-
Solving the mystery of arsenic-contaminated water
Can water ever be too clean? If the intent is to store it underground, the answer, surprisingly, is yes. In a new study, scientists have shown that recycled water percolating into underground storage aquifers in Southern California picked up trace amounts of arsenic because the water was too pure. The research sheds light on a poorly understood aspect of groundwater recharge with purified recycled water, namely the potential mobilization of arsenic. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can cause organ failure and cancer in humans with prolonged exposure above established health thresholds. The findings pose a problem for Orange County, California, which differs from most communities in that it purifies treated wastewater instead of discharging it directly into rivers and oceans – but the problem goes beyond Orange County.
-
-
Smaller cities in developing world unprepared for disaster
While many planners focus on the threat of natural disasters to major metropolises around the world, a new study shows smaller cities are often even less equipped to handle such catastrophes. In India, where his study was focused, the number of people living in such cities grew from 170 to 227 million over the past twenty years. This, however, has not prompted disaster planning experts to focus on how to safeguard these cities from the risk of floods, earthquakes, mudslides, and tidal waves. Many of those threats are even greater now due to climate change.
-
-
Rare but predictable storms could pose big hazards
Researchers at Princeton and MIT have used computer models to show that severe tropical cyclones could hit a number of coastal cities worldwide that are widely seen as unthreatened by such powerful storms.
The researchers call these potentially devastating storms Gray Swans in comparison with the term Black Swan, which has come to mean truly unpredicted events that have a major impact. Gray Swans are highly unlikely, the researchers said, but they can be predicted with a degree of confidence. The researchers examined potential storm hazards for three cities: Tampa, Florida; Cairns, Australia; and Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
-
-
Project develops techniques for tackling asteroids, space debris

Asteroids and space debris represent a significant hazard for space and terrestrial assets; at the same time asteroids also represent an opportunity. In recent years it has become clear that the increasing population of space debris could lead to catastrophic consequences in the near term. The STARDUST project — the first and only network to provide training on space debris and asteroids — was established to address this growing problem.
-
-
A melting Arctic demands more – not less – research on earth science

The Arctic is melting rapidly. Who cares? Anyone who is concerned about the rising price of food, lives near the coast, shoveled snow all winter, can’t water their lawn anymore, pays a bigger premium now for property insurance, or enjoys eating seafood. Did we leave anyone out? Apparently so, yet this group of people should care as much as anyone. The House of Representatives earlier this year slashed NASA’s earth sciences research budget, which funds much of the research U.S. scientists do on the Arctic. Scientific research is not a luxury to be indulged. It is an essential contributor to our national well-being, helping us avoid costly mistakes while finding new ways to improve our security, our economy, and our quality of life. Today, Congress is taking us on a course toward an Arctic legacy of myopia, feebleness, and ignorance. Rather than denying the changes that affect us all, they should be steering our national policies toward scientific excellence and vigorous action on challenges such as Arctic meltdown and its impacts. Nowhere is the evidence clearer; never has the need for research been more urgent. We ignore the Arctic at our peril.
-
-
Nearly 1,000 Chinese chemical plants to relocate in wake of Tianjin explosions
Local governments across China have submitted plans to relocate or upgrade about 1,000 chemical plants in the wake of the massive explosions in Tianjin earlier this month, which killed 147 people. The blast at a warehouse in which large quantities of chemicals were stored was China’s worst industrial accident in recent years. Chinese health authorities said that the levels of sodium cyanide in several reservoirs in Tianjin were up to ten times higher than allowed, and urged city resident to use bottled water until the level of the toxic chemical subsides.
-
-
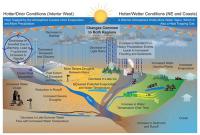
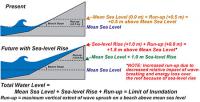
Sea level rise unevenly, which is bad news for some coastal regions

When you fill a sink, the water rises at the same rate to the same height in every corner. This is not the way it works with our rising seas. Tides, winds, and ocean currents play a role in these regional differences, but an increasingly important mover and shaker is the solid Earth itself. Global warming is not just affecting the surface of our world; it is making the Earth move under our feet. These regional differences in sea level change will become even more apparent in the future, as ice sheets melt. For instance, when the Amundsen Sea sector of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is totally gone, the average global sea level will rise four feet. The East Coast of the United States, however, will see an additional fourteen to fifteen inches above that average.
-
-
Sea-level rise handbook to help land managers, coastal planners, and policy makers

