-
More Accurate Climate Change Model Reveals Bleaker Outlook on Electricity, Water Use
By 2030, global warming alone could push Chicago to generate 12 percent more electricity per person each month of the summer. If the city generated any less electricity, it would be risking a power shortage that may require drastic measures to avoid rolling blackouts, according to projections from a model designed by Purdue University researchers.
-
-
American Observers Threatened over Guyana Election Results
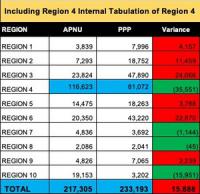
Tensions are rising in newly oil-rich Guyana with nearly 100 percent of the votes now reported from Monday’s national election. The governing APNU party appears to have lost to the opposition Peoples Progressive Party (PPP). International elections observers – mostly Americans – are now being menaced and threatened by APNU to leave or face arrest. Guyana’s election is being watched closely because the winner will be in control of a coming oil boom which will transform Guyana. In December Exxon began commercial exploitation of a huge 2016 oil discovery off the coast, and production is expected to grow from 52,000 barrels per day to over 750,000 by 2025.
-
-
New Flooding Prediction Tool
By incorporating the architecture of city drainage systems and readings from flood gauges into a comprehensive statistical framework, researchers can now accurately predict the evolution of floods in extreme situations like hurricanes. With their new approach, the researchers said their algorithm could forecast the flow of floodwater in almost real-time, which can then lead to more timely emergency response and planning.
-
-
Building a Flood Resilient Future
Seven of the United Kingdom’s ten wettest years on record have occurred since 1998. Its wettest winter in history came in 2013, and the next wettest in 2015. In a single week in November 2019, 400 homes were flooded and 1,200 properties evacuated in northern England. The frequency and severity of these events is expected to increase as a result of climate change, meaning that many more communities will suffer their devastating effects. A new book shows how we can adapt the built and natural environment to be more flood resilient in the face of climate change.
-
-
A Dam Across the North Sea to Protect Europeans from Sea-Level Rise
Engineers say that a 475-km-long dam between the north of Scotland and the west of Norway. and another one of 160 km between the west point of France and the southwest of England, could protect more than 25 million Europeans against the consequences of an expected sea level rise.
-
-
Identifying the Greatest Risk to U.S. Mineral Resource Supplies
Policymakers and the U.S. manufacturing sector now have a powerful tool to help them identify which mineral commodities they rely on that are most at risk to supply disruptions. The risk tool identified 23 mineral commodities whose supply poses the greatest risk, including those used in consumer electronics, renewable energy, aerospace, and defense applications.
-
-
Climate Change Poses “High-to-Catastrophic” Security Threats to U.S. Security: Experts
A comprehensive report finds that plausible climate change trajectories pose “High-to-Catastrophic” threats to U.S. national security. An expert panel analyzed the globe through the lens of the U.S. Geographic Combatant Commands, and concluded that “Even at scenarios of low warming, each region of the world will face severe risks to national and global security in the next three decades. Higher levels of warming will pose catastrophic, and likely irreversible, global security risks over the course of the twenty-first century.”
-
-
“Natural” Flood Management Would Be Overwhelmed by Britain’s Winter Super-Floods
As large swathes of the U.K. endure the worst floods in living memory, hearts and minds are rightly focused on protecting people and property. Once the floods recede, there will doubtless be a period of reflection on what could have been done better. It may be tempting to point the finger of blame or to promote a particular solution. But the hard truth is that there is no silver bullet for “preventing” floods.
-
-
Flood Buyouts Benefit the Whitest At-Risk Neighborhoods
The federal flood buyout program disproportionally benefits at-risk homes in the whitest communities of America’s largest cities, according to a new study. The study provides the first nationwide, peer-reviewed analysis of racial inequalities in the implementation of the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s (FEMA) flood buyout program. The researchers examined data in 500 municipalities across the U.S. between 1990 and 2015.
-
-
Brazil: Court Accepts Homicide Charges over Dam Collapse Which Killed 270
In January 2019, more than 270 were killed, thousands of homes destroyed, and large tracts of agricultural land poisoned when Brazil’s Brumadinho dam collapsed, releasing tons of toxic sludge. Last week, a Brazilian judge accepted the prosecution’s argument that 16 employees of Brazilian mining giant Vale the company’s German safety auditor should stand trial for intentional homicide. Documents show that Vale’s former CEO and the German auditors colluded to falsify engineering reports which warned about the dam’s structural weakness. Separately, German prosecutors said that they would file charged of negligent homicide and bribery against the German safety auditors.
-
-
Researchers Identify Security Vulnerabilities in Voting App
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using internet and mobile technology to increase access to the voting process. At the same time, computer security experts caution that paper ballots are the only secure means of voting. Mobile voting application could allow hackers to alter individual votes and may pose privacy issues for users.
-
-
Arid American West is Moving East as Groundwater Depletes
Loss of groundwater may accelerate drying trends in the eastern United States, according to research that applied supercomputing to create an in-depth model of how groundwater will respond to warming. Even under modest climate warming scenarios, the continental United States faces a significant loss of groundwater – about 119 million cubic meters, or roughly enough to fill Lake Powell four times or one quarter of Lake Erie.
-
-
Sea Level Rise to Cause Major Economic Impact If No Climate Action Is Taken
Rising sea levels, a direct impact of the Earth’s warming climate, is intensifying coastal flooding. The findings of a new study show that the projected negative economy-wide effects of coastal flooding are already significant until 2050, but are then predicted to increase substantially towards the end of the century if no further climate action on mitigation and adaptation is taken.
-
-
New Materials Could Help Clean-Up Chernobyl and Fukushima
Engineers have developed materials that could be used to help decommission the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear power stations. The materials, created in collaboration with colleagues in Ukraine, simulate Lava-like Fuel Containing Materials (LFCMs) – hazardous substances left behind by a nuclear meltdown. The development paves the way for the safe analysis of hazardous materials left behind at Chernobyl and Fukushima.
-
-
Coastal Risks, Land Use Policy in the Face of Sea Level Rise
An Oregon land use policy creates a large economic value for some private homeowners who are allowed to protect their shoreline against erosion, according to a new study. The study highlights the tradeoff between a homeowner’s ability to protect their private property and public access to Oregon’s beaches. The study comes at a time when the future of coastal management in Oregon is up for discussion given the threats of sea-level rise due to climate change.
-
More headlines
The long view
Helping Strengthen America’s Critical Infrastructure
Everyday life depends on a robust infrastructure network that provides access to running water, communications technology and electricity, among other basic necessities. The experts who keep our national infrastructure secure and resilient also need a strong network to share their knowledge and train the next generation of professionals capable of solving complex infrastructure challenges.
AI and the Future of the U.S. Electric Grid
Despite its age, the U.S. electric grid remains one of the great workhorses of modern life. Whether it can maintain that performance over the next few years may determine how well the U.S. competes in an AI-driven world.
Using Liquid Air for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
New research finds liquid air energy storage could be the lowest-cost option for ensuring a continuous power supply on a future grid dominated by carbon-free but intermittent sources of electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems: A Promising Source of Round-the-Clock Energy
With its capacity to provide 24/7 power, many are warming up to the prospect of geothermal energy. Scientists are currently working to advance human-made reservoirs in Earth’s deep subsurface to stimulate the activity that exists within natural geothermal systems.
Experts Discuss Geothermal Potential
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from within Earth—the term comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). It is an energy source that has the potential to power all our energy needs for billions of years.
