-
Harris protests FBI’s Motorola radio upgrade contract
The Harris Corp. has become the second contractor, afterRELM Wireless Corp., formally to protest the FBI’s decision to award a $500 million non-bid contract to Motorola Solutions Inc., claiming the contract to upgrade the FBI’s 30-year-old two-way radio network was “factually unsound, legally unwarranted and wholly unnecessary.”
-
-
Crime rates affected by who has administrative, budgetary responsibility for prisons
In 2011, the U.S. Supreme Court forced California to deal with the massive overcrowding in its prison system. The resulting reform shifted administrative and budgetary responsibility for low-level criminals from the state prison system to county jails. As a result, local California jails now face more overcrowding than ever, and local law enforcement is saddled with additional costs for imprisoning arrestees. In Israel, the trend has been in the opposite direction: an administrative reform which transferred authority over jails from the police to the Prison Authority resulted in the police sending more people to jail. A new study found that police are more inclined to issue arrests when prisons have administrative responsibility for detainees. The effect on crime: crime in Israel dropped as a result of the reform largely because the police — feeling less budgetary pressure — felt free to arrest more suspects, many of whom would have gotten off in the past with a warning.
-
-
Philadelphia refines area 911 call locator technology
In the Philadelphia area and around much of the country, emergency services and first responders are looking to retool the ways in which cell phone locator technology could allow them to aid individuals, and they are calling for the further cooperation of cell phone providers and the government alike. “If you don’t know where the guy is, you can’t help him,” said Edwin Truitt, the Delaware County [Pennsylvania] Emergency Services director.
-
-
SATCOMS vulnerable to hacking
Satellite communications systems (SATCOMS) used by soldiers on the front lines, airplanes, and ships are vulnerable to hacking, according to analyst Ruben Santamarta’s presentation at the recent Black Hatcybersecurity conference.While none of the vulnerabilities discovered could directly cause a plane to crash, or override pilot commands, they could delay or intercept communications, exposing security and classified information to bad actors.
-
-
Tool helps investigators connect bomb fragments to bomb makers
Authorities with the U.S. Special Operations Command (SOCOM), the Canadian military, the U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF), and law enforcement agencies in the United Kingdom have adopted a crowdsourcing system called DFuze to help agencies in twenty-five countries connect bomb fragments to bomb makers or individuals who could be connected to a specific bomb.The technology allows users to share bomb images and data to assist pending investigations.
-
-
Alabama schools deploy 3-D virtual mapping to prepare responders
The Alabama Department of Homeland Security has recently institutionalized a detailed 3-D mapping system, called Virtual Alabama, which aims to create maps of public buildings in order to prepare responders in the event of a security emergency.The tactic behind Virtual Alabama is to immerse local responders to the intricacies of key structures before the knowledge is ever needed.
-
-
Opportunities for regional realignment not likely to be seized
After the first twenty-four hours, the 72-hour Egypt-sponsored Gaza cease-fire appears to be holding – something which could not be said for the previous five cease-fires, which were violated by Hamas within minutes of supposedly going into effect. The Israeli delegation yesterday flew to Cairo to begin negotiations on a longer-term arrangement. The reason why this cease-fire is likely to hold has to do with the realization by Hamas Gaza leaders of their isolation and the growing destruction Israel’s attacks were inflicting on Hamas’s war machine and Gaza’s already-dilapidated infrastructure. A militarily weakened Hamas, a moderate Arab block hostile to militant Islam, and a convergence of interests between Israel and the moderate Arab states provide the foundation for profound strategic transformation in the region. It is doubtful, however, that the Netanyahu government will seize the opportunity for a breakthrough in Israel-Palestinian relations, on which such a transformation depends. During the month-long war, Netanyahu has given no indication that he sees this round of Israel-Hamas war in anything other than tactical terms, and has offered nothing to show that he plans to exploit the military results of the war, together with the changing political context in the region, for a bold and creative initiative which would change Israel’s relations with the PA, transform Israel’s strategic position, and realign regional politics.
-
-
U.S. law enforcement agencies perceive Sovereign citizen movement as top terrorist threat
Sovereign citizen, Islamist extremist, and militia/patriot groups are perceived by U.S. law enforcement agencies to pose the greatest threats to their communities, according to a new study. While sovereign citizens were the top concern of law enforcement, assessments about whether most groups were a serious terrorist threat actually declined for most groups (for example, the KKK; Christian Identity; Neo-Nazis; Racist Skinheads; Environmental Extremists; Animal Rights Extremists) when compared to a previous study. The authors conducted in-depth interviews with officers representing 175 state, local, and tribal (SLT) law enforcement agencies, and found that the Sovereign Citizen movement was the most highly ranked threat, with 86 percent of respondents agreeing or strongly agreeing that it was a serious terrorist threat. Approximately 67 percent agreed or strongly agreed that Islamist extremists were a serious terrorist threat.
