-
Spray-on explosives detector
A chemist at Oklahoma State University has developed a spray-on material that detects explosives made from peroxides and renders them harmless; the material is a type of ink that contains nanoparticles of a compound of molybdenum. The ink changes color, from dark blue to pale yellow or clear, in the presence of explosives
-
-
Algae might help reduce nuclear waste
The humble algae — Closterium moniliferum — might one day soon be used to help separate strontium from calcium in nuclear waste; if successful, the process could lead to a reduction in the amount of nuclear waste that is left over from nuclear power facilities, and might even help in cleanup when accidents occur such as the one in Chernobyl, Ukraine, that spewed great quantities of strontium into the surrounding environment
-
-
Universal detector made of DNA building blocks
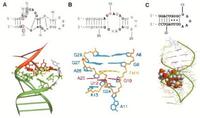
Aptamers are composed of the building blocks of the genetic material DNA; scientists show that aptamers can be used quantitatively to detect and accurately examine multifaceted substances; a method for detecting such diverse substances as antibiotics, narcotics, and explosives - in effect, a universal detector — has been developed by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Mainz
-
-
Japan widens evacuation radius
Japanese officials have enlarged the evacuation zone around the Fukushima Daiichi power plant, as workers continue their struggle to repair the damaged nuclear reactors; last Friday a “voluntary evacuation” of people still living within nineteen miles of the plant was issued; residents within nineteen miles have remained indoors unable to leave their homes to purchase basic supplies and companies have refused to deliver; the voluntary evacuation could add an even greater strain to existing temporary shelters; currently 242,881 people are still living in shelters around the country and officials are struggling to provide enough basic supplies like food, water, and sanitary goods
-
-
Biosensor improves pathogen detection in food, water
A nanotechnology-based biosensor being developed by Kansas State University researchers may allow early detection of both cancer cells and pathogens, leading to increased food safety and reduced health risks
-
-
Sector Report for Monday, 28 March 2011: Detection
This report contains the following stories.
Plus 1 additional story.
-
-
Global nuclear bomb sensors used to track Japan's radiation
A worldwide network of radiation sensors originally built to detect nuclear weapon tests is now being used by scientists to track radiation leaked from Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant; over 280 sensors were installed to detect radiation from nuclear weapons testing; the sensors have detected several radioactive elements that are the byproducts of nuclear fission like iodine-131 and cesium-137 from Japan; experts studying the data disagree on the effect and size of the release, but assure the public that the effects are minimal as much of the radiation is being scattered across the Pacific
-
-
Half of EPA's radiation warning system in California defective
The defective sensors are part of EPA’s RadNet detection system which was created to provide an active warning system that would alert scientists and public health officials of any elevated levels of radiation so they can warn the public or take other protective measures; half of California’s twelve sensors have been sending data with “anomalies” to the EPA’s main laboratory; the faulty data results in delays of up to several hours; officials say that the sensors are fully functional and that the delays are a result of “glitches” in satellite transmissions; there are several other radiation sensors in the United States operated by local, state, and federal agencies
-
-
Washington nuclear sensors capable of detecting faintest amounts of radiation
The radiation detectors developed by the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) in Washington are so sensitive that they can detect trace amounts of radioactive material from hundreds of thousands of miles away; far from being a public health concern, the amount of radiation from Japan detected on the west coast of the United States was far less than what individuals receive from natural sources and is testament to the sensors extraordinary sensitivity; officials say that the PNNL’s sensors are a hundred times more sensitive than other radiation sensors; the PNNL facility is capable of picking up the faintest amounts of radioactive elements produced by nuclear reactions from the vast amounts of air particles in the world
-
-
San Francisco to regulate private biological agent detectors
Some firms have begun selling building owners and companies untested devices designed to detect anthrax and other biological agents, but city officials are worried that these will generate false alarms; in San Francisco city officials estimate that responding to a false alarm generated by a biological agent detector could cost as much as $700,000; legislation has been introduced to regulate these devices; the bill would require those who have biological agent detectors to pay an annual fee and owners would also be fined as much as $10,000 for false alarms; if passed, owners would have ninety days to register with the city
-
-
TSA looking for shoe scanning devices
DHS is seeking companies to which it will award a contract for shoe scanners; according to the Office of Federal Business Opportunities, the Shoe Scanning Device (SSD) system currently sought by the TSA and DHS “will be capable of detecting threat objects concealed in footwear without requiring passengers to remove their footwear as they pass through a security checkpoint. These threat objects include a wide variety of military, commercial, and homemade explosives or explosives devices”
-
-
Authors suggest ways to alleviate L.A. cargo port "constipation"

In January, the port of Los Angeles received more than 330,000 containers; the possibility that one of those 330,000 containers could have contained a dirty bomb, or worse, keeps security experts up at night; experts say that to ensure security and prevent logjams, the best approach to container security would be to replace the current system, which singles out only those containers whose documentation raises questions, with a system which will see terminal operators X-ray every container, regardless of its eventual destination; only those containers flagged during the low-level scan would be subjected to a more thorough search
-
-
Countries closely monitor Japanese food for radiation
On Saturday, Japan announced that radiation was detected in spinach and milk produced near the Fukushima nuclear plant; the levels were low enough to not pose a long-term threat to human health, but they were above the national safety level, so the Japanese government has stopped sales of food products from near the damaged plant; countries importing food products from Japan are on alert
-
-
Nuclear crisis worsening; growing radiation leaks at reactors nos. 3, 4

The situation at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant appears increasingly dire, as efforts to cool overheating reactors have failed; Japanese military fire trucks are now spraying water at the plant’s no. 3 reactor; earlier efforts on Thursday to use helicopters to dump water on the rods have failed; the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission chairman is particularly concerned about reactor no. 4 which houses spent fuel rods; spent fuel rods, placed in cooling tanks, are rapidly overheating as they are boiling away the water they are submerged in; the secondary containment unit at reactor no. 4 has been breached and radiation is now freely leaking out of the plant; high radiation levels are hindering efforts to repair the reactors
-
-
TSA retests body scanners amidst radiation exposure concerns

The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) recently announced that it was retesting all of its full-body scanners over concerns that they were emitting high levels of radiation; maintenance records have shown that some scanners emitted radiation levels ten times higher than expected; TSA says that these increased levels were simply the result of a math mistake and that the machines do not pose a health risk; one type of body scanner in use relies on backscatter X-rays which produce very low levels of ionizing radiation; experts worry about the long-term effects of repeated exposure at low levels
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
