-
Planning for future ecological challenges
How can communities dodge future disasters from Mother Nature before she has dealt the blow? Researchers are taking a unique approach to the issue and gaining input and support from community stakeholders. Researchers conducted a series of one-on-one interviews at Big Hole Valley in Montana and Grand County in Colorado to get an array of community contributors thinking and planning for future ecological hazards, and to consider the impact of those decisions.
-
-
International food trade can alleviate water scarcity

International trade of food crops led to freshwater savings worth $2.4 billion in 2005 and had a major impact on local water stress, a new study finds. Trading food involves the trade of virtually embedded water used for production, and the amount of that water depends heavily on the climatic conditions in the production region: It takes, for instance, 2,700 liters of water to produce one kilo of cereals in Morocco, while the same kilo produced in Germany uses up only 520 liters. The researchers found that it is not the amount of water used that counts most, but the origin of the water.
-
-
Shale may offer long-term home for nuclear waste
About 77,000 tons of spent nuclear fuel currently sit in temporary above-ground storage facilities, and it will remain dangerous for tens or hundreds of thousands of years or longer. Experts say that since the U.S. government abandoned plans to develop a long-term nuclear-waste storage site at Yucca Mountain in Nevada in 2009, finding new long-term storage sites must be a priority. Shale deep under the Earth’s surface could be a solution. France, Switzerland, and Belgium already have plans to use shale repositories to store nuclear waste long-term.
-
-
Storm surges, rising sea levels threaten New Jersey’s beach-centered tourism industry
Sea level at the Jersey Shore could rise by thirty-one inches by the year 2050, posing a threat to New Jersey’s $38 billion tourism industry. Experts say that the potential for more harsh storms and sea level rise calls for better promotion of what else New Jersey has to offer tourists aside from the beach.
-
-
NERC drill finds U.S. grid preparedness insufficient
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) reported that its recent GridEx II exercise has highlighted the fact that nearly all the utilities which took part in the two-day drill last November – a drill aiming to test the preparedness of the U.S. power grid to withstand cyber and physical attacks – admitted that their planning for such attacks was insufficient. NERC’s president, Gerry Cauley, said that protecting utilities against cyber and physical attacks should be considered in the context of measures taken to protect the grid from other threats. He noted that utilities are already hardening their systems against storms like Hurricane Sandy, while working to determine their vulnerability to solar activity that changes the earth’s magnetic field.
-
-
Washington, D.C. area leads nation in cybersecurity jobs

The Washington, D.C metropolitan area had more than 23,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013, making the region the leading destination for cybersecurity jobs, followed by the New York metro area with 15,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013. On a state-by state basis, Virginia ranks second and Maryland ranks sixth, with Virginia reporting 25.1 cybersecurity job postings per 10,000 residents and Maryland posting 18.1 jobs per 10,000 residents.
-
-
Budget proposal cuts funds for nuclear nonproliferation programs
The White House’s fiscal 2015 budget proposal includes more than $220 million in cuts for nuclear security initiatives such as the International Material Protection and Cooperationprogram, which aims to secure and eliminate vulnerable nuclear weapons and materials, and the Global Threat Reduction Initiative, which supports the Energy Department’s efforts to prevent terrorists from acquiring nuclear and radiological materials that could be used in weapons of mass destruction. The administration says that 54 percent of the reduction in the administration’s nonproliferation budget request can be accounted for by the decision to halt the South Carolina Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility(MOX), which would have convert weapons-grade plutonium into nuclear reactor fuel, because the project proved to be too costly.
-
-
Methane from Deepwater Horizon oil spill has entered food web

When millions of gallons of oil spilled into the Gulf of Mexico four years ago, so did large volumes of methane, or natural gas. Now, researchers have confirmed that methane-derived carbon has entered the Gulf’s food web through tiny organic particles floating in the Gulf. The presence of methane is not cause for alarm though, the researchers said. Overall, it has a benign impact on the food that makes it from the sea to people’s dinner tables.
-
-
Libyan PM escapes country after assembly ousts him over oil tanker fiasco
Libya’s General National Congress has approved a no-confidence motion against Prime Minister Ali Zeidan and designated the defense minister as acting prime minister. Zeidan left Libya after the vote, in all likelihood for Italy. The no-confidence vote came after a North Korean-flagged tanker named Morning Glory managed to sail away from the port of al Sidra, carrying 234,000 barrels of crude oil from rebel-held oil fields. Last summer, armed militias in east Libya took over most of the country’s oil fields – and also three ports, with partial control of a fourth — bringing oil exports, which had amounted to 1.6 million barrels a day, to a halt. U.S. describes oil sale by the militias as “theft” from the Libyan people.
-
-
U.S. infrastructure vulnerable to “cascading system failures” caused by weather disasters
Two U.S. government reports released last Thursday warn that U.S. infrastructure is vulnerable to the effects of climate change. One report focuses on energy, the second on infrastructure more generally. The infrastructure-focused report is the first attempt to review climate implications across all sectors and regions. The report analyzes how damage to one infrastructure sector can impact other infrastructure sectors, rather than isolating specific types of infrastructure. The authors warn that climate-fueled weather disasters could cause “cascading system failures” unless changes are adopted to minimize such effects.
-
-
East Europe’s natural gas networks vulnerable during conflicts and crises
Gas networks in Eastern European countries, such as Ukraine and Belarus, are less resilient than the U.K. gas networks during conflicts and crises, according to new research. The authors suggest that a decentralized approach to managing congestion on gas pipeline networks could be crucial for energy security during geopolitical conflicts or natural disasters, for example.
-
-
Radiation from Fukushima to reach West Coast in April
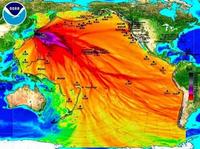
On the third anniversary of the Fukushima nuclear plant incident, scientists are reporting that low levels of radiation from the Fukushima plant will reach ocean waters along the U.S. West Coast by April 2014. The scientists say that the radiation will be at levels too low to harm humans, but they call for more monitoring, including at the federal level.
-
-
Innovative nuclear radiation detector reaches the market

A handheld radiation camera developed by University of Michigan engineering researchers offers nuclear plant operators a faster way to find potentially dangerous hot spots and leaky fuel rods. The new Polaris-H detector lays a gamma-ray map over an image of a room, pinpointing radiation sources with unprecedented precision. At least four U.S. nuclear power plants are using versions of the camera, which is now available commercially through the U-M spinoff company H3D.
-
-
Iona College to Launch BS, BA, MS concentrations in cybersecurity
Iona College announced the launch in fall 2014 of undergraduate and graduate programs in computer science with a concentration in cyber security. The concentration will be offered for the Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Arts, and the Master of Science degrees. The programs will provide students with fundamental cyber security skills, theoretical as well as hands-on experience. Students are exposed to new research ideas across many cyber security areas including software security, Web application security, mobile security, networking security, database security, and cryptography.
-
-
Small biomass power plants could help rural economies, stabilize national power grid

As energy costs rise, more Americans are turning to bioenergy to provide power to their homes and workplaces. Bioenergy is renewable energy made from organic sources, such as biomass. Technology has advanced enough that biomass power plants small enough to fit on a farm can be built at relatively low costs. Researchers have found that creating a bioenergy grid with these small plants could benefit people in rural areas of the country as well as provide relief to an overworked national power grid.
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
