-
Loss of West Antarctic glacier unstoppable, contributing significantly to sea level rise
A rapidly melting section of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet appears to be in irreversible decline, with nothing to stop the entire glacial basin from disappearing into the sea, according to researchers at UC Irvine and NASA. The new study presents multiple lines of evidence — incorporating forty years of observations — that six massive glaciers in the Amundsen Sea sector “have passed the point of no return.” The volume of melted ice would be enough to raise global sea level by four feet.
-
-
Large areas of Plains states now drier than during Dust Bowl

As a result of the drought conditions that have largely remained a constant since 2011, parts of the Texas and Oklahoma panhandles, as well as northeastern New Mexico and southeaster Colorado, are now drier than they were during the infamous Dust Bowl of the 1930s. While experts explain that the possibility of another Dust Bowl is not likely due to modern farming and irrigation techniques which have been enacted as a response in the 1930s, greater erosion due to drought and wind has resulted in a number of vicious dust storms.
-
-
States lack expertise, staff to deal with cyberthreats to utilities
The vulnerability of national electric grids to cyberattacks has caught the attention of federal utility regulators and industry safety groups, but state commissions tasked with regulating local distribution utilities are slow to respond to emerging cybersecurity risks. The annual membership directory of state utility regulators lists hundreds of key staff members of state commissions throughout the country, but not a single staff position had “cybersecurity” in the title.
-
-
Experts: Fracking-induced earthquakes are real, requiring scientific guidelines
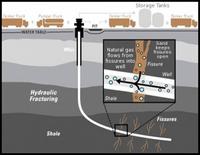
In the wake of increased seismic activity and rare advanced warnings, seismologists are urging the U.S. Geological Survey to include quakes resulting from hydraulic fracturing for underground oil and gas, or fracking, as an estimated hazard.
-
-
Miami “Ground Zero” for risks associated with sea level rise
During a special Senate hearing last month in Miami Beach, Senator Bill Nelson (D-Florida) described Florida as “Ground Zero” for climate change and the threat it poses to coastal communities. Sea level rise is especially worrisome to Floridians because Miami has the most property assets at risk in the world, according to the World Resources Institute(WRI). Miami has $14.7 billion in beach front property. Also, fifteen million out of the state’s twenty million residents live in coastal communities vulnerable to sea level rise.
-
-
Researchers map 198,000 glaciers to improve sea-level rise estimates
An international team of researchers has completed the first mapping of virtually all of the world’s glaciers — including their locations and sizes — allowing for calculations of their volumes and ongoing contributions to global sea rise as the world warms. The team mapped and catalogued some 198,000 glaciers around the world as part of the massive Randolph Glacier Inventory, or RGI, better to understand rising seas over the coming decades as a result of melting glaciers.
-
-
New technology to detect previously undetectable fecal contamination in water
Technology capable of sampling water systems to find indicators of fecal matter contamination that are thousandths and even millionths of times smaller than those found by conventional methods is being developed by researchers. The researchers have developed an ultrasensitive detection method that can detect molecules associated with human and animal fecal matter in water systems. These extremely small indicators, he explains, have been traditionally difficult to detect but can signal greater levels of contamination, which can lead to illness and even death.
-
-
South Carolina withdraws MOX lawsuit against DOE, NNSA
The state of South Carolina said Friday that it would not go ahead with its lawsuit against the Department of Energy and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) in support of the Savannah River Site’s Mixed Oxide (MOX) Fuel Fabrication Facility. The dismissal of the lawsuit follows an announcement last Tuesday by the DOE and NNSA that construction will continue on the MOX facility through the end of the fiscal year. The two agencies made it clear, though, that they still plan to mothball the plant.
-
-
As fracking activity grows in Mexico, so does the number of fracking-induced tremors

Mexico has the fourth largest amount of recoverable shale gas in the world, with 681 trillion cubic feet. As fracking activity has increased in the state of Nuevo Leon, so have the number of tremors. Between January and mid-April, forty-eight tremors, some reaching a magnitude of roughly 4.3, were recorded across the state of Nuevo Leon, compared to two tremors in the same period last year.
-
-
Ice melting in East Antarctica may lead to unstoppable sea-level rise
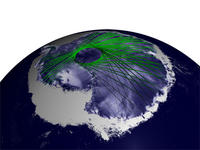
The melting of a rather small ice volume on East Antarctica’s shore could trigger a persistent ice discharge into the ocean, resulting in unstoppable sea-level rise for thousands of years to come, a new study finds. East Antarctica’s Wilkes Basin is like a bottle on a slant, say the study’s authors. Once uncorked, it empties out. The basin is the largest region of marine ice on rocky ground in East Antarctica.
-
-
Energy-subsidy reform can reduce carbon emissions, add years to oil exports: study
Reform of energy subsidies in oil-exporting countries can reduce carbon emissions and add years to oil exports, according to a new study. The study reviews the record of energy-subsidy reforms and argues that big exporters should reduce energy demand by raising prices, and that this can be done without undermining legitimacy of governments that depend on subsidies for political support
-
-
Lawmakers urge NRC not to exempt shut-down nuclear plants from emergency, security regulations
Lawmakers are urging the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to halt exemption of recently- shuttered nuclear power plants from emergency-planning and security regulations. The lawmakers are especially concerned about the nuclear waste which will continue to be stored on the grounds of shut-down nuclear plants, saying that the stored radioactive waste continues to be a security threat whether or not the plant itself is still operational.
-
-
Switching from cattle fields to “carbon farms” to tackle climate change

Changing cattle fields to forests is a cheap way of tackling climate change and saving species threatened with extinction, a new study has found. The main use of land in communities the western Andes of Colombia is cattle farming, but a new study found farmers could make the same or more money by allowing their land naturally to regenerate. Researchers report that under carbon markets designed to stop global warming, these farmers could get paid to change the use of their land from growing cows to “growing carbon” — receiving around $1.99 per ton of carbon dioxide the trees remove from the atmosphere.
-
-
Russia may launch crippling cyberattacks on U.S. in retaliation for Ukraine sanctions
U.S. officials and security experts are warning that Russian hackers may attack the computer networks of U.S. banks and critical infrastructure firms in retaliation for new sanctions by the Obama administration, imposed in response to Russia’s actions in Ukraine. Cybersecurity specialists consider Russian hackers among the best at infiltrating networks and some say that they have already inserted malicious software on computer systems in the United States.
-
-
Innovative U.S. cybersecurity initiative to address cyberthreats
Cyberattacks on computer networks around the world reached 1.7 billion in 2013, up from 1.6 billion in 2012. The administration’s 2012 Enhanced Cybersecurity Services(ECS) program, launched to protect the private sector from hackers by letting approved companies access classified information on cyber threats and sell cybersecurity services to critical infrastructure targets, is still in its early stages fourteen months after its launch.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
By Natasha Lindstaedt
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
By Katie Myers
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
By David Montgomery
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
