-
Ash from olive residue biomass leads to more effective, cheaper concrete
Researchers have produced self-compacting concrete with ash from boiler combustion of olive pruning residue pellets. The plasticity and cohesion of this type of concrete mean no compaction is needed when used in construction and, moreover, it has other advantages with respect to conventional concrete.
-
-
Helping bridges withstand natural disaster
Structural control systems have the potential to help our civil infrastructure, such as bridges, roads, and buildings, withstand natural disasters such as earthquakes or storms. Traditional control systems based on sensors connected by wired networks, however, are costly, labor-intensive, and tend to break during disasters, when they are needed most.Wireless networks that are easier, cheaper, and more resilient to structural damage.
-
-
Software to help plan the smart grid
Researchers have developed a new software tool called the Energy Zones (EZ) Mapping Tool that will help the thirty-nine states which make up the Eastern Interconnection States’ Planning Council, or EISPC identify geographic areas suitable for the development of clean energy resources, which are renewables, natural gas, coal carbon sequestration, and nuclear. Certain forms of energy storage are also included.
-
-
Draft of the 2013 U.S. National Climate Assessment is out
As mandated by the U.S. Global Change Research Act (GCRA), the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) is currently producing a National Climate Assessment (NCA). The NCA is a report to inform the president, the Congress, and the American people about the current state of scientific knowledge regarding climate change effects on U.S. regions and key sectors, now and in the coming decades. The National Research Council (NRC) says that as the United States continues to engage with the threats, opportunities, and surprises of climate change in its many manifestations, the 2013 NCA should prove to be a valuable resource.
-
-
DHS chemical plant security program hobbled by problems, poor oversight
A DHS program responsible for the security of chemical facilities, such as the West Fertilizer Company plant in Texas, has been ineffective owing to a number of issues, leading federal investigators to wonder “whether it can achieve its mission, given the challenges the program continues to face.”
-
-
U.S., South Korea delay nuclear fuel deal
The president of South Korea, Park Geun-Hye, has been campaigning to get the United States to lift the ban on South Korea from enriching uranium and processing spent nuclear fuel. The ban was part of a 1972 treaty, which was set to expire next March. A deal appeared to be on the way at some point this year, but officials from both countries said the deadline would be extended to 2016. What did not help the negotiations were statements by some South Korean officials that the country should build its own nuclear weapons reather than rely on U.S. nuclear umbrella.
-
-
Former lawmakers to hold hearings on aliens
Six former member of Congress have agreed to hold a congressional style hearing on the existence of aliens in space. “It’s a huge universe out there,” former Representative Roscoe Bartlett (D-Maryland) said. “You have to be kind of presumptuous and arrogant to assume we’re the only intelligent life in the universe.”
-
-
EPA slams State Department’s Keystone XL pipeline review
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Monday criticized the State Department’s environmental impact review of the Keystone XL pipeline, saying there was not enough evidence to back up key conclusions in the review on emissions, safety, and alternative routes. The EPA’s comments could have a negative effect on the approval of the project, but if the project is approved, the comments could serve as supporting evidence in any ligation against the pipeline.
-
-
McCaul to draft cybersecurity bill
House Homeland Security chairman Michael McCaul (R-Texas) said he was drafting his own cybersecurity bill, which will define the role of DHS in sharing information with private companies about cyber threats. McCaul hopes to agree on a compromise with the White House, which threatened to veto the bill.
-
-
River beds keep moving, increasing flood risk
A detailed study of shifting river beds could hold the key to more accurate flood prevention. It is commonly believed that the elevation of river beds is more or less constant, so any change in flood risk is due to changes in hydrology. Researchers find, however, that there is a significant trends in the elevation of river beds, an indication that river channels are filling in with sediment or that sediment is being eroded through time.
-
-
Ocean thermal energy conversion power plant to be built off southern China’s coast
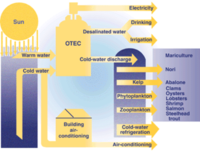
Lockheed Martin has announced that it is working with Chinese company Reignwood Group to develop an Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) pilot power plant off the coast of southern China. The prototype plant will be the first project in the multi-billion dollar clean energy agreement between the two companies. OTEC takes the natural temperature difference found in the ocean in tropical regions and uses it to create power. This technology is well-suited to island and coastal communities.
-
-
U.S., China in high-level military talks
Representatives of China and the United States met on Monday for the highest-level military talks between the two counties in almost two years. In the meeting, a senior Chinese general pledged to work with the United States on cybersecurity because the effects of a major cyber attack “may be as serious as a nuclear bomb.”
-
-
Monitoring elusive collisions in space
Many collisions occur between asteroids and other objects in our solar system, but scientists are not always able to detect or track these impacts from Earth. The “rogue debris” created by such collisions can sometimes catch us by surprise. Space scientists have now devised a way to monitor these types of collisions in interplanetary space by using a new method to determine the mass of magnetic clouds that result from the impacts.
-
-
DOE seizes $21 million from Fisker after company fails to make monthly payment on loan
The administration seized $21 million from auto company Fisker Automotive, less than a month after the automaker laid off three quarters of its employees due to financial and production problems. Fisker, based in Anaheim, California, was awarded a $192 million loan as part of a program started by the Obama administration to boost electric cars and other alternative-fuel vehicles.
-
-
Ammonium nitrate fertilizers are inherently risky, but the benefits are many
The deadly explosion has brought the $10 billion U.S. fertilizer industry to the attention of the mainstream media, but the risks inherent in fertilizer production and storage are not a secret to people close to the industry. Ammonium nitrate may be dangerous, but its benefits cannot be ignored.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
