-
“Lab-on-a-glove” brings nerve-agent detection to a wearer's fingertips
Organophosphate nerve agents, including sarin and VX, are highly toxic and can prevent the nervous system from working properly. Organophosphate pesticides are far less potent but work in a similar way and can cause illness in people who are exposed to them, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Detecting either type of these sets of compounds accurately and quickly could help improve both defense and food security measures.
-
-
Large dose of VX killed Kim Jong-nam in 15-20 minutes

Kim Jong-nam, the half-brother of North Korea’s leader, was attacked with a large doze of VX which caused his death within 15-20 minutes after being poisoned by a nerve agent at Kuala Lumpur airport, the Malaysian health minister, S. Subramaniam, said on Sunday. Some experts have suggested that the two women who attacked him might have each smeared Kim’s face with two different non-lethal elements of VX, which became deadly when mixed on his face.
-
-
Kim Jong-nam killed by VX nerve agent: Malaysian police
Malaysian police have said the substance used in the killing of Kim Jong-nam was a VX nerve agent. North Korea, which is not a member of the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), is in possession of a large stockpiles of chemical weapons — between 2,500 and 5,000 metric tons, with Sarin and VX making up the bulk of the arsenal. Experts say that the public nature of the killing, and the assailants’ disregard for the safety of bystanders, is comparable to the assassination in London of former Russian intelligence officer Alexander Litvinenko. Litvinenko, who became a fierce critic of Vladimir Putin, was killed on Putin’s orders by two agents of the FSB in London in November 2006. The agents placed small quantities of radioactive poison, polonium-210, in his tea.
-
-
Low-cost imaging system detects natural gas leaks in real time
Researchers have developed an infrared imaging system that could one day offer low-cost, real-time detection of methane gas leaks in pipelines and at oil and gas facilities. Leaks of methane, the primary component of natural gas, can be costly and dangerous while also contributing to climate change as a greenhouse gas. Infrared device enables reliable monitoring under a range of environmental conditions.
-
-
Israel’s coming chemical weapons crisis
One of the more iconic and sobering elements of Israeli reality were the gas masks distributed on the street or at post offices to every citizen after Saddam Hussein fired SCUD missiles at Israel during the 1991 Gulf War. They continued to be distributed until early 2014, when the Israeli government decided to end the practice in the wake of an international deal to disarm Syria of its chemical weapons stockpiles. Now, nearly three years later, the issue has resurfaced as a direct result of the Syrian civil war—in particular, the threat from both Hezbollah and the Islamic State.
-
-
Syrian opposition: Israeli airstrike hit chemical weapons intended for Hezbollah

An Israeli air raid on a depot controlled by the Syrian regime two weeks ago hit a supply of chemical weapons being transferred to the Iran-backed terror group Hezbollah, a spokesperson for a Syrian opposition group said Sunday. Israeli Defense Minister Avigdor Liberman obliquely suggested last week that Israel was responsible for the strike and that the target had been Hezbollah-bound chemical weapons; other Israeli leaders have made it clear in public statements and conversations with foreign leaders that they will act to prevent Hezbollah from acquiring “game-changing” weapons or strengthening its positions on Israel’s borders.
-
-
Israeli defense minister suggests Hezbollah was smuggling chemical weapons
Israel is working hard to keep chemical weapons out of the hands of the Iran-backed terror group Hezbollah, Israeli Defense Minister Avigdor Liberman told a Knesset committee Thursday. His comments to the Knesset seemed to suggest that at least one of the strikes Israel carried out the same day at the Mazzeh military airport near Damascus was in order to stop Hezbollah from acquiring chemical weapons.
-
-
$19 million to develop drugs to treat victims of chemical weapons attacks
First used by the German military against Allied troops in the First World War and in subsequent wars including the Iran-Iraq conflict during the 1980s, chemical weapons were more recently used by the Assad regime in Syria and by ISIS in Iraq and Syria. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded Rutgers University a five-year grant for more than $19 million for research that would lead to the development of drugs to treat toxicity from chemical agents used in a terrorist attack.
-
-
UN chief alarmed at “weakening taboo” after Syrian chemical weapons attacks
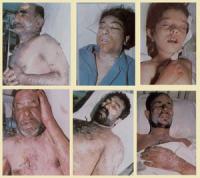
United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon expressed his concerned Monday about “the weakening taboo” against chemical weapons attacks, after numerous reports that more such attacks have taken place in Syria in recent weeks. In a letter to the UN Security Council, Ban expressed fears that the use of chemical weapons could become “normalized in this or any conflict, present or future.”
-
-
Shark antibodies for chemical, biological threat detection, treatment
New research shows that shark antibodies offer new alternatives to chemical and biological threat detection and treatment tools. In an era of Department of Defense belt-tightening, the goal is to find more innovative, cost-effective approaches to protecting our warfighters.
-
-
ISIL uses toxic chemicals in its defense of Mosul
In the run up to the U.S.-led coalition campaign to liberate Mosul, U.S. officials warned that ISIS would likely use chemical weapons to slow down the progress of coalition forces and terrorize the residents. Last Thursday ISIS took the first step in its chemical strategy by setting ablaze the Mishraq Chemical plant and sulphur mine, located thirty km south of Mosul. The toxic cloud includes lethal sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. When combined with residue from burning oil wells, it is deadly for people caught in the open or without gas masks. Military experts say health effects from the toxic fumes from oil and sulphur will likely subside in about eighteen months, but the toxic clouds could harm much of the plant and animal life in the area and make it difficult for local farmers to return to their fields until then.
-
-
Assad regime used chemical weapons: UN
The White House on Saturday sharply condemned the use of chemical weapons by the government of Bashar al-Assad, after an international inquiry found that Syrian government forces used toxic gas in spring 2015 in attacks on two rebel-held towns. The fourth report from the 13-month-long inquiry by the UN and the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), the UN chemical weapons watchdog, blamed Syrian government forces for a toxic gas attack in Qmenas in Idlib governorate on 16 March 2015.
-
-
A nerve agent antidote taken before a chemical weapons attack

Nerve agents are molecular weapons that invade the body and sabotage part of the nervous system, causing horrific symptoms and sometimes death within minutes. Few antidotes exist, and those that do must be administered soon after an attack. Now, scientists an early-stage development of a potential treatment that soldiers or others could take before such agents are unleashed.
-
-
New technology pinpoints water contamination sources

When the local water management agency closes your favorite beach due to unhealthy water quality, how reliable are the tests they base their decisions on? As it turns out, those tests, as well as the standards behind them, have not been updated in decades. Now scientists have developed a highly accurate, DNA-based method to detect and distinguish sources of microbial contamination in water.
-
-
Florida tightens public notification rules for pollution incidents
Last week Governor Rick Scott instructed Florida Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) Secretary Jon Steverson to issue an emergency rule that establishes new requirements for public notification of pollution incidents. The rule is to take effect immediately. Scott issued the instruction following the sewage spill in Pinellas County and the sinkhole at Mosaic’s New Wales facility.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
