-
Quebec deadly accident revives pipeline vs. rail debate

The sharp increase in U.S. domestic oil production in the last four years, and the opening by the Obama administration of new areas for drilling, have greatly benefitted U.S. rail companies, which now enjoy the added business of transporting oil from places where pipelines do not exist.U.S. domestic shipments of oil have increased from 9,500 carloads in 2008 to more than 230,000 carloads last year. The deadly Lac-Megantic, Quebec crude-oil train accident revives the debate about the relative safety merits of two modes of transporting oil over long distances – rail vs. pipeline. Proponents of the Keystone XL pipeline project say the Quebec accident will boost support for their cause.
-
-
Assessing the social, economic effects of Deepwater Horizon spill
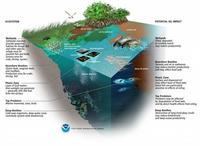
Numerous studies are under way to determine the impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on the Gulf of Mexico, but the extent and severity of these impacts and the value of the resulting losses cannot fully be measured without considering the goods and services provided by the Gulf, says a new report from the National Research Council (NRC). The report offers an approach that could establish a more comprehensive understanding of the impacts and help inform options for restoration activities.
-
-
Brazil’s problem: abundant grain, inadequate storage
Tropical climates that allow for year-round farming would seem to be a tremendous economic advantage, but for corn and soybean farmers in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso it also poses a problem — an abundance of grain followed by about a 10 percent postharvest loss, partially due to a lack of storage.
-
-
Oil-devouring microbe communities a mile deep in the Gulf
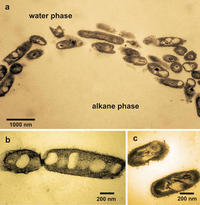
The Deepwater Horizon explosion on 20 April 2010, caused the largest marine oil spill in history, with several million barrels of crude oil released into the Gulf of Mexico over the course of three months. Soon after the spill began, a massive oil slick was visible from orbiting satellites, yet once the underwater gusher was sealed, obvious traces of the crude oil disappeared much sooner than nearly all observers predicted. Some of the oil evaporated; some was skimmed off. Microbes “ate” much of the oil as well.
-
-
U.S. geological carbon dioxide storage potential
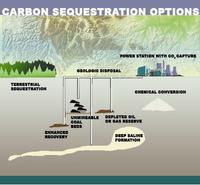
The United States has the potential to store a mean of 3,000 metric gigatons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in geologic basins throughout the country. Technically accessible storage resources are those that can be accessed using today’s technology and pressurization and injection techniques. The most common method of geologic carbon storage involves pressurizing CO2 gas into a liquid, and then injecting it into subsurface rock layers for long-term storage.
-
-
U.S. ports vulnerable to cyberattacks
New study says that the U.S. largest ports are vulnerable to cyberattacks.The study argues that the level of cyber security awareness and culture in U.S. port facilities is relatively low, and that a cyberattack at a major U.S. port would quickly cause significant damage to the economy.
-
-
Growing cybersecurity opportunities for young Americans
With the growing number of cyberattacks on U.S. companies, government agencies, and critical infrastructure, and the likelihood that such attacks will only increase, there has been a corresponding increase in the number of cybersecurity programs and educational opportunities for young Americans.
-
-
Improving the reliability, resiliency of post-Sandy N.J. electric grid
According to NOAA, prolonged electrical outages, largely because of storms, have been steadily increasing in frequency since 1995. Sandia Lab will help East Coast communities devastated by Hurricane Sandy boost the resiliency of their electric grids, so they can be better prepared to deal with natural disasters in the future.
-
-
Increasing food production from existing farmland
A policy known as sustainable intensification could help meet the challenges of increasing demands for food from a growing global population. The goal of sustainable intensification is to increase food production from existing farmland. Sustainable intensification would minimize the pressure on the environment in a world in which land, water, and energy are in short supply.
-
-
New expert network to advice organizations on how to keep data safe
A new expert network which helps organizations safely manage and share sensitive data has been launched. The U.K. Anonymization Network (UKAN) will advise organizations and companies on how to minimize the risk that personal details of individual people are inadvertently revealed when data are used to create valuable services.
-
-
Senate immigration bill could yield billions in federal contracts
The Senate immigration bill will see billions of dollars go to defense and technology companies as a result of billions of dollars in new and expanded federal contracts aiming to bolster border security.
-
-
U.S. tax code has minimal effect on CO2, other greenhouse gas emissions
Current federal tax provisions have minimal net effect on greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new report from the National Research Council. The report found that several existing tax subsidies have unexpected effects, and others yield little reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per dollar of revenue loss.
-
-
NSA revelations raise doubts about passage of cybersecurity legislation
U.S. officials say the revelations about the National Security Agency’s(NSA) domestic surveillance programs could make it harder for lawmakers to pass a cybersecurity bill. Critics of the House cybersecurity bill, known as the Cyber Intelligence Sharing and Protection Act (CISPA), which was passed earlier this year (it is still being debated in the Senate), argued the bill could lead to private information falling into the hands of the NSA.
-
-
Lawmakers want to ease travel to U.S. as part of immigration legislation
A bi-partisan group of House lawmakers is working to include a provision in the House immigration legislation which will make it easier to travel to the United States. Travel industry groups support the effort, having fought for years to get the government to relax security measures. The industry has argued that these measures have turned off many foreigners from traveling to the United States.
-
-
Improving crop resilience, yields in a world of extreme weather
Farmers in the United States witnessed record-breaking extremes in temperature and drought during the last two summers, causing worldwide increases in the costs of food, feed and fiber. Indeed, many climate scientists caution that extreme weather events resulting from climate change is the new normal for farmers in North America and elsewhere, requiring novel agricultural strategies to prevent crop losses. UC Riverside-led research team develops new chemical for improving crop drought tolerance.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
By Katie Myers
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
By David Montgomery
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
