering a CAGR of 8.1 percent during 2014-2020. The market, driven by demand for software solutions, would experience a shift toward the adoption of cloud-based systems. About 80 percent of the top companies today identify with cloud-based security services which have become a prominent market trend.
-
-
A malware more sophisticated than Stuxnet discovered
Security experts at Symantechave discovered the world’s most sophisticated computer malware, Regin. Thought to have been created by a Western intelligence agency, and in many respects more advanced than Stuxnet — which was developed by the U.S. and Israeli government in 2010 to hack the Iranian nuclear program — Regin has targeted Russian, Saudi Arabian, Mexican, Irish, and Iranian Internet service providers and telecoms companies. “Nothing else comes close to this … nothing else we look at compares,” said one security expert.
-
-
Security concerns over purchase of Waldorf Astoria by Chinese company

Citing espionage risk, U.S. officials are expressing concern over the sale of the historic Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City to a Chinese insurance company. The sale of the hotel will likely lead to a review by the U.S. Committee on Foreign Investment (CFIUS) of the Chinese firm’s long-term plans for the site and the finer details of the sale. “Because the agreement calls for major renovations to the hotel, CFIUS will be worried that the Chinese could engage in some form of espionage,” said a former Treasury Department official who managed CFIUS reviews.
-
-
China’s second “great wall” is not so great

China’s coastal regions are only 13 percent of the country’s land area, but contribute 60 percent of its gross domestic product. With that come layers of incentives to turn lush wetlands into engines of development and industry. A new study finds that China’s second great wall, a vast seawall covering more than half of the country’s mainland coastline, is a foundation for financial gain - and also a dyke holding a swelling rush of ecological woes.
-
-
New, updated resource on STEM education, workforce
It just became a lot easier for educators, students, parents, policymakers and business leaders to learn more about national trends in education and jobs in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). The National Science Board (NSB) last month released an interactive, online resource featuring new and updated data and graphics about STEM education and workforce in the United States and providing facts on topics such as student proficiency, college degrees in STEM fields, and jobs in science-related occupations.
-
-
Selling and buying water rights
Trying to sell or buy water rights can be a complicated exercise. First, it takes time and effort for buyers and sellers to find each other, a process that often relies on word-of-mouth, local bulletin boards, even calling friends and neighbors to get the word out. Then they must deal with the maze of rules and regulations involved. Finally, they must reach a fair price. It would be much easier if a computer could do it. Now, one can. Scientists have developed an algorithm that can match potential buyers and sellers, sift through the complexity of local physical and regulatory systems, and reach a fair deal designed especially for them.
-
-
Climate-related businesses growing
The business of climate change has seen significant growth in the last decade, but analysts believe it will take many more years to determine the effectiveness of the solutions proposed by climate-focused businesses. U.S. farmers working more than fifty million acres had subscribed to its Climate Basic Service— a free Web and mobile service that analyzes data to help farmers make planting decisions with “field-level insights, from soil moisture levels, to crop growth stage, to current and future weather.” The group’s free app and Web service may be augmented through its Climate Proand Precision Acrepaid plans.
-
-
Water sector ready for investment, technological innovation

Investors looking for promising growth markets would do well to consider their water bill. Water’s artificially low price in most of the United States is one factor holding back innovative new water technologies, according to the report – but the time is right for change. Across the West, drought has left wide swaths of agricultural land brown, with massive wildfires raging through tinder-dry forests, residential wells tapped out and unemployed farm workers crowding food pantries. The drought is projected to cost the agricultural sector about $2.2 billion in 2014. The social and ecological damage is also profound. Technological innovation in the water sector could bring a raft of benefits ranging from the conservation of scarce water supplies to the expansion of water supplies through technologies that recycle or desalinate, for example.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
