-
Starvation is only one crop breeding cycle away
Global population growth, urbanization, and a changing climate mean staple food crops will need to achieve much higher yields in the near future. New research proposes genetic engineering solutions to improve photosynthetic efficiency of food crops, boosting yield under higher temperatures and carbon dioxide levels. Because it can take twenty to thirty years of breeding and product development efforts before new crops are available to farmers, those efforts must start now.
-
-
Laser cloaking device to help us hide Earth from aliens
Several prominent scientists, including Stephen Hawking, have cautioned against humanity broadcasting our presence to intelligent life on other planets. Two astronomers suggest humanity could use lasers to conceal the Earth from searches by advanced extraterrestrial civilizations.
-
-
Flexible security solution makes life difficult for burglars
Ideally, homeowners want to be warned if a burglar sneaks onto their property, and farmers want to know if horses or sheep are no longer in the paddock or field they were left grazing in. Experimental physicists at Saarland University have developed a flexible security solution that can be used in gardens, driveways, business premises, or on grazing land and in woodland.
-
-
DARPA’s seeking innovative system-level technologies
DARPA’s Tactical Technology Office (TTO) focuses on developing and demonstrating innovative system-level technologies and prototypes that incorporate new and emerging technologies, for the purpose of preserving and extending U.S. military advantages over potential adversaries. To help accomplish these goals and inform potential performers about TTO’s technical objectives, TTO has scheduled its fourth annual Proposers Day for Wednesday and Thursday, 20 and 21 April 2016.
-
-
Water problems in Asia’s future?

Economic and population growth on top of climate change could lead to serious water shortages across a broad swath of Asia by the year 2050. Having run a large number of simulations of future scenarios, the researchers find that the median amounts of projected growth and climate change in the next thirty-five years in Asia would lead to about one billion more people becoming “water-stressed” compared to today.
-
-
1.4 billion people face severe natural disaster risks in South Asia
New data has revealed that 1.4 billion people in South Asia, or 81 percent of the region’s population, are acutely exposed to at least one type of natural hazard and live in areas considered to have insufficient resources to cope with and rebound from an extreme event. Poor governance, weak infrastructure, and high levels of poverty and corruption amplify the economic and humanitarian losses associated with significant natural hazards events – and these factors will exacerbate the consequences of natural disasters especially in Africa, a continent which hosts eight out of the nine countries most vulnerable to natural hazards.
-
-
Quantifying climate-driven impacts on the Colorado Basin, developing response strategies
The Colorado basin — roughly 11 percent of the United States — directly supports water supply for more than thirty million people, accounts for approximately 15 percent of U.S. crops and livestock, and provides 53 gigawatts of power generation capacity. Climate-driven heat-stress and forest mortality on the Colorado River watershed are expected to reduce river flows basin-wide out to the year 2100.
-
-
Mathematics helps search and rescue ships sail more safely in heavy seas

Fast ships deliver all kinds of services in fields such as disaster response, the fight against crime, the provision of supplies for oil and gas platforms, and the transportation of wind farm maintenance personnel. Each year, however, around 100 such ships worldwide are lost or damaged in heavy seas, with around 2,500 casualties in 2013. A unique new computer model built on highly complex mathematics could make it possible to design safer versions of the “fast ships” widely used in search-and-rescue, anti-drugs, anti-piracy, and many other vital offshore operations.
-
-
To avoid multiple climate tipping points, CO2 emissions should be stopped by 2050: Study
To avoid multiple climate tipping points, policy makers need to act now to stop global CO2 emissions by 2050 and meet the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting global warming to 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels, a new study has said. The new research shows that existing studies have massively under-valued the risk that ongoing carbon dioxide emissions pose of triggering damaging tipping points.
-
-
2015 made history with record heat, weather extremes: WMO
The year 2015 made history, with shattered temperature records, intense heatwaves, exceptional rainfall, devastating drought, and unusual tropical cyclone activity, according to the World Meteorological Organization. That record-breaking trend has continued in 2016. The global average surface temperature in 2015 broke all previous records by a wide margin, at about 0.76° Celsius above the 1961-1990 average because of a powerful El Niño and human-caused global warming. With 93 percent of excess heat stored in the oceans, ocean heat content down to 2,000 meters also hit a new record.
-
-
Expanding use of recycled water would benefit the environment, human health
More than 1 in 9 people around the world, about 750 million, do not have access to safe, clean drinking water, and the problem is expected to worsen in step with rising greenhouse gas concentrations, population increases and climate change. Researchers found that found that recycled water has great potential for more efficient use in urban settings and to improve the overall resiliency of the water supply.
-
-
February global temperature sets new record for the globe
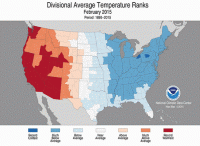
The average temperature for the globe during December-February was 2.03°F above the twentieth century average. This was the highest temperature for December-February in the 1880-2016 record. February 2016 also marks the tenth consecutive month in which a monthly global temperature record has been broken. Record warmth across the globe was aided by a strong El Niño which peaked during the winter.
-
-
Rare earth minerals are in short supply, so researchers seek to extract them from coal
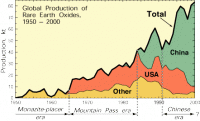
With supplies growing scarce of essential materials needed to make products ranging from smart phones to windmills, researchers are working with academic and industry partners in a $1 million pilot project to recover rare earth elements from coal. The pilot effort is important because rare earth materials, used to create powerful permanent magnets in products as common as computer hard drives to electric motors, are in increasingly short supply, particularly heavy rare earth elements.
-
-
Up to 70 percent of Northeast U.S. coast likely to adapt to rising seas
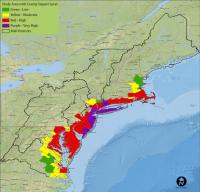
Much of the coast from Maine to Virginia is more likely to change than to simply drown in response to rising seas during the next seventy years or so, according to a new study led by the U.S. Geological Survey. The study is based on a new computer model that captures the potential of the Northeast coast to change, driven by geological and biological forces, in ways that will reshape coastal landscapes.
-
-
Identifying national security threats posed by everyday commercial technologies

For decades, U.S. national security was ensured in large part by a simple advantage: a near-monopoly on access to the most advanced technologies. Increasingly, however, off-the-shelf equipment developed for the transportation, construction, agricultural, and other commercial sectors features highly sophisticated components, which resourceful adversaries can modify or combine to create novel and unanticipated security threats. DARPA’s “Improv” effort asks the innovation community to identify commercial products and processes that could yield unanticipated threats.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
