-
Day of commercially available quantum encryption nears
If implemented on a wide scale, quantum key distribution technology could ensure truly secure commerce, banking, communications, and data transfer. Los Alamos National Laboratory signs the largest information technology agreement in the lab’s history which aims to bring quantum encryption to the marketplace after nearly twenty years of development at the national-security science laboratory.
-
-
Sea level rise affecting the infrastructure, psychology of key mid-Atlantic towns
Scientific research and flooding trends have led many to speculate that the Atlantic coast of the United States is already sinking. Mid-Atlantic towns on the coast stretching from Virginia to South Carolina have been experiencing increased flooding and receiving reports and satellite findings from government agencies, leading many of those living on the mid-Atlantic coast to wonder whether their hometowns are doomed.
-
-
Inexpensive, home-made quake early-warning system can be a life saver

UC Berkeley astrophysics professor Josh Bloom has developed an earthquake early-warning (EEW) device meant for the home or office. Resembling a home fire alarm or carbon monoxide sensor, the device was built using a Raspberry Pi single-board computer, an SD card, wired power speaker, and mini Wi-Fi adapter — costing roughly $110 in parts.
-
-
Florida Keys preparing for rising sea levels
The Florida Keys rank third among East Coast communities at risk of “population displacement” due to higher seas which will flood nearby land. Scientists say that if sea levels continue to rise at the current rate, high waters which drowned the Keys during 2005’s Hurricane Wilma could become a normal part of living in Monroe County by 2060. Officials in Monroe County, Florida are putting together a GreenKeys Sustainability Action Plan which will help residents of the Florida Keys maintain a sustainable lifestyle while under threat of sea-level rise due to climate change.
-
-
Sun-powered desalination for villages in India
Around the world, there is more salty groundwater than fresh, drinkable groundwater. For example, 60 percent of India is underlain by salty water — and much of that area is not served by an electric grid that could run conventional reverse-osmosis desalination plants. MIT researchers show that a different desalination technology called electrodialysis, powered by solar panels, could provide enough clean, palatable drinking water to supply the needs of a typical village.
-
-
NYC bridges need better protection against terrorists: Experts

New York City’s bridges have long been the target of terrorist attacks. In 1993, for example, officials discovered a plot by Omar Abdel-Rahman to target the George Washington Bridge and other sites. Recent security breaches on both the Brooklyn Bridge and Manhattan Bridge have heightened concerns as the anniversary of the 9/11 attacks near. Mayor Bill de Blasio has said that his office would soon offer better ways to secure the Brooklyn Bridge.
-
-
No Fukushima radiation found in California’s coastal areas
Following the 11 March 2011 Fukushima disaster, researches wanted to see whether radioactivity could be found in Bay Area precipitation. They collected weeks’ worth of rainwater around UC Berkeley Campus to find out. The results: low levels of a number of different radioactive nuclei produced by the fission of uranium-235 including, cesium-134, cesium-137, and iodine-131. “The levels we saw were detectable, but low and not a health hazard to anyone,” said UC Berkeley’s nuclear engineering professor Eric Norman.
-
-
Japan boasts an earthquake early-warning system, but critics question its value
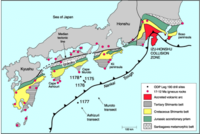
Since 1979, scientists with the Japanese earthquake prediction program have been monitoring a stretch of coastline southwest of Tokyo, watching for ground motion which might signal a pending rupture on the nearby fault zone. If motion is detected, Japanese law requires the prime minister to issue an emergency warning to close schools, secure hospitals, and shut down critical public transportation systems. Critics argue Japan will be unable to predict earthquakes in the same manner meteorologists track approaching typhoons or rain storms, saying that the program offers false hope.
-
-
ShakeAlert’s performance during August Napa tremor should lead to regional deployment: Supporters
Before the magnitude-6 earthquake struck Napa County late August, the Bay Area Rapid Transit received an alert ordering trains to stop, and some 911 operators had a few seconds of warning to brace for an influx of calls from concerned residents. The success of ShakeAlert, California’s earthquake early-warning system currently in the testing phase, has encouraged state lawmakers to push for funding — and deploying — the regional early warning system.
-
-
New Orleans creates economic value out of environmental vulnerability
Following the devastation of Hurricane Katrina in 2005, New Orleans and the state of Louisiana have become so adept at dealing with disaster reconstruction, that their new-found skills are now seen as an economic asset to be shared, for profit, with other states and localities. The area’s new environmental awareness is also a source of economic growth, as analysts now consider “emerging environmental” as one of six key industries in the city and state to focus on development, along with coastal restoration and water management, disaster mitigation and management, hazardous waste disposal, advanced bio fuels and waste water treatment.
-
-
American cities leading on climate change preparedness
Many mid-size American cities are becoming the most innovative responders when it comes to creating infrastructure which is ready for the consequences of climate change on the scale predicted by scientists. With these scientific predictions in mind, and citing deadly and costly “super storms” such as Sandy in 2012 — which killed 130 people, destroyed 650,000 homes, and left 8.5 million people without power —cities have not only looked to rebuild following such natural disasters, but also to create “resiliency” within their infrastructure and communities.
-
-
Experts defend operational earthquake forecasting

After the devastating 2009 L’Aquila earthquake in Italy, critics suggested that operational earthquake forecasting (OEF) is ineffective, distracting, and dangerous. In an editorial published in the Seismological Research Letters, experts defend OEF, arguing the importance of public communication as part of a suite of activities intended to improve public safety and mitigate damage from earthquakes.
-
-
Improving earthquake early warning systems, data collection
Researchers are working on what will be the U.S. first earthquake early warning system available to the public. Once fully implemented, the system will use networks of seismic instrumentation to detect when an earthquake is pending and send alerts via text message or other mass notification systems to people. The researchers are also workingon the Quake-Catcher Network to improve monitoring of earthquake activity around the world. Officials and city planners can use the data provided by Quake-Catcher to help decide where to build critical infrastructure such as power plants, hospitals, and water lines.
-
-
Developing portable water purifying device for the U.S. military

Providing a reliable source of purified drinking water for the U.S. soldiers in the field is the focus of a research grant at the Texas A&M Health Science Center School of Public Health. The research aims to develop a portable water treatment device which uses naturally occurring iron in the environment. Researchers say this iron is easily converted to an environmentally friendly chemical compound called ferrate that can be used as a water treatment disinfectant to purify water.
-
-
Los Angeles thinking of ways to shore up aging infrastructure
Los Angeles, the second-largest city in the nation by population size, has been dealing with crumbling infrastructure for years now. More than 10 percent of the city’s 7,200 miles of water pipes were built ninety years ago. About 40 percent of the region’s 6,500 miles of roads and highways are graded D or F, requiring so much money to fix them that the city is simply concentrating its maintenance efforts on C-graded roads, since they cost less to fix. Additionally, more than 4,000 of the 10,750 miles of sidewalks seriously need repair, according to city officials.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
