-
Washington, D.C. area leads nation in cybersecurity jobs

The Washington, D.C metropolitan area had more than 23,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013, making the region the leading destination for cybersecurity jobs, followed by the New York metro area with 15,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013. On a state-by state basis, Virginia ranks second and Maryland ranks sixth, with Virginia reporting 25.1 cybersecurity job postings per 10,000 residents and Maryland posting 18.1 jobs per 10,000 residents.
-
-
Budget proposal cuts funds for nuclear nonproliferation programs
The White House’s fiscal 2015 budget proposal includes more than $220 million in cuts for nuclear security initiatives such as the International Material Protection and Cooperationprogram, which aims to secure and eliminate vulnerable nuclear weapons and materials, and the Global Threat Reduction Initiative, which supports the Energy Department’s efforts to prevent terrorists from acquiring nuclear and radiological materials that could be used in weapons of mass destruction. The administration says that 54 percent of the reduction in the administration’s nonproliferation budget request can be accounted for by the decision to halt the South Carolina Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility(MOX), which would have convert weapons-grade plutonium into nuclear reactor fuel, because the project proved to be too costly.
-
-
Methane from Deepwater Horizon oil spill has entered food web

When millions of gallons of oil spilled into the Gulf of Mexico four years ago, so did large volumes of methane, or natural gas. Now, researchers have confirmed that methane-derived carbon has entered the Gulf’s food web through tiny organic particles floating in the Gulf. The presence of methane is not cause for alarm though, the researchers said. Overall, it has a benign impact on the food that makes it from the sea to people’s dinner tables.
-
-
Libyan PM escapes country after assembly ousts him over oil tanker fiasco
Libya’s General National Congress has approved a no-confidence motion against Prime Minister Ali Zeidan and designated the defense minister as acting prime minister. Zeidan left Libya after the vote, in all likelihood for Italy. The no-confidence vote came after a North Korean-flagged tanker named Morning Glory managed to sail away from the port of al Sidra, carrying 234,000 barrels of crude oil from rebel-held oil fields. Last summer, armed militias in east Libya took over most of the country’s oil fields – and also three ports, with partial control of a fourth — bringing oil exports, which had amounted to 1.6 million barrels a day, to a halt. U.S. describes oil sale by the militias as “theft” from the Libyan people.
-
-
U.S. infrastructure vulnerable to “cascading system failures” caused by weather disasters
Two U.S. government reports released last Thursday warn that U.S. infrastructure is vulnerable to the effects of climate change. One report focuses on energy, the second on infrastructure more generally. The infrastructure-focused report is the first attempt to review climate implications across all sectors and regions. The report analyzes how damage to one infrastructure sector can impact other infrastructure sectors, rather than isolating specific types of infrastructure. The authors warn that climate-fueled weather disasters could cause “cascading system failures” unless changes are adopted to minimize such effects.
-
-
East Europe’s natural gas networks vulnerable during conflicts and crises
Gas networks in Eastern European countries, such as Ukraine and Belarus, are less resilient than the U.K. gas networks during conflicts and crises, according to new research. The authors suggest that a decentralized approach to managing congestion on gas pipeline networks could be crucial for energy security during geopolitical conflicts or natural disasters, for example.
-
-
Radiation from Fukushima to reach West Coast in April
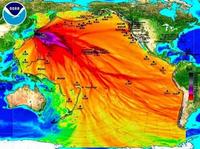
On the third anniversary of the Fukushima nuclear plant incident, scientists are reporting that low levels of radiation from the Fukushima plant will reach ocean waters along the U.S. West Coast by April 2014. The scientists say that the radiation will be at levels too low to harm humans, but they call for more monitoring, including at the federal level.
-
-
Innovative nuclear radiation detector reaches the market

A handheld radiation camera developed by University of Michigan engineering researchers offers nuclear plant operators a faster way to find potentially dangerous hot spots and leaky fuel rods. The new Polaris-H detector lays a gamma-ray map over an image of a room, pinpointing radiation sources with unprecedented precision. At least four U.S. nuclear power plants are using versions of the camera, which is now available commercially through the U-M spinoff company H3D.
-
-
Iona College to Launch BS, BA, MS concentrations in cybersecurity
Iona College announced the launch in fall 2014 of undergraduate and graduate programs in computer science with a concentration in cyber security. The concentration will be offered for the Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Arts, and the Master of Science degrees. The programs will provide students with fundamental cyber security skills, theoretical as well as hands-on experience. Students are exposed to new research ideas across many cyber security areas including software security, Web application security, mobile security, networking security, database security, and cryptography.
-
-
Small biomass power plants could help rural economies, stabilize national power grid

As energy costs rise, more Americans are turning to bioenergy to provide power to their homes and workplaces. Bioenergy is renewable energy made from organic sources, such as biomass. Technology has advanced enough that biomass power plants small enough to fit on a farm can be built at relatively low costs. Researchers have found that creating a bioenergy grid with these small plants could benefit people in rural areas of the country as well as provide relief to an overworked national power grid.
-
-
Underground recovery process at WIPP begins
Nuclear Waste Partnership (NWP), the management and operations contractor at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), said it has initiated the first phase of an underground recovery process which will lead to the resumption of nuclear waste disposal operations at WIPP. Initial results show no airborne radioactive contamination in the underground shafts.
-
-
Determining long-term effects of West Virginia chemical spill
A chemical mixture called crude 4-methylcyclohexane methanol (MCHM) is used during the separation and cleaning of coal products. More than 10,000 gallons of the chemical leaked from a storage tank near Charleston, West Virginia, and entered the river upstream of a water-treatment plant on 9 January. The drinking water of more than 300,000 West Virginians was contaminated. Water restrictions began to be lifted on 13 January, but residents are still detecting the telltale odors of MCHM. Virginia Tech faculty engineers and students are unravelling fundamental chemical and health properties of MCHM.
-
-
“Encouraged” bacteria cleaning up more effectively after oil spills
Bioremediation is nature’s way of cleaning up. Plants, bacterial decomposers, or enzymes are used to remove contaminants and restore the balance of nature in the wake of pollution incidents. What is surprising is that given the right kind of encouragement, bacteria can be even more effective. Researchers in Norway have achieved surprising results by exploiting nature’s own ability to clean up after oil spills.
-
-
New technique allows better monitoring of water quality
Researchers have developed a new technique that uses existing technology to allow researchers and natural resource managers to collect significantly more information on water quality to better inform policy decisions. In addition to its utility for natural resource managers, the technique will also allow researchers to develop more sophisticated models that address water quality questions.
-
-
FERC orders development of physical security standards for transmission grid
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) on Friday directed the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) to develop reliability standards requiring owners and operators of the Bulk-Power System to address risks due to physical security threats and vulnerabilities.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
