-
Bioprinting to help produce an edible cultured meat prototype
Modern Meadow is developing a fundamentally new approach to meat and leather production which is based on the latest advances in tissue engineering and causes no harm to animals; with funding from the Thiel Foundation’s Breakout Labs, they plan to apply the latest advances in tissue engineering beyond medicine to produce novel consumer biomaterials, including an edible cultured meat prototype that can provide a humane and sustainable source of animal protein to consumers around the world
-
-
Wastewater key to addressing growing global water shortage

Parched cities and regions across the globe are using sewage effluent and other wastewater in creative ways to augment drinking water, but four billion people still do not have adequate supplies, and that number will rise in coming decades
-
-
Water sustainability flows through complex human-nature interactions
The fate of water in China mirrors problems across the world: water is fouled, pushed far from its natural origins, squandered, and exploited; China’s crisis is daunting, though not unique: two-thirds of China’s 669 cities have water shortages, more than 40 percent of its rivers are severely polluted, 80 percent of its lakes suffer from eutrophication — an over abundance of nutrients — and about 300 million rural residents lack access to safe drinking water
-
-
USDA’s proposed chicken safety inspection policy could mean trouble for consumers
The federal government has come up with a new proposal to examine chickens for contaminates and diseases, and the proposal has some people concerned and others outright scared; the proposal would reduce the number USDA food safety inspectors at poultry plants from four to one – and rely on plant’s employees to do safety inspections instead
-
-
Dropping lake levels in Michigan are a cause for concern
In a state that boasts 11,000 lakes, Michigan is going through a year long drought that has residents and businesses scrambling as water levels continue to decrease; the low waters is the result of low snowpack last winter and a hot dry summer this year
-
-
Extreme summer heat events, global warming linked: research
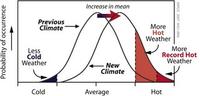
Since the late 1980s researches have been asserting that global warming would reach a point in the coming decades when its connection to extreme events would become more apparent; while some warming should coincide with a noticeable boost in extreme events, the natural variability in climate and weather can be so large as to disguise the trend; to distinguish the trend from natural variability, NASA researchers turned to statistics; the researchers did not focus on the causes of temperature change, analyzing instead surface temperature data
-
-
Surface coal mining destroying West Virginia streams, rivers
More than 22 percent of streams and rivers in southern West Virginia have been degraded to the point they may now qualify as impaired under state criteria; the substantial losses in aquatic insect biodiversity and increases in salinity is linked to sulfates and other pollutants in runoff from mines often located miles upstream
-
-
Chronic 2000-4 U.S. drought, worst in 800 years, may be the "new normal"

The chronic drought that hit western North America from 2000 to 2004 left dying forests and depleted river basins in its wake and was the strongest in 800 years, scientists have concluded, but they say those conditions will become the “new normal” for most of the coming century
-
-
Food prices in U.S., world set to rise as a result of drought
The U.S. Midwest is suffering the worst drought since 1956, and a total of 1,369 counties in thirty-one states across the United States have been designated for disaster aid; the prolonged drought will lead to an increase in food prices in 2013 as animal feed costs increase
-
-
Capturing CO2 directly from air is chemically, economically viable
With a series of papers published in chemistry and chemical engineering journals, researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology have advanced the case for extracting carbon dioxide directly from the air using newly developed adsorbent materials
-
-
Pulling CO2 from air feasible, if still costly, way to curb global warming
Emerging techniques to pull carbon dioxide from the air and store it away to stabilize the climate may become increasingly important as the planet tips into a state of potentially dangerous warming; lower-cost technology is a stumbling block so far
-
-
Researchers discover a molecule's previously unknown role in fighting off E. coli
Escherichia coli (abbreviated as E. coli) are a large and diverse family of bacteria; most strains of E. coli are harmless, but some can be deadly; E. coli creeps into the food supply through contamination by tiny (usually invisible) amounts of human or animal feces; many people may develop mild symptoms, but some suffer severe complications that can lead to kidney failure and death; researchers discover a molecule’s previously unknown role in fighting off E. coli and other bacterial infections, a discovery that could lead to new ways to protect people from these dangerous microorganisms
-
-
Poultry vaccines found to combine into new viruses
Researchers found that two different vaccine viruses — used simultaneously to control the same condition in chickens — have combined to produce new infectious viruses, prompting early response from Australia’s veterinary medicines regulator
-
-
Environmental changes lead stressed cows in southern U.S. to produce less milk

Researchers found that the decline in milk production due to climate change will vary across the United States, since there are significant differences in humidity and how much the temperature swings between night and day across the country; for instance, the humidity and hot nights make the Southeast the most unfriendly place in the country for dairy cows
-
-
A world free of foot-and-mouth disease within sight
The Departments of Homeland Security and Agriculture have developed a novel vaccine for one of the seven strains of the dreaded foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), paving the way for the development of the others; FMD is one of the most economically devastating diseases in the world for those who raise cows, sheep, pigs, goats, deer, and other cloven-hoofed animals is foot-and-mouth disease
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
