-
Report: Hamas spends $100 million annually to build up its military infrastructure
Hamas spends an annual $100 million on its military infrastructure in order to prepare for its next war against Israel. Roughly $40 million is spent on employing around 1,500 diggers to build the Iran-backed terror organization’s network of tunnels. Despite the financial hardships experienced by Gaza residents, Hamas, which in 2014 had a budget of around $530 million, is intent on increasing its military spending. In addition to digging tunnels, it hopes to upgrade its capabilities, which were degraded during its war with Israel two years ago, and is seeking to develop more precise rockets that could evade Israel’s Iron Dome defensive shield.
-
-
Why ratifying the Chemical Weapons Convention is in Israel’s best interest
When the time came to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the first major use of chemical weapons, it seemed there was at last a real chance of ridding the world of all chemical weapons in the very near future. Almost all countries had already joined the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), which commits countries to the supervised destruction of all stockpiles of chemical weapons – with only two states as yet unwilling to sign: North Korea and Egypt. But there’s another exception: Israel, which has signed the convention but is refusing to ratify it. Chemical weapons have no place in a civilized society. They have little to no use as a tactical deterrent, and their effects are indiscriminate and appalling. We have a unique opportunity to rid the world of this scourge, and we’re so close to doing so. It’s high time Israel joined the rest of the world.
-
-
Syria chlorine attack claims: what this chemical is and how it became a weapon
New claims that the Syrian government has dropped barrel bombs full of chlorine on a suburb of Aleppo are the latest in a series of allegations of chemical weapon use. Although the Syrian government denies using chemical weapons, a recent UN-led enquiry found it had used chlorine on at least two occasions. The first gas attack using chlorine was launched on 22 April 1915 in the trenches on the Western front, near Ypres. Gas masks were developed to protect against chlorine attacks and other chemical warfare agents were developed. But chlorine remains the simplest chemical weapon and reappeared on the battlefield during the Iraq War and allegedly now in Syria. In the Second World War, both sides of the conflict knew that the other side had weaponized chlorine and refrained from using it. Today in Syria, it sadly appears this may not have been the case.
-
-
Rules governing targeted killing by U.S. drones need clarifying
Since the beginning of the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan, the United States has dramatically increased use of unmanned drones, developing technology to target and kill those identified as being terrorist leaders. Current U.S. policies on using drones for targeted killing are characterized by ambiguities in interpretations of international law and too many generalities, despite recent efforts by the Obama administration to clarify the policies, a new report finds.
-
-
Strengthening national security by improving intelligence software
An intelligence analyst hunting for answers in a sea of data faces steep challenges: She must choose the right search terms, identify useful results, and organize them in a way that reveals new connections. Making that process quicker and more intuitive could yield faster answers to key national security questions. Researchers are developing intelligence software that allows analysts to interact more closely with their data.
-
-
Tackling rumors during crises
The proliferation of rumors during a crisis can hinder efforts by emergency personnel trying to establish facts. That is why a doctoral student at BGU’s Department of Emergency Medicine has developed a methodology for tracking rumors and guidelines for how to control them.
-
-
Alabama public library threatens jail time for borrowers with overdue books
The Athens-Limestone Public Library in Athens, Alabama, has just about had enough with people who borrow books from the library and then take their time returning them. Accordingly, the library has warned people they could go to jail if they fail to return borrowed books on time.
-
-
White Nationalist groups growing much faster than ISIS on Twitter

The number of White Nationalists and self-identified Nazi sympathizers on Twiter had multiplied more than 600 percent in the last four years — outpacing ISIS in all social media aspects, from the number of follower counts to the number of daily tweets, a new study found. The study’s author notes that ISIS has gained a reputation for effectively using Twitter for propaganda and recruitment, but that White Nationalist groups have excelled even more in exploiting the medium. The report says that unlike the campaign Twitter has been conducting against ISIS, White Nationalists are continuing to use the service with “relative impunity.”
