-
Wildfires in west, southwest forcing hundreds from their homes
The arrival of summer has typically been accompanied by an increase in the number and intensity of wild fires in the U.S. southwest, and this year is no exception.
-
-
Health impact of Chernobyl accident overestimated: study

The impact of the Chernobyl nuclear accident has been seriously overestimated, while unfounded statements presented as scientific facts have been used to strangle the nuclear industry, according to Russian researchers.
-
-
Current methods of reducing arsenic contamination of water are not effective
Arsenic is now recognized to be one of the world’s greatest environmental hazards, threatening the lives of several hundred million people. Naturally occurring arsenic leaches into water from surrounding rocks and once in the water supply it is both toxic and carcinogenic to anyone drinking it. New research finds that most of the current technologies used around the world to reduce arsenic contamination are ineffective.
-
-
Lawmaker offers a way to finance U.S. infrastructure investment -- with no taxpayers’ money

Representative John Delaney (D-Maryland) says has an answer to the nation’s infrastructure problems, and that it will not cost taxpayers a dime. The money will be raised through the sale of special bonds, not guaranteed by the government, to companies that earn profits outside the United States.
-
-
House panel cuts DHS chemical plant monitoring program’s budget
Budget authors in the House proposed cutting almost $9 million from what DHS had requested for high-risk chemical tracking in the 2014 fiscal year. The House Appropriations Committee, indicating its lack of confidence in DHS’s oversight of fertilizer plants like Texas’s West Fertilizer Company, which exploded earlier this year, also withheld $20 million from the program until DHS responded in detail to questions the committee sent the department.
-
-
California Democratic lawmakers want a go-slow approach to fracking
California may be on the verge of an oil rush. It is estimated that hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, at the Monterey Shale formation may tap reserves of fifteen billion barrels of oil. Democratic lawmakers do not see it that way, and have proposed numerous anti-fracking bills aiming to control the use of the controversial technology. Ten bills have been tabled so far, and more are on the way.
-
-
Mitigating fires in the wildland-urban interface

More than forty-six million residential structures in about 70,000 communities in the United States are located in the so-called wildland-urban interface (WUI). On average, WUI fires destroy 3,000 buildings annually. They accounted for six of the ten most costly fires in the United States over the last 100 years. Five of these fires occurred in California, where the incidence of wildfires currently is up 47 percent this year over last.
-
-
Relying on natural gas-fired generators during electric grid failures
Natural gas-fired electricity generators can provide energy security at domestic military installations in the event of electric grid failures. A study found there is minimal risk of interrupted deliveries for a moderate outage (two weeks to three months).
-
-
Improving “crop per drop” boosts global food security, water sustainability
New study shows increasing crop water productivity could feed an additional 110 million people while meeting the domestic water demands of nearly 1.4 billion.
-
-
Chinese government hackers steal designs of advanced U.S. weapons systems
The Chinese government has been conducting a broad, sustained, and disciplined campaign of cyberattacks against U.S. government agencies, critical infrastructure, private companies, and news organizations. The public version of a study prepared for the Pentagon by the Defense Science Board now says that Chinese government hackers have also been able to penetrate the computer networks of all the major U.S. defense contractors, stealing the designs and specifications of the most advanced weapon system in the U.S. arsenal, and gaining insights into broad technologies on which U.S. military advances are based.
-
-
U.S. infrastructure drops in world infrastructure ranking

The U.S. infrastructure has slipped badly in the world’s infrastructure ranking, both in absolute and relative terms, according to the Global Competitiveness Report for 2012-13, published earlier this month by the World Economic Forum.
-
-
Wind energy in cold-climate countries showing significant potential
Wind energy capacity is growing rapidly in the cold climates of the world. According to the latest forecasts, between 45 and 50 gigawatts of wind energy will be built in cold climates by 2017, which would mean an increase of as much as 72 per cent since the end of 2012 and investments amounting to approximately 75 billion euro.
-
-
A majority on Earth will soon face severe, self-inflicted water shortage: scientists

A conference of 500 leading water scientists from around the world, held last week in Bonn, issued a stark warning that, without major reforms, “in the short span of one or two generations, the majority of the nine billion people on Earth will be living under the handicap of severe pressure on fresh water, an absolutely essential natural resource for which there is no substitute. This handicap will be self-inflicted and is, we believe, entirely avoidable.”
-
-
New filtration material to make petroleum refining cheaper, more efficient
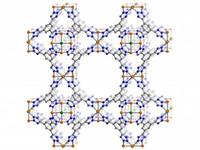
A newly synthesized material might provide a dramatically improved method for separating the highest-octane components of gasoline. The material is a metal-organic framework, or MOF, which can be imagined as a sponge with microscopic holes.
-
-
Report: U.S. companies should consider counter-hacking Chinese hackers
A group studying how the United States should respond to the sustained campaign of cyberattacks conducted by Chinese government hackers against U.S. companies, said the United States should seriously consider a campaign of retaliatory cyberattacks against the hackers.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
