-
Where should U.S. radioactive waste be buried?
In the United States, about 70,000 metric tons of spent commercial nuclear fuel are located at more than seventy sites in thirty-five states. Shales and other clay-rich (argillaceous) rocks have never been seriously considered for holding America’s spent nuclear fuel, but it is different overseas. France, Switzerland, and Belgium are planning to put waste in tunnels mined out of shale formations, and Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom are evaluating the idea.
-
-
Nuclear fuel withstands accident conditions’ high-temperature

A safer and more efficient nuclear fuel is on the horizon. A team of researchers have reached a new milestone with tristructural-isotropic (TRISO) fuel, showing that this fourth-generation reactor fuel might be even more robust than previously thought. Byproducts of the fission process have the potential to escape the fuel, especially at very high temperatures. Controlled, high-temperature testing of irradiated TRISO) fuel demonstrated that fission product release remains relatively low at high temperatures postulated to occur in accidents and beyond.
-
-
Sharp increase in radioactive water leaks at Fukushima
Tokyo Electric Power(TEPCO) has reported a rise in groundwater radiation levels, saying a tank at the firm’s Fukushima plant leaked 300 metric tons of toxic water in August 2013. Water samples from wells, taken in mid-October, show a record-high concentration of beta-ray emitting substances, and a sharp increase in the presence of radioactive tritium. Japanese prime ministerShinzo Abe, in a tacit admission that Japan cannot effectively handle the continuing radiation leaks from the stricken plant, said Japan would be interested in receiving foreign help to contain widening radioactive water leaks at Fukushima.
-
-
New method to help coastal communities adapt to sea-level rise
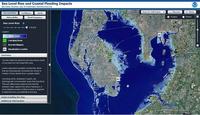
Future sea-level rise seems inevitable, although the rates and geographical patterns of change remain uncertain. Given the large and growing populations and economic activity in coastal zones, as well as the importance of coastal ecosystems, the potential impacts of sea-level change are far-reaching. Current methods to assess the potential impact of sea-level rise have varied significantly and hindered the development of useful scenarios and, in turn, suitable adaption policies and planning.
-
-
Preventing a Bhopal-like catastrophe in New Jersey
New Jersey is home to ninety facilities which produce and store large quantities of highly toxic chemicals. A superstorm or terrorist attack could doom millions of people around southern New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania to a Bhopal, 1984-like fate if either of these facilities and their storage tanks were affected.Typically, in the aftermath of major disasters, a blue ribbon panel is created to review preventative measures that could have been taken before the disaster. Security experts say that there is no need to wait for a post-disaster blue ribbon panel investigation to know what sensible safety measures should be implemented now.
-
-
Burping for power: Tapping cow burps for natural gas
Scientists in Argentina have developed a method to transform the gas created by cows’ digestive systems into fuel. The technique channels the digestive gases from bovine stomach cavities through a tube and into a tank, where the gases, called eruptos (burps) in Spanish, are processed to separate methane from other gases such as carbon dioxide.
-
-
NIST releases Preliminary Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on Tuesday released its Preliminary Cybersecurity Framework to help critical infrastructure owners and operators reduce cybersecurity risks in industries such as power generation, transportation, and telecommunications. In the coming days, NIST will open a 45-day public comment period on the Preliminary Framework and plans to release the official framework in February 2014.
-
-
$32 million NSF grants for improving prediction of, response to natural disasters
With Sandy’s one-year anniversary – 29 October – next week, how do scientists better predict and respond to natural hazards such as hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, and wildfires? To find answers, the National Science Foundation (NSF) recently awarded twelve new research grants totaling $32 million. The awards will advance understanding of natural hazards and of technological hazards linked with natural phenomena, as scientists study ways of predicting and responding to hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, earthquakes, tsunamis, wildfires.
-
-
More than 500 million people could face increasing water scarcity
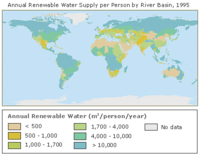
Both freshwater availability for many millions of people and the stability of ecosystems such as the Siberian tundra or Indian grasslands are put at risk by climate change. Even if global warming is limited to 2 degrees above pre-industrial levels, 500 million people could be subject to increased water scarcity.
-
-
Cyber Grand Challenge for automated network security-correcting systems
What if computers had a “check engine” light that could indicate new, novel security problems? What if computers could go one step further and heal security problems before they happen? To find out, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) intends to hold the Cyber Grand Challenge (CGC) — the first-ever tournament for fully automatic network defense systems. The Challenge will see teams creating automated systems that would compete against each other to evaluate software, test for vulnerabilities, generate security patches, and apply them to protected computers on a network. The winning team in the CGC finals would receive a cash prize of $2 million, with second place earning $1 million and third place taking home $750,000.
-
-
Quake-triggered landslides a significant hazard for Seattle

Seattle is prone to strong shaking as it sits atop the Seattle Basin — a deep sedimentary basin that amplifies ground motion and generates strong seismic waves that tend to increase the duration of the shaking. A new study suggests the next big quake on the Seattle fault may cause devastating damage from landslides, greater than previously thought and beyond the areas currently defined as prone to landslides.
-
-
U.S. first nuke in thirty years mired in costly legal wrangling
The U.S. first nuclear construction project in thirty years is the center of a $900 million lawsuit pitting Westinghouse Electric Co. against Georgia Power. The $14 billion project is about twenty months behind schedule and $900 million over budget, and each side blames the other for the delays and cost overruns.
-
-
The only effective asteroid defense: early detection – and evacuation of impact area

For the threat of meteor strikes large or small, early detection is key, and evacuation may be the only defense needed within the next 1,000 years, according to an asteroid impact expert. He says that the best investment in asteroid defense is not in weapons to deflect them, but in telescopes and surveys to find them.
-
-
Irish heritage groups sues U.K. over nuclear power plant
An Taisce, an Irish charity group promoting the preservation of Ireland’s heritage, is taking the British government to the High Court in London in December seeking a judicial review of the legality of British energy minister Ed Davey’s decision to approve the construction of a nuclear power plant just 150 miles from the Irish coast without consulting the Irish public.
-
-
Weatherizing U.S. homes to uniform standard to save $33 billion a year
The U.S. residential sector — 113 million homes — uses about 23 percent of total U.S. source energy annually (source energy includes site energy, the energy consumed by buildings for heating and electricity, as well as the raw energy required to transmit, deliver and produce it). A new study finds that upgrading buildings’ airtightness to a uniform level could achieve as much as $33 billion in annual energy savings.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
By Corinne Dionisio
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
By Doug Irving
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
By Nancy W. Stauffer
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
By Julie Bobyock and Christina Procopiou
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
By Graeme Beardsmore and Rachel Webster, University of Melbourne
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
