-
U.K. facing flood crisis, as prime minister warns victims they are in for “long haul”
David Cameron warns flooding victims that they are in for a “long haul,” as the weather service says the weather will get worse this week, leaving thousands more homes at risk. There is a growing anger at the government by residents who complain that in addition to lack of preparation and response – thus, there were many complaints that sandbags intended for the worst-hit areas being “hijacked” and unavailable to stem the rising water – government agencies have not provided enough security after resident were ordered to evacuate, leading to looting of vacant homes. Officials have predicted that thousands more homes will be flooded over the coming days and said restoring the country’s battered rail network could take months.
-
-
Improving common furniture fire test
In the United States, fires in which upholstered furniture is the first item ignited account for about 6,700 home fires annually and result in 480 civilian deaths, or almost 20 percent of home fire deaths between 2006 and 2010. A new study finds that the bench-scale test widely used to evaluate whether a burning cigarette will ignite upholstered furniture may underestimate the tendency of component materials to smolder when these materials are used in sofas and chairs supported by springs or cloth.
-
-
More than 60 percent of California suffers drought conditions, with no relief in sight
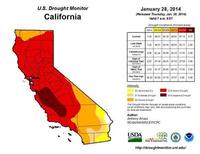
The entire west coast of the United States is changing color as the deepest drought in more than a century unfolds. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture and NOAA, dry conditions have become extreme across more than 62 percent of California’s land area — and there is little relief in sight. “Up and down California, from Oregon to Mexico, it’s dry as a bone,” say a NAA scientist. “To make matters worse, the snowpack in the water-storing Sierras is less than 20 percent of normal for this time of the year.”
-
-
Lawmakers want mandatory security standards for national grid
Lawmakers have urged the imposition of federal security standards on grid operator in order to protect the U.S. national electric grid from attack. The new push follows stories, first reported in the Wall Street Journal reported last Wednesday, about a 16 April 2013sniper attack which disabled seventeen transformer in a San Jose, California substation for twenty-seven days, causing about $16 million in damage. Federal cybersecurity standards for protecting the grid are in place and mandated, but rules for protecting physical sites such as transformers and substations are voluntary.
-
-
Coastal areas must adapt to sea-level rise and storm surges or suffer massive damage
A new study presents, for the first time, comprehensive global simulation results on future flood damages to buildings and infrastructure in coastal flood plains. Drastic increases in these damages are expected due to both rising sea levels and population and economic growth in the coastal zone. Asia and Africa may be particularly hard hit because of their rapidly growing coastal mega-cities, such as Shanghai, Manila, and Lagos.
-
-
Quake-vulnerable concrete buildings in Los Angeles area identified

Researchers have identified nonductile concrete buildings constructed before roughly 1980 in the Los Angeles area. This category of buildings is known from experience in previous earthquakes to have the potential for catastrophic collapse during strong earthquakes. Nonductile concrete buildings were a prevalent construction type in seismically active zones of the United States before the enforcement of codes for ductile concrete which were introduced in the mid-1970s. A companion study estimates that approximately 17,000 nonductile reinforced concrete buildings are located in the most highly seismic areas of California. More than seventy-five million Americans in thirty-nine states live in towns and cities at risk for earthquake devastation.
-
-
Protecting cities from floods cheaper than post-flood damage repairs