Coastal managers and planners now have access to a new U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) handbook which, for the first time, comprehensively describes the various models used to study and predict sea-level rise and its potential impacts on coasts. The handbook, designed for the benefit of land managers, coastal planners, and policy makers in the United States and around the world, explains many of the contributing factors that account for sea-level change.
-
-
Experts urge negotiators to include water in climate agreement
The impact of climate change is felt through water, with flooding, erratic rain patterns, prolonged droughts, and other extreme weather events. Water is also critical for successful climate change mitigation, as many efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions depend on reliable access to water resources. World Water Week closed on Friday in Stockholm, with the Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) urging climate negotiators to ensure that water is integrated in the global 2015 climate agreement.
-
-
FIU launches Sea Level Solutions Center

With rising seas threatening coastal communities all across the world, Florida International University (FIU) has launched the Sea Level Solutions Center to help people understand, adapt and persevere. FIU says that the center combines expertise in the natural, physical, and social sciences, along with architecture, engineering, computer sciences, law, communications, business, health, and tourism management to develop long-term strategies in the face of rising seas, noting that FIU’s Miami location will be key in advancing the center’s mission. South Florida is particularly vulnerable because of the large number of assets exposed to the effects of sea level rise.
-
-
Restoring and sustaining Louisiana’s eroding coast

Measures taken over the last ninety years to prevent a repetition of the 1927 New Orleans flood — the construction of improved levees, spillways, and dams as well as associated flood and additional navigation management structures designed to contain overflows and manage and stabilize a deep-water channel – have starved adjacent wetlands of the freshwater and sediment needed to stave off the Gulf of Mexico’s rising tides. The resulting land loss across the Delta is leading toward catastrophic collapse. Over the last century, almost 1,900 square miles of deltaic wetlands, an area approximately the size of Delaware, have disappeared from Louisiana. Every hour, a football field-sized swath of land drowns in the Gulf’s advancing tides. A Louisiana independent initiative, with the support and participation of the State of Louisiana and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, has called on experts from the private sector to develop and assess new designs for the Lower Mississippi River (below New Orleans). The winning proposals were announced last week.
-
-
Coastal uplift along Pacific Coast lower than expected, exacerbating sea-level rise impact
A new study shows that uplift rates across the Pacific Coast of the United States and northern Mexico have been overestimated by an average of more than 40 percent. These lower uplift rates this may have important implications for coastal management, including earthquake hazards and the potential impact of sea-level rise to coastlines across the Pacific Coast. If the Pacific Coast’s uplift rate is lower than had been estimated, this means that sea-level rise would have an even greater impact on coastal communities and infrastructure. Higher coastal uplift rates would have negated some of the effects of rising sea levels, something lower uplift rate will not do.
-
-
Draft guide to help energy companies reduce cyber risk

DHS reported that 5 percent of the cybersecurity incidents its Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team responded to in fiscal year 2014 were tied to weak authentication. Four percent were tied to abuse of access authority. The National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) is requesting comments on a draft guide to help energy companies better control who has access to their networked resources, including buildings, equipment, information technology, and industrial control systems.
-
-
Post-Katrina flood damage resulted from Corps of Engineers' errors, was preventable
A decade after hurricane Katrina hit New Orleans, experts say the flooding that caused over 1,800 deaths and billions of dollars in property damage could have been prevented had the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers retained an external review board to double-check its flood-wall designs. Researchers contend that the main fault in the failure of the flood walls along the city’s principal drainage canals was the misinterpretation of a full-scale load test carried out by the Corps in the Atachafalaya Basin a few years prior to Katrina. After these so-called E-99 tests, it was determined that flood walls in the city should be installed at a depth of 17 feet, instead of the initially estimated depths of 31 to 46 feet.
-
-
U.S. coastal communities face increasing risk of compound floods

In 2010, 39 percent of the U.S. population lived in coastal communities — a number which is expected to continue to increase in the next five years. The confluence of storm surges and heavy precipitation can bring dangerous flooding to low-lying coastal regions, including major metropolitan areas. A new study of the United States coastline has found the risk of such flooding is higher on the Atlantic coast than the Pacific, and the number of these compound events has increased significantly in many major cities in the past century.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
