-
Sector Report for Monday, 16 May 2011: Infrastructure protection
This report contains the following stories.
-
-
Historic, desperate measures to control Mississippi River

The historic levels of water swelling the Mississippi River required the Army Corps of Engineers to take historic measures to prevent catastrophic flooding of Baton Rough and News Orleans: first, the Morganza control structure, located 186 miles upriver of New Orleans and completed in 1954 as part of the Army Corps of Engineers’ broad flood-protection upgrades in the wake of the Great Flood of 1927, was opened for only the second time to allow water to flow out of the river and into the Atchafalaya basin, a designated flood relief area; the Corps says that Saturday marked the first time in history that all three floodways built by corps after 1927 flood — the Morganza Floodway, the Bonnet Carre Spillway, and the Birds Point floodway in Missouri — have been in operation at the same time; about 25,000 people and 11,000 structures are in harm’s way, as up to 25 feet of flooding is expected in a 3,000 square-mile area of Louisiana
-
-
How safe are U.S. railroads?
Following the revelation that al Qaeda had aspired to attack U.S. railways, security experts, the media, and lawmakers have turned their attention to improving security for American trains; in a recent interview with CNN, Brian Michael Jenkins, the director of the Mineta Transportation Institute’s (MTI) National Transportation Security Center of Excellence, discussed the current state of railway security, how realistic creating an airline style screening system for railroads would be, and what measures need to be taken to secure railroads; to realistically improve rail security in a cost effective manner, Jenkins urged passengers to begin taking a more active role; Jenkins also urged the United States “to be more realistic about risk”
-
-
U.S. mayors want greater input in federal transportation funding decisions
Last week the U.S. Conference of Mayors (USCM) released the results of a recent survey of mayors in 176 cities on local infrastructure investment; the study revealed that mayors want the federal government to spend more money on infrastructure projects in metropolitan areas rather than highway expansion projects; 96 percent of mayors believed the federal government needed to increase spending on transportation infrastructure to fix rapidly deteriorating public infrastructure; a strong majority supported raising the gas tax to provide additional funds to improve infrastructure
-
-
Early warning system helped save lives in Japanese quake
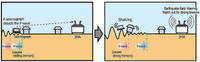
Japan has spent millions of dollars to build a sophisticated early warning system for earthquakes and experts say that it helped save millions of lives and mitigated the damage from the 11 March earthquake and tsunami; while the massive 9.0 magnitude earthquake and tsunami flattened much of northeastern Japan, the damage would have been far worse had Japan not had its early warning system in place; the system can provide anywhere from ten to thirty seconds of advance notice before an earthquake strikes giving Japan’s residents just enough time to slow down trains so they do not derail, shut off dangerous machinery, and send people to find cover
-
-
Rebuilding Seattle's viaduct will not result in nightmare commutes

Debate about how to replace Seattle’s deteriorating waterfront highway has centered on uncertainties in the project’s price tag; drilling a deep-bore tunnel and building an underground highway is estimated to cost around $4 billion, but some worry the final price could be higher, as it was for Boston’s infamous Big Dig; University of Washington statisticians have, for the first time, explored a different subject of uncertainty, namely: how much commuters might benefit from the project
-
-
Informed response to threat of asteroid collision
Surveys using ground and space-based telescopes, such as the NASA Spaceguard, have identified many Near Earth Objects (NEOs) that pass close to the Earth, including the 400 meter asteroid 2005 YU55 which will approach to within 325,000 km of the Earth in November this year; early detection of NEOs, and determination which of them is more threatening to Earth, are essential for decisionmakers; Southampton University researchers developed a new software system that could support decisions on how to respond to potential NEO impacts on Earth
-
-
Engineering students win wastewater treatment competition
In a surprise win, Humboldt State University (HSU) students recently bested engineering students at top ranked California universities to gain first place at the annual American Society of Civil Engineers Mid-Pacific Water Treatment Competition; this year teams were asked to build a system that would treat contaminated water that was heading toward a sensitive wetland ecosystem after an earthen levy around a biosolids compost facility had been breached; the teams were challenged to either design a containment system for the water or a treatment system; the HSU team won the competition beating U.C. Berkeley by more than thirty points
-
-
Turkey plans two earthquake resistant cities to move residents from vulnerable Istanbul

To encourage residents to move away from seismically unsafe neighborhoods, Turkey’s government recently announced that it will begin building two earthquake-resistant developments near Istanbul; the city of more than twelve million people currently sits near a major fault-line that could potentially kill thousands in the event of a major earthquake; engineers and seismic experts warn that Istanbul’s poor construction, shoddy city planning, and overcrowding would result in many fatalities in the event of an earthquake; officials plan for the new urban centers to be home to roughly 1 million residents each; any move to the new settlements would be entirely voluntary
-
-
Direct removal of carbon dioxide from air infeasible
A group of experts looked at technologies known as Direct Air Capture, or DAC, which would involve using chemicals to absorb carbon dioxide from the open air, concentrating the carbon dioxide, and then storing it safely underground; they conclude that these technologies are unlikely to offer an economically feasible way to slow human-driven climate change for several decades
-
-
New technology quickly detects bioattacks on water supply systems
If pathogens enter into a city water supply network, many people may fall ill quickly; to protect against this biological threat, researchers have developed a detection system, partly based on nanotechnology, that can warn authorities in time
-
-
Difficult decisions for Japanese living near Fukushima
Japanese residents living just outside the twelve mile evacuation zone of the Fukushima Daiichi power plant have struggled with their daily lives as the plant has continued to spew radiation; while Japanese officials have said that the radiation levels outside the evacuation zone are not high enough to cause observable health risks, many residents and scientists are still worried as radiation is still several times above the normal level; experts acknowledge their limited understanding of the health risks for long term exposure to low doses of radiation has made it difficult for scientists and policy makers to come to an agreement on what levels of radiation are safe and what areas need to be evacuated
-
-
Japan attempts "cold shutdown" at reactor no. 1

Officials at the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) hope to bring reactor no. 1 at the beleaguered Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant to a “cold shutdown” by the end of the week; plant operators will attempt to bring the temperature inside the reactor below the boiling point of water so that it will no longer produce radioactive steam; the building housing reactor no. 1 must be vented so that all the radioactive air that has accumulated is released allowing workers to approach the reactor; once inside workers will inject cold water into the reactor’s primary containment structure; injecting tons of water into a damaged containment unit that houses uranium makes some scientists uneasy
-
-
Men arrested outside U.K. largest nuclear plant, then released

Five young men of Bangladeshi origin were arrested outside Sellafield, the U.K.’s largest nuclear facility hours after President Obama announced the killing of OBL; the men were arrested for taking pictures and behaving suspiciously (the Civil Nuclear Constabulary said that the men were “unable to give a satisfactory account of their actions”); after being questioned the men were released as it appears that they had taken a wrong turn; the men told police they were traveling along the road only because their in-car satellite navigation system had taken them the wrong way on the remote road just off the coast of Cumbria, close to the Lake District; Sellafield is one of only four nuclear fuel reprocessing plants in the world
-
-
Recipe for radioactive materials helps in studies of nuclear waste and fuel storage pools
Easy-to-follow recipes for radioactive compounds like those found in nuclear fuel storage pools, liquid waste containment areas, and other contaminated aqueous environments have been developed by researchers at Sandia National Laboratories; the trick to the recipes is choosing the right templates; these are atoms or molecules that direct the growth of compounds in much the way islands act as templates for coral reefs
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
