-
U.S. faces more – and more intense – wildfire

Scientists using NASA satellite data and climate models have projected drier conditions likely will cause increased fire activity across the United States in coming decades; the researchers calculated results for low and high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios; in both cases, results suggest more fire seasons that are longer and stronger across all regions of the United States in the next 30-50 years; specifically, high fire years like 2012 would likely occur two to four times per decade by mid-century, instead of once per decade under current climate conditions
-
-
Geoengineering could disrupt global rainfall patterns
Tackling climate change by reducing the solar radiation reaching our planet using climate engineering, known also as geoengineering, could result in undesirable effects for the Earth and humankind; in particular, new research shows that disruption of global and regional rainfall patterns is likely in a geoengineered climate
-
-
Revamped DARPA inventor mentorship programs increases funding
DARPA says it wants to ensure that young scientists with novel ideas which may advance U.S. national security receive the funding and mentorship needed to investigate them; as the DARPA Young Faculty Award (YFA) program enters its seventh year, changes in scope mean that 2013 recipients can expect higher levels of funding — up to $1 million available for elite young researchers — for a potentially longer duration in a program that has been reworked to involve even more direct interaction with DARPA program managers
-
-
Two small, long-endurance UAVs unveiled

Danvers, Massachusetts-based CyPhy Works, a new robotics company, the other day unveiled two revolutionary small unmanned air vehicles (UAVs): EASE and PARC; the Extreme Access System for Entry (EASE) is an indoor flying UAV to help police, soldiers, and inspectors remain at safe standoff distances; the Persistent Aerial Reconnaissance and Communications (PARC) is designed to fly vertically and remain hovering for unprecedented long durations without operator intervention
-
-
TVA considering raising height of dams to prevent future floods
The dams located on the upper Tennessee River never had flood waters top them, and government officials want to keep it that way, saying that due to recent disasters such as the 2010 Nashville flood and the 2011Fukushima tsunami, they need to prepare the worst possible situation
-
-
Removing sea defenses may reduce impact of coastal flooding
Coastal defenses put in place over the last century or so have re-shaped the U.K. coastline, artificially protecting some areas, but at the expense of beaches in adjacent areas; this man-made situation increases the risk of flooding in low lying coastal settlements where beaches act as a natural flood defense; beach levels can be artificially recharged, but maintaining this indefinitely along large stretches of coastline is costly and likely to be unsustainable
-
-
Pulverized rocks used to strip CO2 from emissions of steel, coal, cement plants
Researchers in Quebec are developing a process which would see steel, coal, and cement plants as well as oil and gas facilities remove most of the carbon dioxide (CO2) from their emissions through chemical reactions with various types of crushed rocks in the stacks
-
-
Critics: post-Fukushima nuclear power may be safer, but it is still not cost effective
The Southern Company wants to show its customers that it has learned from the Fukushima disaster in Japan and has protected its nuclear reactors to make sure the same thing does not happen in the United .States’ critics of nuclear power are not convinced – and also, they say, alternative energy sources, such as natural gas, are much cheaper to produce
-
-
The potential for self-driving cars in the U.K.
Researchers explored what it would take for driverless vehicles to become commonplace on U.K. roads; they highlight the potential benefits of self-driving cars, such as increased road safety and less traffic, but stress that a range of barriers need to be overcome before people buy them en masse
-
-
Israel to test advanced Arrow 3 anti-missile missile
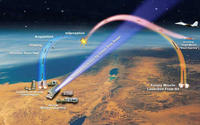
The official in charge of developing Israel’s missile defense system said yesterday that in the coming days Israel would conduct a test of the advanced Arrow 3 missile; the Arrow 3 has been developed to shoot down Iranian ballistic missiles on their way to Israel; the Arrow 3 has been designed to intercept missiles carrying nuclear warheads – and intercept them outside the atmosphere
-
-
Andrew Cuomo heads to Washington to push for disaster aid
Governor Andrew Cuomo says that New York needs $33 billion to cover storm cleanup and another $9 billion for new programs to protect against future storms; Governor Chris Christie of New Jersey says his state will need $36.8 billion to recover from Sandy; it is not clear how Congress and the administration, locked in a tug of war over differing deficit cut plans, will respond
-
-
Tunnel disaster shows age of Japan’s infrastructure, but there is no money to fix it

The collapse of hundreds of concrete ceiling slabs in a tunnel just outside Tokyo has focused the attention of the Japanese on the country’s has citizens calling for Japan to fix its aging infrastructure; the amounts of money needed for this refurbishing are large, and , but signs indicate that Japan may not have the money, as the public debt is already more than 200 percent of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
-
-
Life of U.K. nuclear power plants extended

U.K. operator EDF Energy has announced it will extend the expected operating life of two of its nuclear power stations by seven years; Hinkley Point B and Hunterston B power stations are now expected to remain operational until at least 2023, generating enough electricity for around two million homes; the decision follows the five year extensions to Heysham 1 and Hartlepool announced in 2010 and come after extensive reviews of the plants’ safety cases and continuing work with the independent nuclear regulator
-
-
Squirrels-inspired deceptive robots to help the military

Using deceptive behavioral patterns of squirrels and birds, researchers have developed robots that are able to deceive each other; the applications could be implemented by the military in the future
-
-
Responding to future oil spills: lessons learned from Deepwater Horizon
A special collection of articles about the Deepwater Horizon oil spill provides the first comprehensive analysis and synthesis of the science used in the unprecedented response effort by the government, academia, and industry;with the benefit of hindsight and additional analyses, these papers evaluate the accuracy of the information that was used in real-time to inform the response team and the public
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
