-
Hundreds of cyber specialists to compete at NetWars Tournament of Champions

SANS Institute’s NetWars Tournament of Champions will be held in Washington, D.C., in mid-December. Hundreds of the brightest security professionals from around the world will compete with each other in order to determine who has the best skills in tackling cyber security challenges.
-
-
U.S. financial industry pushes Congress to pass cybersecurity bill
Three financial-industry trade groups have issued a letter to senior members of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligenceto re-energize a campaign for moving forward with cybersecurity legislation. The trade groups, representing the U.S. largest financial institutions, said their ability to prevent cyberattacks will be hindered unless Congress acts.
-
-
Using biological organisms to convert natural gas to liquid transportation fuel

Researchers will use their expertise in protein expression, enzyme engineering, and high-throughput assays as part of a multiproject, $34 million effort by the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) aimed at developing advanced biocatalyst technologies that can convert natural gas to liquid fuel for transportation.
-
-
Inkblots bolster security of online passwords
Computer scientists have developed a new password system that incorporates inkblots to provide an extra measure of protection when, as so often occurs, lists of passwords get stolen from websites. This new type of password, dubbed a GOTCHA (Generating panOptic Turing Tests to Tell Computers and Humans Apart), could foil growing problem of automated brute force attacks, and would be suitable for protecting high-value accounts, such as bank accounts, medical records, and other sensitive information.
-
-
Coordinating responses to cloud, infrastructure vulnerabilities
Cybercrime presents a significant threat to individual privacy, commerce, and national security. In order to tackle this cross-border threat properly, agents involved in managing and monitoring cyber-risk-critical assets need to be able to cooperate and co-ordinate their prevention strategies. Platforms enabling coordinated cross-border responses already work well for handling malicious activity on the traditional Internet. The advent of cloud computing, however, has created a new set of challenges for security professionals in securing the platforms that deliver the cloud.
-
-
New drone to monitor radiation following nuclear disasters

Researchers have unveiled a large semi-autonomous drone called the ARM system which could be used to provide visual and thermal monitoring of radiation after a release of nuclear material. The system was developed in response to requirements for radiation monitoring in event of the release of radioactive materials.
-
-
DOE to resume transient testing of nuclear fuels and materials

Transient testing of nuclear fuel involves placing fuel or material into the core of a nuclear reactor and subjecting it to short bursts of intense, high-power radiation in order to analyze the effects of the radiation. The Idaho National Laboratory (INL) Transient Reactor Test Facility began operating on 23 February 1959 and was a principal reactor safety testing facility in the United States for thirty-five years. The U.S. Department of Energy invites the public to read and comment on a draft environmental assessment it has prepared for a proposal to resume transient testing of nuclear fuels and materials.
-
-
U.S. oil production exceeds imports for first time in two decades
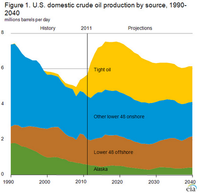
The United States is well on its way to energy independence, with the Obama administration announcing Wednesday that domestic oil production surpassed imports for the first time in nearly two decades. A report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) offers proof that the United States has managed both to increase domestic oil and gas drilling and reduce the nation’s carbon emissions, which have dropped to a 20-year low. Since 2008, U.S. crude oil output has increased 50 percent, while imports have fallen about 20 percent.
-
-
Drive-by charging: Advancing wireless power transfer for vehicles
Researchers have developed new technology and techniques for transmitting power wirelessly from a stationary source to a mobile receiver — moving engineers closer to their goal of creating highway “stations” that can recharge electric vehicles wirelessly as the vehicles drive by.
-
-
The Philippines is victim of geography, poor infrastructure, poverty
Owing to its location and geography, the Philippines is one of the most natural disaster-prone countries in the world. On average the country experiences nine major typhoons and 900 earthquakes annually, and it has twenty-five active volcanoes. Poor infrastructure and pervasive poverty exacerbate the impact of disasters, making them even more deadly and destructive. “In a cruel cycle, poverty and underdevelopment make disasters worse, and disasters make poverty and underdevelopment worse,” one observer notes.
-
-
Japan hopes off-shore wind turbines can replace shut-down nukes

Japan inaugurated a floating offshore wind turbine on Monday, symbolizing the country’s effort to reduce its dependency on nuclear energy and fossil fuels and shift to renewable energy sources. The floating platform is anchored thirteen miles offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, which has been out of commission since the reactor’s meltdown disasterof March 2011. The platform is anchored to the seabed 400 feet below surface. It is the first project of its kind in Japan, and it aims to show that the country can exploit the country’s powerful offshore winds to create a sustainable energy source.
-
-
National grid in mock power emergency drill today and tomorrow
North American power companies will participate in a mock power emergency scenario today and tomorrow (13-14 November) to test their ability to respond to physical or cyberattacks that may lead to widespread power outages and long term blackouts. The exercise, known as GridEx II, is the second emergency response exercise conducted by North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) intended to task North American electric utility companies with reviewing their security and crisis response strategies.
-
-
Climate scientists say renewables are not enough
Some of the world’s top climatologists have declared their support for nuclear energy as a complementary energy source, alongside wind and solar as energy, which would cut fossil fuel pollution and reduce the growth of global warming. The scientists say that opposing fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources offer but a limited solution.
-
-
U.S. mix of fuels used for power generation is changing

The mix of fuels used to generate the electricity in homes, factories, and businesses across the United States has changed in the past few years as coal, still the largest single fuel used for electricity, has lost some of its share of the generation market to natural gas and non-hydroelectric renewables.
-
-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
