-
California hospitals to pay billions for seismic safety upgrades
California hospitals would need to make substantial investments—between $34 billion and $143 billion statewide—to meet 2030 state seismic safety standards, according to a new report.
-
-
Recaptured Italian former militant Battisti admits 1970s murders

Former communist militant Cesare Battisti has admitted four murders carried out in the 1970s, during Italy’s so-called “Years of Lead,” weeks after being jailed in Italy for the killings that were part of a failed bid to spark a far-left revolution.
-
-
Mapping out virtual world for U.S. military

When the U.S. military interviewed more than 100 experts about conflicts in Syria and Iraq, the resulting intelligence was so extensive that analysts joked about needing executive summaries for the executive summaries. Scientists at Argonne National Laboratory convert complex data into 3D digital visualizations to provide spatial and geographic context.
-
-
Russia sends military planes to Venezuela

Russia, a key ally of under-siege President Nicolas Maduro of Venezuela, sent two planes with military supplies and troops to shore up the Maduro regime. Russia had already sent two Tu-160 strategic bombers to Venezuela in December to support Maduro. Three months ago the two nations held military exercises in Venezuela.
-
-
Chances of UN banning killer robots looking increasingly remote

The Campaign to Stop Killer Robots warns chances of achieving a U.N. treaty banning the development, production and use of fully autonomous lethal weapons, also known as killer robots, are looking increasingly remote. Experts from some 80 countries are attending a weeklong meeting to discuss the prospect of negotiating an international treaty.
-
-
Detecting radioactive material remotely
Physicists have developed a powerful new method to detect radioactive material. By using an infrared laser beam to induce a phenomenon known as an electron avalanche breakdown near the material, the new technique is able to detect shielded material from a distance. The method improves upon current technologies that require close proximity to the radioactive material.
-
-
More mass shooting in states with permissive gun laws
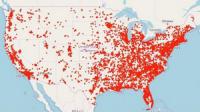
States with more permissive gun laws and greater gun ownership have higher rates of mass shootings, and a growing divide is emerging between states with restrictive versus permissive gun laws. According to a new study, researchers found that in most years permissive states had higher mass shooting rates compared to restrictive states.
-
-
Dunford: Google’s work with China “challenges” U.S. military advantage

The top U.S. military officer has called out U.S. technology giant Google for its artificial intelligence venture in China, saying it “creates a challenge” in maintaining a U.S. military advantage over the Chinese.
-
-
Satellite technology detects, and may prevent, genocide
Many of the world’s worst human rights abuses, including genocides, occur in areas that are difficult to observe. “Smallsat” — short for small satellite — technology can detect human rights abuses and violations. The information collected by this technology provides evidence that can be used to corroborate refugee accounts of atrocities in international courts.
-
-
Measuring progress toward resilience more effectively
A new report from the National Academies of Sciences recommends steps U.S. communities can take to better measure their progress in building resilience to disasters, including measuring resilience around multiple dimensions of a community, and incentivizing the measurement of resilience. The report also recommends that the National Academies’ Gulf Research Program develop a major, coordinated initiative around building or enhancing community resilience across the Gulf of Mexico region.
-
-
Cyber toolkit for criminal investigations
cybercrimes reached a six-year high in 2017, when more than 300,000 people in the United States fell victim to such crimes. Losses topped $1.2 billion. Cybercriminals can run, but they cannot hide from their digital fingerprints.
-
-
Studying how hate and extremism spread on social media
The ADL and the Network Contagion Research Institute will partner to produce a series of reports that take an in-depth look into how extremism and hate spread on social media – and provide recommendations on how to combat both.
-
-
Combatting human trafficking
Law enforcement organizations across the United States have recently arrested multiple people charged with various crimes that include organizing, operating or paying for services from human trafficking rings. “Human trafficking is not synonymous with human smuggling,” notes one expert.
-
-
A new way to sense earthquakes could improve early warning systems

Every year earthquakes worldwide claim hundreds or even thousands of lives. Forewarning allows people to head for safety and a matter of seconds could spell the difference between life and death. Researchers demonstrate a new earthquake detection method — their technique exploits subtle telltale gravitational signals traveling ahead of the tremors. Future research could boost early warning systems.
-
-
Easier access to radioactive waste
At the Hanford Site, waste retrieval has been completed in 17 of 149 large concrete underground single-shell tanks. The tanks were constructed of carbon steel and reinforced concrete between 1943 and 1964 to store a radioactive mix of sludge and saltcake waste from past nuclear processing activities. Hanford is installing new access holes in the tank domes for future retrieval efforts.
-
More headlines
The long view
AI-Controlled Fighter Jets May Be Closer Than We Think — and Would Change the Face of Warfare
Could we be on the verge of an era where fighter jets take flight without pilots – and are controlled by artificial intelligence (AI)? US R Adm Michael Donnelly recently said that an upcoming combat jet could be the navy’s last one with a pilot in the cockpit.
What We’ve Learned from Survivors of the Atomic Bombs
Q&A with Dr. Preetha Rajaraman, New Vice Chair for the Radiation Effects Research Foundation in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan.
Need for National Information Clearinghouse for Cybercrime Data, Categorization of Cybercrimes: Report
There is an acute need for the U.S. to address its lack of overall governance and coordination of cybercrime statistics. A new report recommends that relevant federal agencies create or designate a national information clearinghouse to draw information from multiple sources of cybercrime data and establish connections to assist in criminal investigations.
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Twenty-One Things That Are True in Los Angeles
To understand the dangers inherent in deploying the California National Guard – over the strenuous objections of the California governor – and active-duty Marines to deal with anti-ICE protesters, we should remind ourselves of a few elementary truths, writes Benjamin Wittes. Among these truths: “Not all lawful exercises of authority are wise, prudent, or smart”; “Not all crimes require a federal response”; “Avoiding tragic and unnecessary confrontations is generally desirable”; and “It is thus unwise, imprudent, and stupid to take actions for performative reasons that one might reasonably anticipate would increase the risks of such confrontations.”
Luigi Mangione and the Making of a ‘Terrorist’
Discretion is crucial to the American tradition of criminal law, Jacob Ware and Ania Zolyniak write, noting that “lawmakers enact broader statutes to empower prosecutors to pursue justice while entrusting that they will stay within the confines of their authority and screen out the inevitable “absurd” cases that may arise.” Discretion is also vital to maintaining the legitimacy of the legal system. In the prosecution’s case against Luigi Mangione, they charge, “That discretion was abused.”
