-
Debate continues over controversial lawsuit-killing Louisiana oil bill
Governor Bobby Jindal (R-Louisiana) is facing a difficult decision over whether or not to veto a measure which would kill a contentious lawsuit filed by the Southeast Louisiana Flood Protection Authority-East (SLFPA-E) against ninety-seven different oil and gas companies regarding long-term environmental damage claims, including those of the 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion.
-
-
NNSA says security at Y-12 National Security Complex has improved
Retired Air Force lieutenant-general and now National Nuclear Security Administration(NNSA) chief Frank Klotz asserted last week that security at the Y-12 National Security Complexat Oak Ridge National Laboratory(ORNL) has improved significantly since a 28 July 2012 break-inat the plant when three aging peace activists, led by an 82-year old nun, managed to breach the facility’s supposedly impregnable perimeter security systems.
-
-
Recession-related cost measures blamed for U.S. infrastructure lagging development
In an alarming fall, the United States is currently ranked 19th in the quality of its infrastructure, according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Report. Additionally, the American Society for Civil Engineers (ASCE) has given the country a D+ on its annual Infrastructure Report Card, arguing that $3.6 trillion is needed by 2020 for maintenance and upgrades.
-
-
Connecticut preparing for sea level rise, adapting to climate change
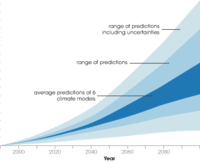
Earlier this year the University of Connecticut announced the creation of the Institute for Community Resiliency and Climate Adaptation. the Institute is designed to increase the resilience and sustainability of vulnerable communities and individuals along Connecticut’s coast and inland waterways as they are affected by the growing impact of climate change on the environment.
-
-
Connecting dead ends increases power grid stability
Climate change mitigation strategies such as the German Energiewende – the post-Fukushima German policy of phasing out nuclear power — require linking vast numbers of new power generation facilities to the grid. As the input from many renewable sources is rather volatile, depending on how much the wind blows or the sun shines, there is a higher risk of local power instabilities and eventually blackouts. Scientists now employed a novel concept from nonlinear systems analysis called basin stability to tackle this challenge.
-
-
Six more bugs found in popular OpenSSL security tool
OpenSSL is a security tool that provides facilities to other computer programs to communicate securely over the public Internet. OpenSSL is also used in some common consumer applications, such as software in Google’s Android smartphones. So when the Heartbleed vulnerability in OpenSSL was discovered and widely publicized in April this year, system administrators had to rush to update their systems to protect against it. Computer system administrators around the world are groaning again as six new security problems have been found in the OpenSSL security library.
-
-
Security guard industry lacks standards, training

Despite playing a more important role in the wake of 9/11, the security guard industry remains plagued by inadequate training and standards in many states, new study of the $7 billion-a-year industry finds. Formal training of the nation’s one million-plus private security officers is widely neglected, a surprising finding when contrasted with other private occupations such as paramedics, childcare workers, and even cosmetologists.
-
-
Nationwide effort launched to weather-harden Canadian cities
The frequency and magnitude of extreme weather events in Canada — from the floods in Southern Alberta and Toronto to the December ice storm in Central and Eastern Canada — are increasing, causing billions of dollars in damage to infrastructure, businesses and homeowners. Intact Financial Corporation and the University of Waterloo announced a national initiative involving the implementation of twenty climate change adaptation projects designed to reduce the physical, financial, and social impacts of extreme weather events in Canada.
-
-
It is almost certain there are aliens out there, but can we find the money to find them?

UC Berkley Professor Dan Werthimer last month updated members of the House Subcommittee on Science, Space and Technology on the search for extraterrestrial life, and provided a generally upbeat evaluation: ET microbial life likely is ubiquitous throughout the galaxy, and new technologies have improved the chances of detecting signals from advanced alien civilizations.
-
-
Adm. Michael Rogers: Businesses must “own” cybersecurity threats

Cybersecurity threats are a vital issue for the nation, and like the Defense Department, businesses must own the problem to successfully carry out their missions, DOD’s top cybersecurity expert told a forum of businesspeople.
-
-
Better building design, maintenance would cut building sector’s emissions by around 80%
The construction industry, which uses half of the 1.5 billion tons of steel produced each year, could slash its carbon emissions by as much as 50 percent by optimizing the design of new buildings, which currently use double the amount of steel and concrete required by safety codes. If buildings are also maintained for their full design life and not replaced early, the sector’s emissions could in total be cut by around 80 percent.
-
-
DARPA’s Cyber Grand Challenge aims to see fully automated network security systems developed

There is an increasingly serious cybersecurity problem: the inadequacy of current network security systems, which require expert programmers to identify and repair system weaknesses — typically after attackers have taken advantage of those weaknesses to steal data or disrupt processes. Such disruptions pose greater risks than ever as more and more devices, including vehicles and homes, get networked in what has become known as “the Internet of things.” DARPA is addressing this problem, with teams from around the world starting a two-year track toward the world’s first tournament of fully automated network security systems. Computer security experts from academia, industry, and the larger security community have organized themselves into more than thirty teams to compete in DARPA’s Cyber Grand Challenge — first-of-its-kind tournament designed to speed the development of automated security systems able to defend against cyberattacks as fast as they are launched.
-
-
Roots of Trust research focuses on protecting cyber physical systems
“Roots of Trust” refers to a set of security functions in a device or system, which are implicitly trusted by the device’s operating system and applications, and which constitute the foundation for security. The Cyber Security Research Alliance (CSRA) the other day said it will prioritize research in Roots of Trust for cyber physical systems (CPS), to help address growing cyber security threats to public and private critical infrastructure.
-
-
New material captures CO2 at natural gas wellheads
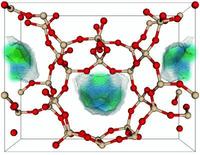
Natural gas is the cleanest fossil fuel. Development of cost-effective means to separate carbon dioxide during the production process will improve this advantage over other fossil fuels and enable the economic production of gas resources with higher carbon dioxide content that would be too costly to recover using current carbon capture technologies. Rice University chemists invented a porous material which sequesters carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, at ambient temperature with pressure provided by the wellhead, and lets it go once the pressure is released. The material shows promise to replace more costly and energy-intensive processes.
-
-
Federal oversight of ammonium nitrate exceedingly weak
A new Government Accountability Office(GAO) report found that the federal government has no way of fully knowing which chemical facilities stockammonium nitrate, a widely used fertilizer which was the cause of the explosion last year at a West, Texas fertilizer plan, which resulted in the death of fourteen people – and which was used by Timothy McVeigh in Oklahoma City twenty years ago. Poor data sharing with states, outdated federal policies, and numerous industry exemptions have contributed to a weak federal oversight. Without improved monitoring, regulators “will not know the extent to which dangerous conditions at some facilities may continue to exist,’’ the GAO report said.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
