-
California hospitals to pay billions for seismic safety upgrades
California hospitals would need to make substantial investments—between $34 billion and $143 billion statewide—to meet 2030 state seismic safety standards, according to a new report.
-
-
Rapidly melting tall ice-cliffs may trigger faster sea-level rise
Glaciers that drain ice sheets such as Antarctica or Greenland often flow into the ocean, ending in near-vertical cliffs. As the glacier flows into the sea, chunks of the ice break off in calving events. Although much calving occurs when the ocean melts the front of the ice, and ice cliff above falls down, a new study presents another method of calving: slumping. And this process could break off much larger chunks of ice at a quicker rate.
-
-
Geothermal plant caused South Korea’ 2017 tremor
A rare earthquake in South Korea was triggered by the country’s first experimental geothermal power plant, government officials said Wednesday. The southeastern port city of Pohang was rattled by a 5.4-magnitude earthquake in November 2017— the second-most powerful tremor ever in the normally seismically stable South.
-
-
Mitigating impact of rising seas, storms along California’s coast
New coastal modeling research presents state, federal, and commercial entities with varying storm and sea level-rise scenarios to assist with planning for future infrastructure and mitigation needs along the California coast.
-
-
A new way to sense earthquakes could improve early warning systems

Every year earthquakes worldwide claim hundreds or even thousands of lives. Forewarning allows people to head for safety and a matter of seconds could spell the difference between life and death. Researchers demonstrate a new earthquake detection method — their technique exploits subtle telltale gravitational signals traveling ahead of the tremors. Future research could boost early warning systems.
-
-
China's Huawei sues U.S. government over ban

Chinese tech giant Huawei has sued the U.S. government, arguing that legislation Congress passed last year that restricts its business in the United States is “unconstitutional.” The case, which analysts see more as a public relations move, is but the latest in an intensifying effort by the telecommunications company to fight U.S. security concerns, which Huawei argues are unfair and unfounded.
-
-
Forecasters use Iron Dome science to handle disasters

Typhoons, floods, droughts, earthquakes, hurricanes, wildfires — the frequency and intensity of natural disasters across the globe are worsening, and these deadly events could continue plaguing the planet as a result of climate change. Iron Dome tech firm uses rocket science to enable utilities to plan for and manage effects of wildfires, storms, hurricanes and earthquakes.
-
-
Using concrete for space colonies
“Be prepared.” This famous mantra isn’t just for the Boy Scouts of America. The need to build durable infrastructure on other planets is coming, and we must be ready. To prepare, researchers have been exploring how cement solidifies in microgravity environments.
-
-
“Clustering” land buyouts could improve flood resiliency after Hurricane Harvey
A new study analyzes flood loss claims and estimates from over 74,000 properties impacted by Hurricane Harvey in Houston’s Harris County. The study finds that a strategic land buyout approach that prioritizes the purchase of land parcels in ‘clusters,’ as well as proximity to existing open space, is just as cost-effective as the traditional, piecemeal approach but with major added ecological and social benefits.
-
-
Resilience and adaptation strategies can address the impacts of climate change
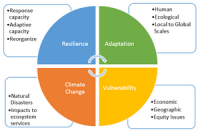
By the end of this century, Chicago could face the kind of searing summer heat that Las Vegas sees now. Phoenix could hit 110 degrees, 60 or more days a year. That’s not wild speculation. It’s the official position of 13 federal agencies on climate change, released late last year with a warning: Local governments need to do more to prepare. Every road they build, every storm drain they put in, will have to hold up under conditions that modern civilization has never seen. How do you plan for that? Researchers at RAND have been working on that problem for a while now.
-
-
Simulating forest and fire dynamics to understand area burn of future wildfires

Climate change and wildfire – it’s a combustible mix with costly devastation and deadly consequences. With a goal of understanding the link between the two variables, researchers over the years have studied the effects of climate and wildfire interactions in the Sierra Nevada mountain range. That research has evolved into learning about the distribution of trees, the extent of forest cover and carbon dynamics.
-
-
Long-distance earthquake detection
In traditional seismology, researchers studying how the earth moves in the moments before, during, and after an earthquake rely on sensors that cost tens of thousands of dollars to make and install underground. Now researchers have figured out a way to overcome these hurdles by turning parts of a 13,000-mile-long testbed of “dark fiber,” unused fiber-optic cable, owned by the DOE Energy Sciences Network (ESnet), into a highly sensitive seismic activity sensor that could potentially augment the performance of earthquake early warning systems currently being developed in the western United States.
-
-
L.A. showcases quake alert system
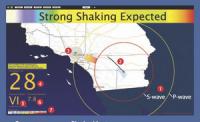
California is earthquake country, and residents of Los Angeles can now get some critical warning, when conditions are right, after a quake has started and seismic waves are heading their way. The long-delayed system, called ShakeAlertLA, is the first of its kind in the United States.
-
-
Marine organisms as detectors of enemy undersea activity
Goliath grouper, black sea bass, and snapping shrimp, along with bioluminescent plankton and other microorganisms, are set to be the unlikely additions to protecting U.S. assets. Researchers are developing new types of sensor systems that detect and record the behaviors of these marine organisms and interpret them to identify, characterize, and report on the presence of manned and unmanned underwater vehicles operating in strategic waters. The incorporation of biological signals will extend the range, lifetime, and performance of undersea surveillance technologies in strategic waters.
-
-
And now, land may be sinking
In the coming decades, cities and towns up and down the eastern seaboard will have to come to terms with the impact of rising sea level due to climate change. A new study, however, is suggesting that rising sea levels may be only part of the picture — because the land along the coast is also sinking.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
