-
N.Y. lawmakers oppose proposed hikes in U.S.-Canada border crossing fees
The U.S. government is considering charging a new fee for every vehicle or pedestrian crossing the U.S.–Canada border. This has upset lawmakers in New York who argue the toll would hurt trans-boundary commerce and undermine efforts to ease the flow of traffic and goods between the two countries. Moreover they suggest that the real purpose of the proposed fees is to subsidize the more expensive security operations along the U.S.-Mexico border.
-
-
FAA furloughs begin with impact on flights slight so far
Sunday was the first day of FAA furloughs, but commercial airline flights ran smoothly throughout the country. There were delays in New York area airports, but nothing that was considered significant. There were also delays in Florida, but they were caused by thunderstorms.
-
-
FAA certifies Boeing 787 can fly again after fixes to over-heating battery

The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has approved Boeing’s proposed improvements to the lithium-ion battery systems on its 787 passenger jets. The jets have been grounded since January and are now ready to return to the skies.
-
-
Ammonium nitrate fertilizers are inherently risky, but the benefits are many
The deadly explosion has brought the $10 billion U.S. fertilizer industry to the attention of the mainstream media, but the risks inherent in fertilizer production and storage are not a secret to people close to the industry. Ammonium nitrate may be dangerous, but its benefits cannot be ignored.
-
-
Hagel reassures Israel, discusses large arms deal
U.S. Defense Secretary Chuck Hagel arrived in Israel Sunday for his first visit in the country as secretary of defense. Some elements in the pro-Israel lobby in the United States campaigned against Hagel’s nomination, and Hagel went out of his way to assure Israelis that his position on Israel is not what it was portrayed to be. One of the main reasons for Hagel’s visit is to discuss a major U.S. arms deal that would offer Israel missiles for its fighter aircraft – but also plus KC-135 refueling planes which could be used in a long-range strike on a country such as Iran. Until now, the United States refused to sell refueling tankers to Israel.
-
-
Airlines ask court to stop FAA furloughs
The FAA’s annual budget is $16 billion. As part of the sequester, the agency must reduce its budget by $637 million between now and the end of September. The agency says that the only way it can achieve these saving is by imposing a 2-week furlough on its 47,000 employees – including 15,000 air traffic controllers. A coalition of U.S. airlines has petitioned a federal court to stop the furloughs, which began yesterday, saying they would leas to the cancellation of 6,700 flights a day.
-
-
Reinvestment in U.S. water infrastructure should be a top national priority
The U.S. water infrastructure is often called the “invisible infrastructure” – a vast, largely invisible network of pipes and tunnels — nearly 1.4 million miles span across the United States, which is eight times the length of the U.S. highway system. Much of the U.S. infrastructure was built more than a century ago, and currently around 10 percent of these systems are at the end of their service life. If not addressed by 2020, this number could rise to 44 percent. A summit meeting of the U.S. water community calls on Congress to make water infrastructure a top national priority.
-
-
Interior Dept. releases progress report on U.S. Water Census
The U.S. Interior Department issued released a report to Congress on the progress of the National Water Census. As competition for water grows — for irrigation of crops, for use by cities and communities, for energy production, and for the environment — the need for the National Water Census and related information and tools to aid water resource managers also grows. The Water Census will assist water and resource managers in understanding and quantifying water supply and demand, and will support more sustainable management of water resources.
-
-
White House threatens to veto House cybersecurity bill
The White House on Tuesday threatened to veto the cybersecurity bill drafted by the House of Representatives. The house is expected to vote on the bill later this week. The cybersecurity bill died in the Senate last August after the White House said it would veto the bill.
-
-
Lawmakers want FAA to allow use of electronic gadgets during flights

Lawmakers have questioned whether personal electronic devices interfere with the electrical equipment of an airliner’s cockpit, and they want the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to allow more such gadgets on planes.
-
-
First U.S. commercial enhanced geothermal system connected to the grid
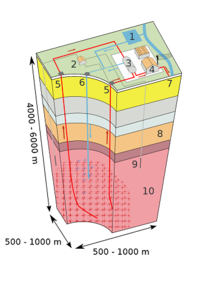
Enhanced geothermal system (EGS) projects capture power from intensely hot rocks, buried thousands of feet below the surface, which lack the permeability or fluid saturation found in naturally occurring geothermal systems. The Energy Department the other day announced the U.S. first commercial EGS project which supplies electricity to the grid.
-
-
Former NRC chairman: all 104 U.S. nuclear reactors suffer from “irreparable” safety issues
According to former U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) chairman Gregory Jaczko, all 104 nuclear reactors in the United States currently have irreparable safety issues and should be shut down and replaced. Jaczko was the NRC chairman from 2009 through 2012.
-
-
FAA to inspect Boeing’s 737 planes for faulty parts
Federal aviation regulators will order special inspections more than 1,000 Boeing 737 jets, and possibly replace improperly manufactured parts which could cause pilots to lose control of the planes.
-
-
Large DHS ammunition purchase continues to be a topic of debate

Conservative lawmakers and commentators continue to question why DHS is purchasing 1.6 billion rounds of ammunition, and will the agency do with so many bullets. DHS says it is cheaper to buy things in bulk, and that the rounds will be used in target practice and training for government agencies’ employees.
-
-
Reducing border inspections delays will benefit U.S. economy
Inspection of people and vehicles at U.S. border crossings are vital to homeland security. Inspections, however, generate various spillover effects relating to the delays in the flows of passengers and cargo across U.S. borders. A new study concludes that adding thirty-three customs and border protection officers (one at each of the selected thirty-three land and airport locations studied) will potentially lead to an increase in GDP of $61.8 million and employment gains of 1,053 jobs in the United States.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
