-
Next-gen weather satellites to improve tornado warnings in South
More than a quarter of the 1,688 twisters confirmed across the United States in 2011 occurred in the four-state region of Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, and Tennessee – and most of the 73 tornadoes hitting the United States in January 2012 occurred in those four states; southern tornadoes are especially insidious and challenging to track, and NASA’s weather satellites are now paying special attention to them
-
-
DARPA holds $40,000 competition to test social media in disasters
To better understand how emergency responders can leverage social media tools, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is holding the$40,000 CLIQR Quest Challenge
-
-
New report paints dire picture of Japanese Fukushima response

A new report reveals that last year’s nuclear crisis at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi atomic energy plant was dangerously close to spiraling out of control as senior officials bickered internally, lacked critical information on the extent of the damage, and covertly considered the possibility of evacuating Tokyo
-
-
Nebraska debates disaster housing fund
Legislators in Nebraska are currently debating a law that would create a $2.5 million temporary housing fund for families who lose their homes in natural disasters
-
-
Study finds majority of Americans unprepared for disasters
According to the latest survey by the Persuadable Research Corporation, half of the poll’s respondents believe they are unprepared for a disaster
-
-
Virginia receives $40 million in federal disaster aid following quake
Following the rare east coast earthquake last year, Virginia has received nearly $40 million in federal disaster aid
-
-
New York overhauls emergency response capabilities post-Irene

Last week New York Governor Andrew Cuomo proposed a series of major initiatives to bolster the state’s emergency response capabilities; the proposals specifically incorporate lessons learned from the state’s response to Hurricane Irene and Tropical Storm Lee
-
-
Fukushima accident caused only low levels of fallout in U.S.
Fallout from the 2011 Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power facility in Japan was measured in minimal amounts in precipitation in the United States in about 20 percent of 167 sites
-
-
2010 Russian heat wave caused by both manmade, natural causes
The heat wave that struck western Russia in summer 2010 killed 55,000 people and caused $15 billion in damage; a new study concludes that soaring temperatures were within the natural range for a Russian summer, but that due to human-induced climate change, the chance of such an extreme heat wave has tripled over the past several decades
-
-
Japan considers referendum to end nuclear power
Lawmakers in Osaka, Japan are currently mulling over whether to abandon nuclear power all together following the catastrophic nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi atomic energy plant
-
-
Study finds disaster survivors more prone to fatal mistakes
A new study concludes that survivors of traumatic natural disasters may suffer from a decline in mental capabilities causing them to make grave errors in their daily lives
-
-
Caring for New York’s elderly in a disaster
Given the recent spate of natural disasters that struck the United States and New York City itself, community leaders there are concerned about disaster preparedness particularly for the city’s elderly and disabled populations
-
-
Invisibility cloak to protect buildings from earthquakes
Scientists show that by cloaking components of structures with pressurized rubber, powerful waves such as those produced by an earthquake would not “see” the building — they would simply pass around the structure and thus prevent serious damage or destruction
-
-
Preventing earthquake-induced soil liquefaction to protect buildings
When earthquakes occur, buildings can shift or fall; often, the failure is because of soil liquefaction, a phenomenon that occurs when loose, water-saturated soils lose strength in response to the sudden shaking from an earthquake, causing the soil to behave like a liquid; scientists have come up with a way to minimize liquefaction
-
-
Shape-memory alloys for earthquake-resistant structures
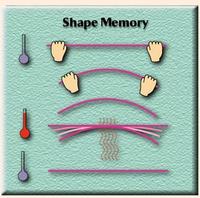
To improve the performance of structures during earthquakes, researchers have been investigating the use of “smart” materials, such as shape-memory alloys, which can bounce back after experiencing large loads
-
More headlines
The long view
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
