-
UN report indicates Syrian army used chlorine in April attacks on rebel-held villages
The Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) said that a toxic chemical, probably chlorine, was used as a weapon to attack three Syrian villages in April. The agency investigators did not specify who had launched the chlorine attacks, but the full report, which so far has been shared only with governments, leaves little doubt that the Syrian government was responsible for the attacks.
-
-
New device improves radiation detection
In a move that could have important implications for national security, researchers have created a very sensitive and tiny detector that is capable of detecting radiation from various sources at room temperature. The detector is eight to nine orders of magnitude —100 million to as high as 1 billion — times faster than the existing technology. The researchers sought to utilize the exceptional electronic carrier properties of graphene to create the photo detector device. Graphene is made of carbon atoms that are arranged in a honeycomb-like geometrical structure (the diameter of a human hair is 300,000 times thicker than a two-dimensional sheet of graphene).
-
-
No Fukushima radiation found in California’s coastal areas
Following the 11 March 2011 Fukushima disaster, researches wanted to see whether radioactivity could be found in Bay Area precipitation. They collected weeks’ worth of rainwater around UC Berkeley Campus to find out. The results: low levels of a number of different radioactive nuclei produced by the fission of uranium-235 including, cesium-134, cesium-137, and iodine-131. “The levels we saw were detectable, but low and not a health hazard to anyone,” said UC Berkeley’s nuclear engineering professor Eric Norman.
-
-
Scientists improve accuracy, reliability of nuclear tests inspection
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) operates the International Monitoring System (IMS) — 279 sensors-equipped facilities around the world which detect four types of physical phenomena that can provide evidence of a nuclear explosion having taken place: seismic waves, radioactive nuclei, underwater sound waves, and infrasonic waves. The evidence from the IMS is not always enough to convince signatories of the CTBT that a nuclear test has taken place. Scientists are trying to improve the accuracy and reliability of the IMS system.
-
-
Security flaws found in backscatter X-ray scanners
A team of researchers has discovered several security vulnerabilities in full-body backscatter X-ray scanners deployed to U.S. airports between 2009 and 2013. Secure 1000 scanners were removed from airports in 2013 due to privacy concerns, and are now being repurposed to jails, courthouses, and other government facilities. “The system’s designers seem to have assumed that attackers would not have access to a Secure 1000 to test and refine their attacks,” said one of the researchers. The researchers, however, were able to purchase a government-surplus machine found on eBay and subject it to laboratory testing.
-
-
Neumedicines receives $14m for acute radiation exposure countermeasures
Neumedicines receives $14 million from BARDA to support advanced development of HemaMax, including advanced GMP manufacturing activities and a Phase 2 clinical safety study in 200 healthy human volunteers. The company says its efficacy studies have shown that a single, low-dose, subcutaneous injection of HemaMax at twenty-four hours after exposure to lethal radiation increases survival by an average of more than 2-fold without any supportive care or antibiotics.
-
-
Electric bugs harnessed to detect water pollution
Scientists have developed a low-cost device that could be used in developing countries to monitor the quality of drinking water in real time without costly lab equipment. The sensor contains bacteria that produce a small measurable electric current as they feed and grow. The researchers found that when the bacteria are disturbed by coming into contact with toxins in the water, the electric current drops, alerting to the presence of pollutants in the water.
-
-
Tool helps investigators connect bomb fragments to bomb makers
Authorities with the U.S. Special Operations Command (SOCOM), the Canadian military, the U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF), and law enforcement agencies in the United Kingdom have adopted a crowdsourcing system called DFuze to help agencies in twenty-five countries connect bomb fragments to bomb makers or individuals who could be connected to a specific bomb.The technology allows users to share bomb images and data to assist pending investigations.
-
-
Continued funding for S.C. mixed-oxide fuel (MOX) plant – at least until fall
Federal legislators have secured the funds to keep the mixed-oxide fuelplant (MOX) at the Savannah River Sitein South Carolina moving forward at least into fall, according to South Carolina governor Nikki Haley and members of the state’s congressional delegation. The 310-square mile site once produced components for nuclear weapons, but since the agreement with Russia to turn nuclear weapons into reactor fuel, the site has focused on repurposing and cleanup.
-
-
Backscatter body scanner making a comeback
Airline passengers have already said bon voyage to the controversial backscatter X-ray security scanners, pulled from U.S. airports in 2013 over concerns about privacy and potential radiation risks. The devices may, however, be reintroduced in the future, in part because they produce superior images of many concealed threats, and Congress still wants to know whether these systems — currently used in prisons, in diamond mines, and by the military — produce safe levels of radiation for screeners and the people they screen.
-
-
U.S. nuclear plant licensees should seek, act on nuclear plant hazards information
A new report concludes that the overarching lesson learned from the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident is that nuclear plant licensees and their regulators must actively seek out and act on new information about hazards with the potential to affect the safety of nuclear plants. The committee that wrote the report examined the causes of the Japan accident and identified findings and recommendations for improving nuclear plant safety and offsite emergency responses to nuclear plant accidents in the United States.
-
-
DOE chief to visit WIPP to discuss funding for recovery efforts
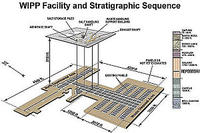
Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz will visit Carlsbad, New Mexico on 12 August to discuss funding for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) recovery efforts.Traces of americium and plutonium were released from a nuclear waste drum on 14 February and were detected in the air almost a half-mile outside WIPP. On 15 May, the DOE confirmed that the damage occurred on a waste drum from Los Alamos National Laboratory.
-
-
U.K. launches inquiry into radiation poisoning of former KGB agent
British authorities have announced that a public inquiry will be held into the death of former Russian KGB officer who became a British citizen, Alexander Litvinenko.Litvinenko, 43, died in 2006 after he was poisoned with radioactive polonium while drinking tea with two former KGB agents at a London hotel.
-
-
Fire shuts down nuclear repository, but DOE still recognizes operator for “excellent” performance
Five days after an underground truck fire closed the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), the Energy Department (DOE) awarded Nuclear Waste Partnership (NWP), the operating contractor of the nuclear repository, $1.9 million for “excellent” performance during the past year.Shortly after the truck fire, WIPP was shut down because of radiation leak, Still, “No federal or contractor official has lost their job, been transferred, been moved off the WIPP contract or otherwise held accountable. No leadership has changed at the federal level. No company has lost a contract,” noted an industry observer.
-
-
Japan testing underground nuclear waste storage depot, despite local concerns
Data is being collected at the Horonobe Underground Research Center, in Horonobe, Japan to determine whether the site is able to begin storing radioactive waste in conditions which could last for 100,000 years.Japanese utility systems have produced more that 17,000 tons of “spent” nuclear fuel rods from power plants which are no longer useful but are expected to remain radioactive for around several thousand years.
-
More headlines
The long view
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