-
-
Iran received secret exemptions from complying with some facets of nuclear deal

The nuclear deal between the P5+1 powers and Iran – the official named is the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) — placed detailed limitations on facets of Iran’s nuclear program that needed to be met by Implementation Day, which took place on 16 January 2016. Most of the conditions were met by Iran, but some nuclear stocks and facilities were not in accordance with JCPOA limits on Implementation Day. In anticipation, the Joint Commission had earlier and secretly exempted them from the JCPOA limits. “Since the JCPOA is public, any rationale for keeping these exemptions secret appears unjustified,” say two experts. “Moreover, the Joint Commission’s secretive decision making process risks advantaging Iran by allowing it to try to systematically weaken the JCPOA. It appears to be succeeding in several key areas.”
-
-
A new generation of low-cost, networked, nuclear-radiation detectors
A DARPA program aimed at preventing attacks involving radiological “dirty bombs” and other nuclear threats has successfully developed and demonstrated a network of smartphone-sized mobile devices that can detect the tiniest traces of radioactive materials. Combined with larger detectors along major roadways, bridges, other fixed infrastructure, and in vehicles, the new networked devices promise significantly enhanced awareness of radiation sources and greater advance warning of possible threats.
-
-
The building evacuation needs of the mobility impaired
A fire alarm sounds. An announcement comes over the office public address system: “A fire has been reported in the building. This is not a drill. Please move to the nearest stairwell and exit the building.” As your colleagues leave their desks, you loosen the wheel locks on your wheelchair and wonder, “Will I be able to get out of the building?” This scenario is among the most common concerns reported in a new study detailing the challenges faced by people with mobility impairments during emergency evacuation from multistory buildings.
-
-
North Korea creates specials nuclear backpack units to infiltrate the South
North Korea has established a special infantry unit whose soldiers are being trained for a one-way mission: in the event of war with South Korea, they will infiltrate the South carrying nuclear devices in backpacks and detonate their weapons in the middle of population centers. North Korean military issued calls to the nation’s soldiers to become human “nuclear arsenals” in the event of war in the region. Military analysts said the units are, in effect, suicide squads, resembling the Japanese kamikaze pilots sent to attack Allied warships toward the end of the Second World War.
-
-
Libya’s remaining chemical weapons materials removed
The director-general of the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), ambassador Ahmet Üzümcü, announced a milestone in the operation to verifiably eliminate Libya’s remaining chemical weapons stocks by confirming that the chemicals have been successfully removed from Libya on 27 August 2016.
-
-
Looking from space for nuclear detonations
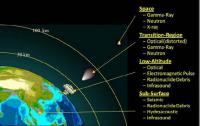
Sandia has been in the business of nuclear detonation detection for more than fifty years, starting with the 1963 launch of the first of twelve U.S. Vela satellites to detect atmospheric nuclear testing and verify compliance with the Limited Test Ban Treaty of 1963 and subsequently the Threshold Test Ban Treaty of 1974. That marked the start of the U.S. Nuclear Detonation Detection System that supports treaty monitoring. The Global Burst Detection (GBD) system launched 5 February from Cape Canaveral aboard the 70th Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite. The GBD looks for nuclear detonations around the world, offering real-time information about potential activity to U.S. policymakers. The launch was the 12th and final of the Block IIF (GPSIIF) series of GPS satellites in medium Earth orbit.
-
-
Europol deploys 200 counterterrorism officers to Greece to thwart ISIS infiltration
Rob Wainwright, the chief of Europol, the EU’s law enforcement agency, said that 200 counter terrorism officers will be deployed to the Greek islands within weeks in an effort to thwart a “strategic”-level campaign by ISIS to infiltrate terrorists into Europe. The new task force will be deployed alongside Greek border guards and use technologies developed by British security forces at Heathrow to help spot potential terrorists.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Male Grievance Fuels Radicalization and Extremist Violence
Social extremism is evolving in reach and form. While traditional racial supremacy ideologies remain, contemporary movements are now often fueled by something more personal and emotionally resonant: male grievance.
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
