-
Could devastating floods help Bosnians heal their war wounds?
The violent breakup of Yugoslavia in the 1990s and the subsequent war in Bosnia between 1992 and 1995 took the lives of more than 100,000 Bosnians and left two million homeless. Two decades later those survivors have been forced once again to abandon their homes — this time by floodwaters rather than bullets. The heaviest rainfalls ever recorded in the Balkans have led to catastrophic flooding in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Swelled by weeks of rain, the devastating floodwaters swamped more than 60 percent of the country last month, destroying more than 100,000 homes and displacing around 950,000 citizens. The floods also damaged vital infrastructure, destroyed industrial assets, and killed livestock. It is difficult to find a ray of light in this grim story of disaster, except this: Over the past weeks, media outlets have been flooded with stories and images of bravery, camaraderie, and community spirit where ethnicity suddenly became irrelevant. It remains to be seen how this feeling of camaraderie and community can be harvested to mobilize the people of Bosnia ahead of the general elections in October. Such a movement would have the potential to force corrupted political elites into the corner by draining them of their political capital.
-
-
Smart infrastructure sensors are powered by the pavement, bridges they monitor

As states look to improve its infrastructure — roads and bridges — researchers think they may have one solution. They are creating smart infrastructure sensors that are powered by the pavement and bridges they are designed to monitor. These small sensors will self-diagnose damage and mechanical failure in pavements and bridges.
-
-
IT security at U.S. ports weak: GAO
The Government Accountability Office (GAO) reports that maritime security policies and plans at three high-risk U.S. ports do not effectively address how to assess, manage, and respond to cybersecurity threats. While all three ports have strategies to deal with physical security, there were few policies that specifically addressed cybersecurity.
-
-
Debate continues over controversial lawsuit-killing Louisiana oil bill
Governor Bobby Jindal (R-Louisiana) is facing a difficult decision over whether or not to veto a measure which would kill a contentious lawsuit filed by the Southeast Louisiana Flood Protection Authority-East (SLFPA-E) against ninety-seven different oil and gas companies regarding long-term environmental damage claims, including those of the 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion.
-
-
Recession-related cost measures blamed for U.S. infrastructure lagging development
In an alarming fall, the United States is currently ranked 19th in the quality of its infrastructure, according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Report. Additionally, the American Society for Civil Engineers (ASCE) has given the country a D+ on its annual Infrastructure Report Card, arguing that $3.6 trillion is needed by 2020 for maintenance and upgrades.
-
-
Connecticut preparing for sea level rise, adapting to climate change
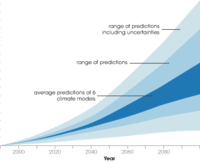
Earlier this year the University of Connecticut announced the creation of the Institute for Community Resiliency and Climate Adaptation. the Institute is designed to increase the resilience and sustainability of vulnerable communities and individuals along Connecticut’s coast and inland waterways as they are affected by the growing impact of climate change on the environment.
-
-
Six more bugs found in popular OpenSSL security tool
OpenSSL is a security tool that provides facilities to other computer programs to communicate securely over the public Internet. OpenSSL is also used in some common consumer applications, such as software in Google’s Android smartphones. So when the Heartbleed vulnerability in OpenSSL was discovered and widely publicized in April this year, system administrators had to rush to update their systems to protect against it. Computer system administrators around the world are groaning again as six new security problems have been found in the OpenSSL security library.
-
-
Nationwide effort launched to weather-harden Canadian cities
The frequency and magnitude of extreme weather events in Canada — from the floods in Southern Alberta and Toronto to the December ice storm in Central and Eastern Canada — are increasing, causing billions of dollars in damage to infrastructure, businesses and homeowners. Intact Financial Corporation and the University of Waterloo announced a national initiative involving the implementation of twenty climate change adaptation projects designed to reduce the physical, financial, and social impacts of extreme weather events in Canada.
-
-
It is almost certain there are aliens out there, but can we find the money to find them?

UC Berkley Professor Dan Werthimer last month updated members of the House Subcommittee on Science, Space and Technology on the search for extraterrestrial life, and provided a generally upbeat evaluation: ET microbial life likely is ubiquitous throughout the galaxy, and new technologies have improved the chances of detecting signals from advanced alien civilizations.
-
-
Adm. Michael Rogers: Businesses must “own” cybersecurity threats

Cybersecurity threats are a vital issue for the nation, and like the Defense Department, businesses must own the problem to successfully carry out their missions, DOD’s top cybersecurity expert told a forum of businesspeople.
-
-
Better building design, maintenance would cut building sector’s emissions by around 80%
The construction industry, which uses half of the 1.5 billion tons of steel produced each year, could slash its carbon emissions by as much as 50 percent by optimizing the design of new buildings, which currently use double the amount of steel and concrete required by safety codes. If buildings are also maintained for their full design life and not replaced early, the sector’s emissions could in total be cut by around 80 percent.
-
-
DARPA’s Cyber Grand Challenge aims to see fully automated network security systems developed

There is an increasingly serious cybersecurity problem: the inadequacy of current network security systems, which require expert programmers to identify and repair system weaknesses — typically after attackers have taken advantage of those weaknesses to steal data or disrupt processes. Such disruptions pose greater risks than ever as more and more devices, including vehicles and homes, get networked in what has become known as “the Internet of things.” DARPA is addressing this problem, with teams from around the world starting a two-year track toward the world’s first tournament of fully automated network security systems. Computer security experts from academia, industry, and the larger security community have organized themselves into more than thirty teams to compete in DARPA’s Cyber Grand Challenge — first-of-its-kind tournament designed to speed the development of automated security systems able to defend against cyberattacks as fast as they are launched.
-
-
Roots of Trust research focuses on protecting cyber physical systems
“Roots of Trust” refers to a set of security functions in a device or system, which are implicitly trusted by the device’s operating system and applications, and which constitute the foundation for security. The Cyber Security Research Alliance (CSRA) the other day said it will prioritize research in Roots of Trust for cyber physical systems (CPS), to help address growing cyber security threats to public and private critical infrastructure.
-
-
Santa Monica to require retrofit of earthquake-vulnerable buildings
Last week, the Santa Monica City Councilauthorized city officials to hire engineering consultants to help identify buildings built before 1996 which could potentially be at risk in a major earthquake.. Owners of vulnerable buildings would be notified and provided recommendations on how to best retrofit their buildings to make them more resilient. Santa Monica will become the first city in California to require retrofitting for concrete, steel, and wood-frame. San Francisco last year required similar retrofitting, but only for wood apartment buildings.
-
-
Hurricanes with female names deadlier than male-named storms
In the coming Atlantic hurricane season, watch out for hurricanes with benign-sounding names like Dolly, Fay, or Hanna. According to a new study, hurricanes with feminine names are likely to cause significantly more deaths than hurricanes with masculine names, apparently because storms with feminine names are perceived as less threatening.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