-
-
Encouraging innovation for better preparedness, recovery, and resilience tools
Last week the White House hosted innovators in technology and emergency management to discuss new tools that can improve preparedness, recovery, and resilience in the wake of a disaster. The White House Innovation for Disaster Response and Recovery Initiative Demo Dayshowcased innovations from the private sector and government agencies aimed at aiding survivors of large-scale emergencies. The key goal was to “find the most efficient and effective ways to empower survivors to help themselves,” said U.S. Chief Technology Officer Todd Park.
-
-
U.S. to spend more money on modernizing its nuclear arsenal, less on nonproliferation programs
President Barack Obama has made gains in his quest to secure nuclear weapons and materials. In March, at the Nuclear Security Summitin Holland, Obama declared “it is important for us not to relax but rather accelerate our efforts over the next two years.” The Obama administration, however, is allocating more resources toward refurbishing and modernizing current nuclear weapons than advancing nuclear nonproliferation programs. Civilian institutions, including research labs, today hold enough nuclear explosive materials to put together 40,000 atomic bombs, but the administration has missed a self-imposed deadline of April 2013 for ensuring that nuclear materials were safe from terrorist organizations.
-
-
Civilian deaths in Gaza conflict are not automatically a war crime
Civilian shielding of its facilities is a declared Hamas military tactic. The evidence of rocket pits and weapon dumps located in, around and under mosques, schools, homes and hospitals is incontrovertible. Constant broadcasts calling upon, as well as occasional physical forcing of, the populace to protect Hamas assets with their bodies are well-documented. It is sickening that Hamas chose not to build public bomb shelters in Gaza, despite using hundreds of thousands of tons of concrete on military tunnels to initiate hostilities with Israel. The tragic Palestinian death toll does not demonstrate Israeli attacks are disproportionate to legitimate military objectives. It does display a disgusting strategic decision by Hamas to exploit civilians to shield its combatants. Its civilian deaths generate selective outrage in support of its political and economic goals. This atrocity committed by Hamas against its own Gazan population is where an honest war crime investigation would begin.
-
-
Continued funding for S.C. mixed-oxide fuel (MOX) plant – at least until fall
Federal legislators have secured the funds to keep the mixed-oxide fuelplant (MOX) at the Savannah River Sitein South Carolina moving forward at least into fall, according to South Carolina governor Nikki Haley and members of the state’s congressional delegation. The 310-square mile site once produced components for nuclear weapons, but since the agreement with Russia to turn nuclear weapons into reactor fuel, the site has focused on repurposing and cleanup.
-
-
U.S. faces serious future threats in space
Gen. William Shelton, the commander of Air Force Space Command, said last week that U.S. dominance in space will be challenged by very real threats in the years ahead. The general said that those threats might consist of “jammers, lasers and tactical space nukes,” with any of these challenges exponentially more dangerous than in the past as the technology becomes more common.
-
-
Sandia makes sure U.S. nuclear weapons deterrent remain effective, credible
It may sound strange to say that nuclear weapons must survive radiation. Sandia National Laboratories says, however, that as part of its mission of ensuring the nation’s stockpile is safe, secure, and effective as a deterrent, the laboratory must make sure crucial parts can function if they are hit by radiation, especially a type called fast neutrons. Sandia developed a new way to do that after its facility for creating fast neutrons, the Sandia Pulsed Reactor (SPR), was shut down due to increased post-9/11 security concerns about its highly enriched uranium.
-
-
DOE chief to visit WIPP to discuss funding for recovery efforts
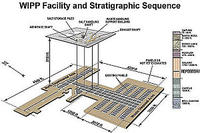
Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz will visit Carlsbad, New Mexico on 12 August to discuss funding for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) recovery efforts.Traces of americium and plutonium were released from a nuclear waste drum on 14 February and were detected in the air almost a half-mile outside WIPP. On 15 May, the DOE confirmed that the damage occurred on a waste drum from Los Alamos National Laboratory.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Male Grievance Fuels Radicalization and Extremist Violence
Social extremism is evolving in reach and form. While traditional racial supremacy ideologies remain, contemporary movements are now often fueled by something more personal and emotionally resonant: male grievance.
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
