-
NY, NJ brace for nor’easter
East Coast resident are still coping with the destruction wreaked by Hurricane Sandy, but now they have to prepare for another potentially destructive storm – a nor’easter which is expected to hit New York and new Jersey on Wednesday; the nor’easter will likely stay 50-100 miles off shore, but its western edges will bring winds of up to 55 mph, coastal flooding, up to two inches of rain along the shore, and several inches of snow to Pennsylvania and New York
-
-
Many NYC buildings to remain closed for weeks, months for clean-up, repairs
Water and winds produced by Hurricane Sandy destroyed mechanical and electrical systems in many commercial and residential buildings in Lower Manhattan; as a result, many buildings in the area are weeks or months away from being repaired and fully operational
-
-
Protecting New York City from storms, surges
Almost a week after Hurricane Sandy hit New York City; people are still picking up the pieces of their former lives; for New York officials, the next step is decide how best to protect New York City from a similar disaster in the future; there are many ideas and proposals, ranging from moveable sea gates, to expanding protective marshlands and wetlands, to creating a system of artificial reefs in the channel along the Red Hook and Gowanus neighborhoods of Brooklyn, made out of rocks, shells, and fuzzy rope that will promote the growth of oysters
-
-
Nuclear energy facilities proved themselves resilience during Hurricane Sandy

There are thirty-four nuclear energy facilities in the area hit by Hurricane Sandy; all of them have responded well and safely to the powerful storm; the industry says that careful planning and preparations days in advance of the storm paid off at all of these facilities
-
-
Hurricane Sandy offered support for reliance on nuclear power
A Scientific American writer is impressed with the way nuclear power facilities were able safely to withstand the wrath of Hurricane Sandy; the lesson he draws from this experience: “Global warming is increasing the probability and destructiveness of extreme weather events like Sandy. (I don’t see the point of dithering over this claim any more.) The last thing we should do in the face of this threat is abandon nuclear energy. If anything, we need more nuclear power, not less, to curb global warming”
-
-
Fracking: fact vs. fiction
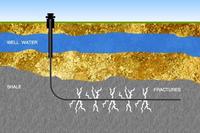
In communities across the United States, people are hearing more and more about a controversial oil and gas extraction technique called hydraulic fracturing — aka, hydro-fracking; controversies pivot on some basic questions: Can hydro-fracking contaminate domestic wells? Does it cause earthquakes? How can we know? What can be done about these things if they are true? Experts making presentations at the Geological Society of America (GSA) meeting this week in Charlotte, North Carolina, will address these and related critical questions
-
-
Study supports move toward common U.S. math standards
A new study analyzing the previous math standards of each state provides strong support for adoption of common standards, which U.S. students desperately need to keep pace with their counterparts around the globe
-
-
USGS sampling water in Hurricane Sandy’s aftermath to ensure public health
Excessive nutrients in U.S. rivers, streams, and coastal areas are a major issue for water managers, because they cause algal blooms that increase costs to treat drinking water, limit recreational activities, and threaten valuable commercial and recreational fisheries; U.S. Geological Survey crews are sampling water for nutrients, sediment, and pesticides to document water quality in areas affected by the hurricane
-
-
The science of hurricanes is imprecise, but delayed decisions on preparedness and adaptation may cost lives

It is difficult to tie a specific storm like Hurricane Sandy to the phenomenon of climate change; a professor of civil and environmental engineering says that this is a perfect example where the climate science may not yet be as precise as we would like, but important preparedness decisions still need to be made with some urgency; this is also an example where delayed decisions on preparedness and adaptation may cost human lives, destroy critical infrastructures, and damage economies; the importance of adaptation and preparedness in this context cannot be overstated
-
-
California worried about its own extreme weather
California will not see a superstorm like Hurricane Sandy because the Pacific Ocean is too cold to feed that kind of weather system, but researchers monitoring precipitation and snowpack say weather can have comparable effects
-
-
Sandy in perspective
Hurricane Sandy has left death and destruction in its path, and it broke a few records, but there were worse hurricanes; since 1900, 242 hurricanes have hit the United States; if Sandy causes $20 billion in damage, in 2012 dollars, it would rank as the seventeenth most damaging hurricane or tropical storm out of these 242; the Great Miami Hurricane of 1926 tops the list; Hurricane Katrina ranks fourth; from August 1954 through August 1955, the East Coast saw three different storms make landfall — Carol, Hazel, and Diane; each, in 2012, would have caused about twice as much damage as Sandy
-
-
Sea levels are rising ahead of predictions; scientists explain why
The last official Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report in 2007 projected a global sea level rise between 0.2 and 0.5 meters by the year 2100; current sea-level rise measurements meet or exceed the high end of that range and suggest a rise of one meter or more by the end of the century; scientists meeting next week at the Geological Society of America annual meeting will discuss whether estimates of the rate of future sea-level rise are too low
-
-
Flying robot avoids obstacles
Researchers have created an autonomous flying robot which is as smart as a bird when it comes to maneuvering around obstacles; able to guide itself through forests, tunnels, or damaged buildings, the machine could have tremendous value in search-and-rescue operations
-
-
Experts: German nuclear exit offers economic, environmental benefits
Following the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011, the German government took the nation’s eight oldest reactors offline immediately and passed legislation which will close the last nuclear power plant by 2022; this nuclear phase-out had overwhelming political support in Germany; elsewhere, many saw it as “panic politics”; a new collection of studies shows that the nuclear shutdown and an accompanying move toward renewable energy are already yielding measurable economic and environmental benefits
-
-
Quick-cook method turns algae into oil
It looks like Mother Nature was wasting her time with a multimillion-year process to produce crude oil; University of Michigan engineering researchers can “pressure-cook” algae for as little as a minute and transform an unprecedented 65 percent of the green slime into biocrude
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
