-
Electronic nose detects airborne toxins down to the parts per billion level
Research create an electronic nose device with applications in agriculture, industry, homeland security, and the military; the device can detect small quantities of harmful airborne substances
-
-
Invasion at “Fort Knox of Uranium” raises security concerns

The Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, is regarded asthe Fort Knox of Uranium, so the fact that three anti-nuclear activists, one of them an 82-year old nun, were able to breach the high-security complex’s protective fences is not reassuring; that they did so using nothing more than bolt cutters, after announcing their arrival from half-a-mile away, and that they could stay, undetected, in a highly secure area on the nuclear complex’s ground for two hours, is even more worrisome
-
-
Y-12 and operator error
Three anti-nuclear activists, led by an 82-year old nun, breached the perimeter security system of the supposedly highly secure Y-2 nuclear facility at Oak Ridge, Tennessee, where nuclear weapons components are manufactured (note that the Oak Ridge National Laboratory [ONRL] is not affiliated with the Y-12 National Security Complex); they then spent several hours in a secure area of the facility, leisurely spray-painting slogans on the facility’s walls – without the facility’s security staff, or the sophisticated $500 million security cameras and sensors, detecting them; to understand what happened at Y-2, we must accept that operator error is an essential problem in national security, and that the problem is pervasive and normal; the only way to deal with the operator error phenomenon is to build redundancies into the system
-
-
China’s food production characterized by corruption, health-threatening practices

A report on Chinese TV showed rotten peaches spiked with sodium metabisulfite to make the fruit look fresh, seasoned in bleaching agents and additives harmful to the human liver and kidneys, and pickled in outdoor pools surrounded by garbage; the peaches are then packed in dirty bags which were previously used to hold animal feed, and shipped off to big brand stores; trouble is, this story is typical of, rather than an exception to, food production practices in China
-
-
Simple new test combats counterfeit drugs in developing countries
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that at least 10 percent of the drug supply in developing countries consists of counterfeit medicines, causing thousands of deaths every year; many of the deaths occur among people who unknowingly take counterfeit antibiotics and anti-malaria medicines that do not contain the active ingredient to combat those diseases; in addition to lacking the active ingredient, counterfeit medicines may harm people by containing ingredients that are potentially toxic
-
-
Long Beach Police Department purchases underwater inspection system for port
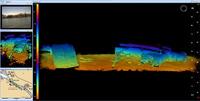
The Port of Long Beach is the second busiest seaport in the United States and is a major gateway for trade with Asia, handling more than six million containers annually; to enhance port security, the City of Long Beach Police Department has purchased an Underwater Inspection System (UIS) from Cod Octopus
-
-
World could be in for higher food prices
This has been one of the driest summers in American history, but the weather is not only affecting the United States; weak monsoons in India and other weather issues across the globe are affecting crops and could lead to higher food prices in 2013
-
-
Bacteria in tap water traced to the water treatment process
Most of the bacteria that remain in drinking water when it gets to the tap can be traced to filters used in the water treatment process, rather than to the aquifers or rivers where they originated; the findings could open the door to more sustainable water treatment processes that use fewer chemicals and, as a result, produce lower levels of byproducts that may pose health risks; eventually, the work could enable engineers to control the types of microbes in drinking water to improve human health
-
-
New technology combats global pandemic of drug counterfeiting
Drug counterfeiting is so common in some developing countries – in some studies, 50 percent of the drug samples from Southeast Asia have been counterfeit — that patients with serious diseases are at risk of getting a poor-quality drug instead of one with ingredients that really treat their illness
-
-
Remote monitoring market exceeds $29 billion in 2011
A new reports says that the world market for remote monitoring services was worth more than $29 billion in 2011, equivalent to $2.4 billion in recurring monthly revenues (RMR) across the year; the report also estimated that, in the same year, 54 million accounts, or customer locations, were provided with services
-
-
Aerospace materials for on-site building of pipes of infinite length

Concrete and steel pipes are built in short sections to fit on standard 18-wheel trucks; the heavy industrial manufacturing processes, long-distance trucking, and leak-prone joints used in steel and concrete pipe construction exact a heavy toll on the environment, not to mention bottom line; the solution: a new pipe design, consisting of a central layer of lightweight plastic honeycomb, which can be built onsite as a single section of virtually infinite length
-
-
Bioprinting to help produce an edible cultured meat prototype
Modern Meadow is developing a fundamentally new approach to meat and leather production which is based on the latest advances in tissue engineering and causes no harm to animals; with funding from the Thiel Foundation’s Breakout Labs, they plan to apply the latest advances in tissue engineering beyond medicine to produce novel consumer biomaterials, including an edible cultured meat prototype that can provide a humane and sustainable source of animal protein to consumers around the world
-
-
Toilet Challenge, 1: Caltech’s solar-powered toilet wins Reinvent Toilet Challenge
The World Health Organization reports that 2.5 billion people around the globe are without access to sanitary toilets, which results in the spread of deadly diseases; every year, 1.5 million people, mostly those under the age of five, die from diarrhea; Caltech scientist awarded grant to develop solar-powered sanitation system
-
-
Toilet Challenge, 2: Loughborough’s hydrocarbonization design wins second Reinvent the Toilet Challenge prize
Researchers from Loughborough University, located in Leicestershire, United Kingdom , won second prize in the Reinvent the Toilet Challenge; their toilet uses a process called Continuous Thermal Hydrocarbonization which kills all pathogens to create safe to handle, valuable material and uses power from heat generated during processing
-
-
Toilet Challenge, 3: U Toronto wins toilet challenge third place for sand filter and UV-ray design
The U of T solution is novel in its simplicity. It uses a sand filter and UV-ray disinfecting chamber to process liquid waste and a smolder chamber, similar to a charcoal barbeque, to incinerate solid waste that has been flattened and dried in a roller/belt assembly
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
