-
Facebook new search feature has cyber experts worried
A new Facebook search feature has security experts concerned. They are warning users of the site to strengthen their security settings to avoid embarrassment and to protect themselves from cybercriminals.
-
-
Wastewater from fracking is often highly radioactive
New studies have found that waste from fracking operations can be highly radioactive. A geological survey reported that millions of barrels of wastewater from unconventional wells in Pennsylvania and conventional wells in New York are 3,609 times more radioactive than the federal limit for drinking water, and 300 times more radioactive than a Nuclear Regulatory Commission limit for nuclear plant discharges.
-
-
Climate change threatens public health, safety, economy along U.S. coasts
A new technical study from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency (NOAA) and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) reports that the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities’ social, economic, and natural systems. All U.S. coasts are highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change such as sea-level rise, erosion, storms, and flooding, especially in the more populated low-lying parts of the U.S. coast along the Gulf of Mexico, Mid-Atlantic, northern Alaska, Hawaii, and island territories. The report says that the financial risks associated with both private and public hazard insurance are expected to increase dramatically.
-
-
U.S. tech companies hope visa reform for high-skilled immigrants is near
U.S. technology companies hope that what appears to be a more bi-partisan approach to immigration reform will not overlook the need to address the issue of high-skilled immigrants. The current number for H-1B visas fir skilled immigrants is 65,000 a year. “A 65,000 starting point is just not feasible for this economy. That’s the same number we started with in 1990, when the economy was one-third the size it is today,” say a high-tech industry representative.
-
-
New bridge construction technologies to shore up U.S. infrastructure
Experts agree that there is an urgent need to construct and repair bridges across the United States. Around 70,000 bridges in the country are considered “structurally deficient” by government standards. New technology could help the United States manage its growing, and aging, infrastructure without breaking the bank or levying high taxes on citizens.
-
-
U.S. to adopt tougher stance toward China’s persistent cyberattacks

The Obama administration let it be known that it is examining the adoption of a more assertive stance against China in response to a persistent cyber-espionage campaign waged by Chinese government hackers against U.S. companies and government agencies. The administration is preparing a new National Intelligence Estimate (NIE) which will detail the cyberthreat, particularly from China, as a growing economic problem.
-
-
Chinese hackers infiltrate Wall Street Journal’s computer systems
Chinese hackers with government connections have infiltrated the computer systems of the Wall Street Journal, in the second such Chinese attack on a major U.S. media outlet. WSJ says the hackers were trying to monitor its coverage of Chinese affairs.
-
-
Google wants to limit law enforcement’s access to e-mails, users’ information
In 2012 Google received 16,407 requests for user data, which affected 31,072 users or accounts. More than half of the requests were accompanied with a subpoena, the others were not. Google is planning on lobbying Washington this year to persuade lawmakers that they should make it harder for law enforcement to gain access to e-mails and other digital messages.
-
-
The historical probability of drought

Droughts can severely limit crop growth, causing yearly losses of around $8 billion in the United States. It may be possible, however, to minimize those losses if farmers can synchronize the growth of crops with periods of time when drought is less likely to occur. Researchers are working to create a reliable “calendar” of seasonal drought patterns that could help farmers optimize crop production by avoiding days prone to drought.
-
-
Twitter’s information policy frustrates police, delights customers
Twitter’s robust approach to customers’ privacy has caused consternation among law enforcement agencies, who say that Twitter’s refusal to hand over information on users of the service, except in rare cases, has frustrated criminal investigations. Twitter’s user, though, appreciate the company’s scruples.
-
-
Military electronic devices disappear into the surroundings after use

Electronic devices have become necessary for military operations, but it is almost impossible to track and recover every device. At the end of operations, these devices are often found scattered across the battlefield and might be captured by the enemy and repurposed or studied to compromise DoD’s strategic technological advantage. New DARPA program — Vanishing Programmable Resources (VAPR) program — seeks transient electronics, that is, devices which would maintain the current functionality and ruggedness of conventional electronics, but, when triggered, be able to degrade partially or completely into their surroundings.
-
-
Bipartisan group of senators offers sweeping immigration reform
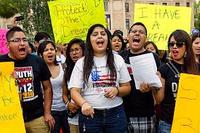
A bipartisan group of eight senators yesterday unveiled a proposal to overhaul the U.S. immigration system, a proposal which will form the basis of a bill that its backers hope to introduce to the Senate by March. Today, President Barack Obama is delivering a major speech on immigration in Nevada, and White house sources say that the specific proposals in his speech will dovetail with the senators’ proposal.
-
-
Lawmakers propose bill which would increase visas for highly skilled immigrants
Four senators plan to introduce a more narrowly tailored immigration reform bill which focuses on increasing the number of temporary visas available for highly skilled immigrants. The bill would also free up green cards so more of these highly skilled immigrants could settle in the United States and eventually become citizens.
-
-
Laser scanner documents crimes scenes quickly, accurately
The Carlsbad, California police is using a new laser scanner to capture what happened at crime scene. Thenew technology cuts the time it takes to document a crime scene, from the size of the room to the bullet holes in the wall, by up to 80 percent.
-
-
Americans’ health worst among high-income countries
On average, Americans die sooner and experience higher rates of disease and injury than people in other high-income countries. This health disadvantage exists even though the United States spends more per capita on health care than any other nation. A new study offers a comprehensive comparison of the United States with sixteen peer nations — affluent democracies that include Australia, Canada, Japan, and many Western European countries. Among these countries, the United States is at or near the bottom in the nine key areas of health to study examined.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
