-
Helping farmers plow through new, complex food safety regulations
The recently passed Food Safety Modernization Act set safety standards on how farmers grow, harvest, and handle fresh produce to reduce the risk of foodborne diseases. The new regulations to minimize food safety risk include testing for water safety and better managing manure storage. Agricultural extension educators should take a flexible approach in teaching farmers about the changing landscape of food safety regulations, researchers say.
-
-
Bolstering water security in a crowded world
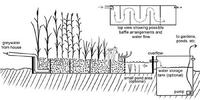
With limited water and the increasing number of people depending on it – there will be more than nine billion people on the planet by 2050 — water security is tenuous. Integrated water management plans using “blue,” “green,” and “gray” water, however, can increase water security by allowing agriculture to rise to the challenge of feeding a growing world population while leaving enough water for other uses.
-
-
Serious IT consequences if shutdown lasts
The shutdown of the federal government, if it lasts no more than a week or so, will not seriously damage government IT operations, experts and industry insiders say. A longer shutdown, which would lead to extended furloughs for non-essential employees, will have more serious effects, as it will further depress the federal technology workforce and will deter top graduates from applying for government jobs. If Congress refuses to allow payment to furloughed employees for the time they were idled, the effect will be even more pernicious, these experts said.
-
-
Terrorism hobbles business investment in north, east Africa

Images of the terrorist attack in Nairobi’s Westgate Mall have reinforced the belief that business investment in those parts of Africa where terrorist groups are active is risky despite improvements in living standards.
-
-
Advancing U.S.-Canada dialogue on border issues
US/Canada Border Conference laid the foundation for a successful annual gathering focused on increased border security and the facilitation of legitimate trade and travel between the United States and Canada.
-
-
How one transportation company survived Hurricane Sandy
In a year-long case study of a major American transportation company, researchers have uncovered the strategies that helped the company maintain safety and meet customer demand during 2012’s Hurricane Sandy. One key to the company’s effective response was its setup of a weather event management team, an ad hoc group that set planning priorities as the storm approached the United States, ensuring the protection of personnel and equipment in hurricane’s path.
-
-
Radioactive shale gas contaminants seep into a Pennsylvania creek

Researchers examined the quality of shale gas wastewater from hydraulic fracturing and the stream water above and below the disposal site in western Pennsylvania. Elevated levels of radioactivity, salts, and metals have been found in river water and sediments at a site where treated water from oil and gas operations is discharged into a creek.
-
-
Harnessing lightning power to charge a mobile phone

Scientists from the University of Southampton have collaborated with Nokia on ground-breaking, proof-of-concept research into harnessing the power of lightning for personal use, an industry first that could potentially see consumers tap one of nature’s significant energy sources to charge their devices in a sustainable manner.
-
-
Arbor Day meets Kyoto: Tree planting promotes carbon capture, green neighborhoods
Schemes which offer economic incentives for growing trees for carbon present an opportunity to reverse trends in land clearing but also to restore ecosystem services — such as pest control, pollination, soil and water conservation. Best practice carbon farming that considers more than just the carbon in trees is thus needed if the full benefits of trees in the landscape are to be realized by farmers, landholders, and the community.
-
-
Hand scanners as mark of the beast
The Equal Opportunity Employment Commission (EEOC) sues a Pennsylvania mining company for forcing an employee into an early retirement after he refused to use a biometric hand scanner to track his hours. The employee argued that using the scanner would violate his Evangelical Christian beliefs in the Bible’s mark of the beast prophecy. According to the Christian Bible, the mark is implanted on the forehead or right hand and symbolizes allegiance to the antichrist.
-
-
U.S. nuclear power industry facing dire prospects
The U.S. nuclear industry is facing several daunting challenges, with industry experts concluding that it may well be an energy source of the past. New construction of nuclear plants has come to a halt, older nuclear plants are closing, and plant expansions are put on hold. The main culprits: the price of natural gas is dropping fast because of new resources becoming available as a result of fracking, and wind and solar are making steady, if slow, gains.
-
-
U.S. to face an increased risk of severe thunderstorms

Severe thunderstorms, often exhibiting destructive rainfall, hail and tornadoes, are one of the primary causes of catastrophic losses in the United States. In 2012, eleven weather disasters in the United States crossed the billion-dollar threshold in economic losses. Seven of those events were related to severe thunderstorms. New climate analyses indicate that global warming is likely to cause a robust increase in the conditions that produce these types of storms across much of the country over the next century.
-
-
Calculating emissions, costs of increased wind, solar in the West
New research quantifies the potential impacts of increasing wind and solar power generation on the operators of fossil-fueled power plants in the West. To accommodate higher amounts of wind and solar power on the electric grid, utilities must ramp down and ramp up or stop and start conventional generators more frequently to provide reliable power for their customers — a practice called cycling.
-
-
Evaluating the IT security posture of business partners
Evaluating the IT security of businesses is increasingly becoming a necessity when forming new business relationships. A start-up has launched a rating service, similar to a credit rating, to measure the security posture of a company based on a number of factors.
-
-
ASIS releases updated, expanded edition of “Career Opportunities in Security”
ASIS International (ASIS) announced the publication of the updated and expanded new edition of Career Opportunities in Security. The 36-page booklet provides information of interest to those seeking to learn more about security, and serves as a resource to those considering a career in security management, or wanting to further their existing careers in the industry.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
