-
U.S. General: troops unprepared for nuke risks in Japan
A U.S. general admitted that U.S. troops stationed in Japan did not have the proper training or equipment to handle radiation exposure in the days immediately following the nuclear crisis at the Fukushima Daiichi power plant caused by the 11 March earthquake and tsunami
-
-
Blue ribbon commission calls for interim off site waste storage

After deciding to stop the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository project, President Obama appointed a blue Ribbon commission to examine alternatives; the first report from the commission calls for interim storage of nuclear waste not on the site of nuclear power plants, and for the creation of a new corporation to develop one or more deep geological repositories “as expeditiously as possible”
-
-
Averting bridge disasters: new sensors could save hundreds of lives
One of every four U.S. highway bridges has known structural problems or exceeded its intended life-span. Most only get inspected once every one or two years; University of Maryland researcher has developed a new sensor that measures indicators of a bridge’s structural health, such as strain, vibration, flexibility, and development of metal cracks; the sensors are expected to last more than a decade, with each costing about $20
-
-
Earthquakes: scientists will shake 5-story building in Japan
Landmark earthquake engineering tests this summer in Japan could open the door for earthquake-proofing technology applied to hospitals, nuclear power plants, and emergency-response facilities to be more common in the United States, and confirm the capabilities for the technology used in Japan and the rest of the world
-
-
Bridge destruction to offer clues about 'fracture-critical' spans
A civil engineer at Purdue University is taking advantage of the demolition of a bridge spanning the Ohio River to learn more about how bridges collapse in efforts to reduce the annual cost of inspecting large spans
-
-
Sensing "skin" protects concrete structures
Scientists have developed a sensing “skin” which is made of stretchy thermoplastic elastomer mixed with titanium dioxde; patches of the skin are painted with black carbon to measure changes in the electrical charge of the skin; the skin will be rolled out in patches across structures such as bridges and dams; the formation of a crack would cause a movement in the concrete under the patch, which would change the capacitance, or stored energy, of the skin; daily check by computers would detect the change the capacitance, and issue and alert
-
-
Protecting water utilities from terrorist attacks and contaminants
In 1993, a cryptosporidiosis outbreak in Milwaukee contaminated the city’s water supplies, hastened the deaths of dozens of citizens, made more than 400,000 residents ill, and cost more than $96 million in medical expenses and lost productivity; Sandia’s CANARY software protects water utilities from terrorist attacks and contaminants
-
-
Water purification unit generates its own energy
A new biological water purification facility developed by Siemens generates enough methane gas to power its own operations; it also produces much less sludge than conventional systems; the test facility is mlocated in Singapore, and the city state is building a much larger pilot facility — one that will process 300 times more effluent than its predecessor, or about as much sewage water as is produced by around 1,000 people
-
-
Sector Report for Monday, 25 July 2011: Infrastructure protection
This report contains the following stories.
Plus 1 additional story.
-
-
Another Iranian nuclear scientist killed in Tehran

On Saturday, Darioush Rezaei, a 35-year-old physics professor involved in Iran’s nuclear program, was killed outside is Tehran home by assailants on a motorcycle; Rezaei’s expertise — neutron transport — is at the heart of nuclear chain reactions in reactors and bombs; Rezaei joins an ever-growing list of Iranian nuclear scientists who have met an untimely death at the hands of mysterious assailants; the systematic, covert killing of nuclear scientists to prevent a country from building a bomb is a method Israel used successfully — if, at times, with collateral damage — against Egypt in the early 1960s and against Iraq in the 1980s; the precision and lethality of the current Israeli campaign against Iran’s nuclear weapons scientists shows Israel learned important operational lessons from those two campaigns
-
-
DHS warns utilities at risk from insider threats
Last week DHS warned critical infrastructure operators like chemical facilities, nuclear power plants, and electric utility companies that terrorists could be targeting major facilities from the inside; officials cautioned that “violent extremists have, in fact, obtained insider positions,” and that “outsiders have attempted to solicit utility-sector employees” for damaging physical and cyber attacks.
-
-
A first: China connects fast-neutron reactor to the grid

Fast-neutron reactors use uranium sixty times more efficiently than a normal reactor; if adopted, the reactors would make current uranium reserves go longer; the reactor design also minimizes radioactive waste from nuclear energy; China is the first country to connect a fast-neutron reactor to its grid
-
-
U.S. shale gas weakening Russian, Iranian petro-power
Rising U.S. natural gas production from shale formations has already played a critical role in weakening Russia’s ability to wield an “energy weapon” over its European customers, and this trend will accelerate in the coming decades
-
-
Mathematical framework converts junk energy into useful power

Researchers have developed a mathematical framework that could one day form the basis of technologies that turn road vibrations, airport runway noise, and other “junk”energy into useful power;
-
-
Nanotechnology to help purify water
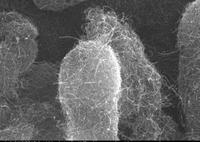
Among many potential applications, carbon nanotubes are great candidate materials for cleaning polluted water; many water pollutants have very high affinity for carbon nanotubes and pollutants could be removed from contaminated water by filters made of this nanomaterial — for example, water soluble drugs which can hardly be separated from water by activated carbon
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