Researchers say that global warming is here to stay, and thus it is time to start making plans for dealing with the inevitable flooding which will occur as ocean levels rise as a result of warmer water and melting snow and ice. Approximately a billion people currently live in areas which are most at risk — low-lying coastal areas. It is not likely that towns and cities will be moved farther inland, so other measures need to be taken. The researchers say that flood prevention strategies are well established, for example, building levees, barrier islands, etc., so it is not difficult to draw up estimates for such schemes for individual areas.
-
-
Total California water supplies at near-decade low
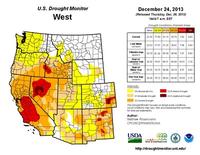
Advisory from UC Center for Hydrologic Modeling finds California’s statewide averages of snow, surface water, and soil moisture near 10-year lows. The threat of multi-year period of unsustainable groundwater depletion imminent if drought continues. The data show particularly steep water losses between November 2011 and November 2013, the early phase of the current drought. The researchers estimate that the Sacramento and San Joaquin River basins have already lost ten cubic kilometers of fresh water in each of the last two years — equivalent to virtually all of California’s urban and household water use each year.
-
-
Aging grid cannot keep up with growing demand for electricity
The demand for electricity in the United States increased by around 20 percent from 1999 to 2009, but transmission capacity only increased by around 7 percent in that time. From 2000 to 2004, there were 140 instances of power outages which each affected 50,000 or more consumers. This number increased to 303 from 2005 to 2009. Between 2010 and 2012, there were 226 such outages. The average age of a power plant is 30-years old, and around 75 percent of America’s power lines are 25-years old. Economists estimate that these power outages cost the country more than $70 billion in annual economic loss.
-
-
Making the U.S. grid sturdier, smarter, and more secure to thwart blackouts

In August 2003, fifty million customers throughout the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada lost power for up to two days. More than ten years later, the U.S. electric power system continues to be challenged. In the United States, 149 power outages affecting at least 50,000 customers occurred between 2000 and 2004, a number which grew to 349 between 2005 and 2009. In 2012, the prolonged power outages in New York and New Jersey caused by Hurricane Sandy once again demonstrated the system’s vulnerability. A broad, multidisciplinary effort by Georgia Tech researchers aims to revolutionize the delivery of electricity, advance the smart grid, thwart blackouts, integrate renewable energy sources, and secure utilities from cyberattacks.
-
-
Smartphones to help find avalanche victims
Not a winter goes by without an avalanche incident. In the search for those buried beneath the snow, every second counts. On average, rescuers have fifteen minutes to recover victims alive. This is why an avalanche transceiver is an essential piece of kit for anyone spending significant time off-piste. These transceivers do not come cheap, however, ranging in price from 200 and over 500 euros — perhaps one reason why many walkers and skiers still do not carry one with them. Now smartphones equipped with functions of an avalanche transceiver should help locate the victims quickly.
-
-
Senegal climate change-induced flooding reaching crisis proportions: UN

Margareta Wahlstrom, the head of the UN disaster risk, last week warned that climate change-induced flooding had reached crisis proportions in Senegal, with some towns and villages now finding themselves underwater for large parts of the year. Wahlstrom, who was in Senegal for a 3-day visit as part of the UN preparations for a new global disaster risk-reduction strategy, said that mayors of coastal and riverside towns and villages told her their streets were flooded ten months out of twelve.
-
-
Clouds influence how greenhouse gases affect climate
The warming effect of human-induced greenhouse gases is a given, but to what extent can we predict its future influence? That is an issue on which science is making progress, but the answers are still far from exact, say researchers. Indeed, one could say that the picture is a “cloudy” one, since the determination of the greenhouse gas effect involves multifaceted interactions with cloud cover.
-
-
Some citizens of low-lying Pacific island nations seeking climate-change refugee status
More and more resident of Pacific island nations and territories are trying to claim refugee status in Australia and New Zealand, arguing that rising sea levels, caused by climate change, are forcing them out of their homes and destroying their livelihood. The New Zealand High Court has rejected the refugee status petition of Loane Teitota and his family, citizens of Kiribati, a low-lying Pacific Island nation near the equator, saying that Teitota’s argument was “novel” and “optimistic.” The court cautioned that if the argument were adopted, then millions of people suffering from the effects of climate change would seek refugee status in New Zealand or any other country.
-
-
Federal, state chemical safety agencies increasingly hampered by budget cuts
The budgets of state and federal agencies tasked with responding to the Elk River chemical spill have recently been cut, and these cuts have limited these agencies’ ability to prevent or respond to disasters such as the water crisis in West Virginia. “We do less,” said a CDC financial official, when asked the results of cuts. “What [the CDC director] has often been quoted as saying is that threats are not going down and so it is concerning to not be able to grow with the public health threats.”
-
More headlines
The long view
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
