-
First U.S. commercial enhanced geothermal system connected to the grid
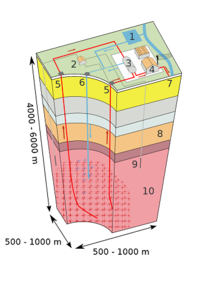
Enhanced geothermal system (EGS) projects capture power from intensely hot rocks, buried thousands of feet below the surface, which lack the permeability or fluid saturation found in naturally occurring geothermal systems. The Energy Department the other day announced the U.S. first commercial EGS project which supplies electricity to the grid.
-
-
Former NRC chairman: all 104 U.S. nuclear reactors suffer from “irreparable” safety issues
According to former U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) chairman Gregory Jaczko, all 104 nuclear reactors in the United States currently have irreparable safety issues and should be shut down and replaced. Jaczko was the NRC chairman from 2009 through 2012.
-
-
Critics: Fukushima-influenced U.S. nuclear accident response procedures are flawed
The U.S. government is using the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan two years ago as a model for rewriting its plans on how to respond to radiation contamination — emphasizing long-term cleanup and return of residents to affected areas instead of emergency response. Critics say this is a mistake.
-
-
Giant snails invade Florida

South Florida has found itself in battle with a destructive invasive species known as the giant African land snail. The snail can grow as big as a rat and can eat plaster.
-
-
Direct CO2 removal could lower costs of climate mitigation
Two broad strategies are typically offered to protect infrastructure from the consequences of climate change: reducing to emissions of CO2 into the atmosphere by using less fossil fuels, and mitigation (building sea walls, dams, and levees; changing building codes, etc.). Both approaches are costly. Scientists suggest that directly removing CO2 from the air could alter the costs of climate change mitigation. It could allow prolonging greenhouse-gas emissions from sectors like transport which are difficult, and thus expensive, to turn away from using fossil fuels.
-
-
Population growth a challenge to secure supplies of energy, food, water
Mention great challenges in feeding a soaring world population, and thoughts turn to providing a bare subsistence diet for poverty-stricken people in developing countries. An expert says, however, that there is a parallel and often-overlooked challenge: the global population will rise from seven billion today to almost nine billion people by 2040. Providing enough food to prevent starvation and famine certainly will be a daunting problem.
-
-
L.A County to turn rain water into drinking water
Residents of Los Angeles County know that on the rare occasion that it rains, staying away from the beach is a good idea. Runoff from rain typically brings heavy metals, pesticides, cigarette butts, animal waste, and other pollutants into the streams and rivers which go into the Pacific Ocean. Now, local officials are getting together to find a solution to the water pollution and water scarcity, with an ambitious plan to make the runoff water drinkable.
-
-
Oregon citizens preparing for the Big One

A new study concludes that an earthquake of a magnitude 8.0 or above will strike off the coast of the state within the next fifty years. The Cascadia Fault, which runs from Northern California to British Columbia, Canada, causes a massive earthquake every 300 years or so, and the last time an earthquake hit the region was in the year 1700.
-
-
Making concrete “greener”

Many factors determine the overall energy and environmental impact of concrete. Reducing the amount of portland cement, which reacts with water to bind all the sand, stone, and the other constituents of concrete as it hardens, provides the biggest opportunity. Portland cement manufacturing accounts for more than 5 percent of U.S. industrial carbon-dioxide emissions. In addition, the U.S. cement industry consumes 400 gigajoules of energy annually.
-
-
Renewable energy could economically replace fossil-based energy in Australia
A carbon price of between AU$50 and AU$100 per ton of carbon dioxide would make coal-fired and gas-fired power in Australia less economical than renewable electricity. A new study says that all fossil-fuelled power stations in Australia’s National Electricity Market could be phased out and replaced economically and reliably with commercially available renewable energy technologies by increasing the carbon price to this “medium” level.
-
-
U.S. nuclear industry faces a wave of nuclear power station retirements
A wave of U.S. nuclear power station retirements is on the horizon. The typical design life of a nuclear power plant is 40 years. There are 104 nuclear power plants in the United States, and their average age is 34 years — only a few years short of, and fast approaching, their design life. Almost 30 U.S. commercial and research reactors already have started decommissioning. A $400 million is regarded as the bargain basement price tag for cleaning up a single reactor.
-
-
China catches 12 times more fish beyond its waters than it reports
Chinese fishing boats catch about $11.5 billion worth of fish from beyond their country’s own waters each year — and most of it goes unreported. Researchers estimate Chinese foreign fishing at 4.6 million tons per year, taken from the waters of at least ninety countries — including 3.1 million tons from African waters, mainly West Africa.
-
-
Same-day water test keeps beaches open, swimmers’ health protected

With warm summer days at the beach on the minds of millions of winter-weary people, scientists are reporting that use of a new water quality test this year could prevent unnecessary beach closures, while better protecting the health of swimmers.
-
-
Large robotic jellyfish to patrol the oceans

The Office of Naval Research wants to place self-powering, autonomous machines in waters for the purposes of surveillance and monitoring the environment, in addition to other uses such as studying aquatic life, mapping ocean floors, and monitoring ocean currents. Researchers have built a device for that purpose — a life-like, autonomous robotic jellyfish the size and weight of a grown man, 5 foot 7 inches in length and weighing 170 pounds.
-
-
Water treatment plant ozone upgrade wins civil engineering award
The Ozone Upgrade and Expansion Project of the Alvarado Water Treatment Plant in San Diego, California, was named the winner of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) 2013 Outstanding Civil Engineering Achievement (OCEA) Award. In addition to expanding plant capacity by 67 percent, the city of San Diego converted from chlorine to ozone disinfection. The incorporation of ozone enabled the city to provide not only safer water with lower levels of carcinogenic disinfection by-products, but also water that is odorless and better tasting.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
