-
Feds, Calif. disagree on seismic safety of U.S. tallest dam

At 742 feet, Oroville Dam in Oroville, California is the tallest dam in the United States. It is 45-year old, and federal inspectors say it needs a comprehensive earthquake safety assessment. The California Department of Water Resources (DWR) insists that the dam, which holds 3.5 million acre-feet of water, is safe, and that such an assessment would be an “unjustified expense.” David Gutierrez, chief of California Division of Safety of Dams (DSD), says his agency will decide in January 2014 whether earthquake assessments will be made, but notes: “Oroville is not one that keeps me up at night from a seismic stability standpoint.”
-
-
Virtual wall to build invisible barrier for oil spills
The outer shell of a droplet of oil on a surface has a thin skin which allows it to hold its shape like a small dome; this shell is referred to as the liquid’s surface tension. Now, researchers have developed a technique to form a virtual wall for oily liquids that will help confine them to a certain area, aiding researchers who are studying these complex molecules. This development will have future implications in the guided delivery of oil and effective blockage of oil spreading.
-
-
Humans threaten wetlands' ability to overcome sea level rise
Left to themselves, coastal wetlands can resist rapid sea level rise. The reason: an intricate system of feedbacks which make wetlands remarkably good at building up soils to outpace sea level rise. Humans, however, could be sabotaging some of wetlands’ best defenses, according to results of a new study. The study examines two questions: when do wetlands reach their limit, and how are humans lowering that point?
-
-
Seeds from Moringa oleifera trees better then chemicals for purifying water
Clean water is essential for good health. In many countries it is still difficult to obtain clean water. Even developed countries can benefit from a process that treats waste water without addition of further synthetic chemicals. Seeds from Moringa oleifera trees can be used to purify water. Researchers have discovered that seed material can offer a more efficient purification process than conventional synthetic materials in use today.
-
-
Earthquake early warning? There’s an app for that
Researchers from the University of California have unveiled a smartphone app designed to provide users an early warning of approaching earthquakes. Based on the proximity of the user to the earthquake’s epicenter, the app will provide alerts of between a few seconds and one minute before a tremor hits.
-
-
Better earthquake early-warning system
Geophysicists have developed a new way of calculating the magnitude of an imminent earthquake by making better use of measurements of the compression waves produced early in the event. They say that the technique could be used to create a better early-warning system for earthquakes that could be used worldwide.
-
-
Y-12 security breach update: Old nun awaits sentencing while costs of new Y-12 facility not to be released until 2015
On 28 July 2012, three senior citizens, led by an 83-year old nun, easily breached the supposedly impregnable security systems protecting the Y-12 National Security Complex at Oak Ridge, Tennessee. The three peace activists wondered the grounds of the maximum security facility for a while before being noticed by security personnel. While the three aging protesters are awaiting sentencing, the two companies — Bechtel Corporation and Babcock and Wilcox – which were responsible for designing and implementing security at Y-12, have been named as the primary construction contractors for planning and design of the new uranium processing facility (UPF) to be built at Y-12.
-
-
Early warning system to detect abrupt climate change impacts
Climate change has increased concern over possible large and rapid changes in the physical climate system, which includes the Earth’s atmosphere, land surfaces, and oceans. Some of these changes could occur within a few decades or even years, leaving little time for society and ecosystems to adapt. A new report from the National Research Council states that even steady, gradual change in the physical climate system can have abrupt impacts elsewhere — in human infrastructure and ecosystems for example — if critical thresholds are crossed. The report calls for the development of an early warning system that could help society better anticipate sudden changes and emerging impacts.
-
-
Key to protecting Earth from asteroids: time

Scientists say that humanity can address the threats from asteroids of any size if given enough time and notice of the asteroid’s existence and trajectory. Even an asteroid the size of the 10-kilometer-wide space rock which scientists hold responsible for the extinction of dinosaurs sixty-five million years ago, can be destroyed, although it would take hitting the asteroid with multiple spacecrafts over a period of several decades.
-
-
Defending against electromagnetic-pulse attacks

We are all familiar with the power of electromagnetic attacks from the movies: in “Ocean’s Eleven,” George Clooney’s gang disables Las Vegas’ power grid, and Keanu Reeves’ henchmen hold off the enemy robot fighters from their spaceship in the “Matrix Trilogy.” The heroes in the films succeed by sending out a very strong electromagnetic pulse, which changes the voltage in the vicinity so that regulators, switches, and circuit boards in electronic equipment go crazy. Researchers are now trying to figure out how such attacks can be detected. They have developed a measurement instrument for this purpose that is capable of determining the strength, frequency, and direction of electromagnetic attacks.
-
-
Digital privacy services enjoying a surge in demand
Digital privacy services such as encrypted e-mail, secure instant messaging, and services that provide hard-to-track IP addresses are enjoying a surge in demand as individuals and businesses seek to protect information from spies and hackers in the wake of the National Security Agency’s (NSA) surveillance program revelations. These services promise security, but may also slow down computer performance. Moreover, they are not likely to deter those who are determined to hack into a particular computer network.
-
-
Deflecting asteroids to avoid Armageddon

It sounds like the script for a Hollywood film: a giant meteorite from outer space heading straight for the Earth and threatening the destruction of mankind. Yet such a scenario does represent a real threat to our planet, as researchers reckon that we can expect an asteroid to collide with Earth every few hundred years. In real life, though, nobody wants to rely on a rescue plan hastily improvised at the last minute. Scientists with the European-funded research project NEOShield are working to develop concepts designed to help avert these impacts and to alter asteroids’ orbits as they race toward Earth.
-
-
Indian Ocean phenomenon helps in predicting extreme weather
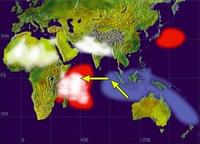
The Indian Ocean Dipole is the difference in sea-surface temperatures between the western and eastern part of the Indian Ocean. A better understanding of the relationship between the Indian Ocean Dipole and extreme weather events will enable farmers, industry, communities, and governments better to anticipate and prepare for droughts and increased bushfire risk, up to six months in advance of the event.
-
-
Developing cyber resilience to meet increasing cyberthreats
Managing resilience for cyber systems requires metrics that reflect the relationships among system components in physical, information, cognitive, and social domains. In a paper, researchers describe a framework for understanding the concept of cyber resilience, and lay out a systematic method by which to generate resilience metrics for cyber systems.
-
-
Modeling earthquakes and explosives reactions
Researchers are developing mathematical models that can help in reducing rock fracturing and soil liquefaction caused by natural or man-made disasters. The outcomes of the research could improve safety levels in the mining and petroleum industries, and play a critical role in the ability of civil infrastructure to withstand disasters such as earthquakes and explosions.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
